Megaduodenum might sound like a creature from a sci-fi movie, but it's actually a rare medical condition. Ever wondered what happens when the duodenum, a part of the small intestine, becomes abnormally enlarged? This condition can cause a range of symptoms, from abdominal pain to nausea. Understanding megaduodenum is crucial for those affected and their loved ones. In this blog post, we'll dive into 30 fascinating facts about this condition, shedding light on its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. Whether you're a medical student, a curious reader, or someone seeking answers, these facts will provide valuable insights into the world of megaduodenum.
Key Takeaways:
- Megaduodenum is a rare condition where the first part of the small intestine becomes abnormally enlarged, causing digestive issues like abdominal pain and bloating. It can be diagnosed through X-rays and treated with dietary changes, medications, or surgery.
- Living with megaduodenum involves regular check-ups, small frequent meals, and staying hydrated. Ongoing research aims to improve understanding and treatment, offering hope for better management in the future.
What is Megaduodenum?
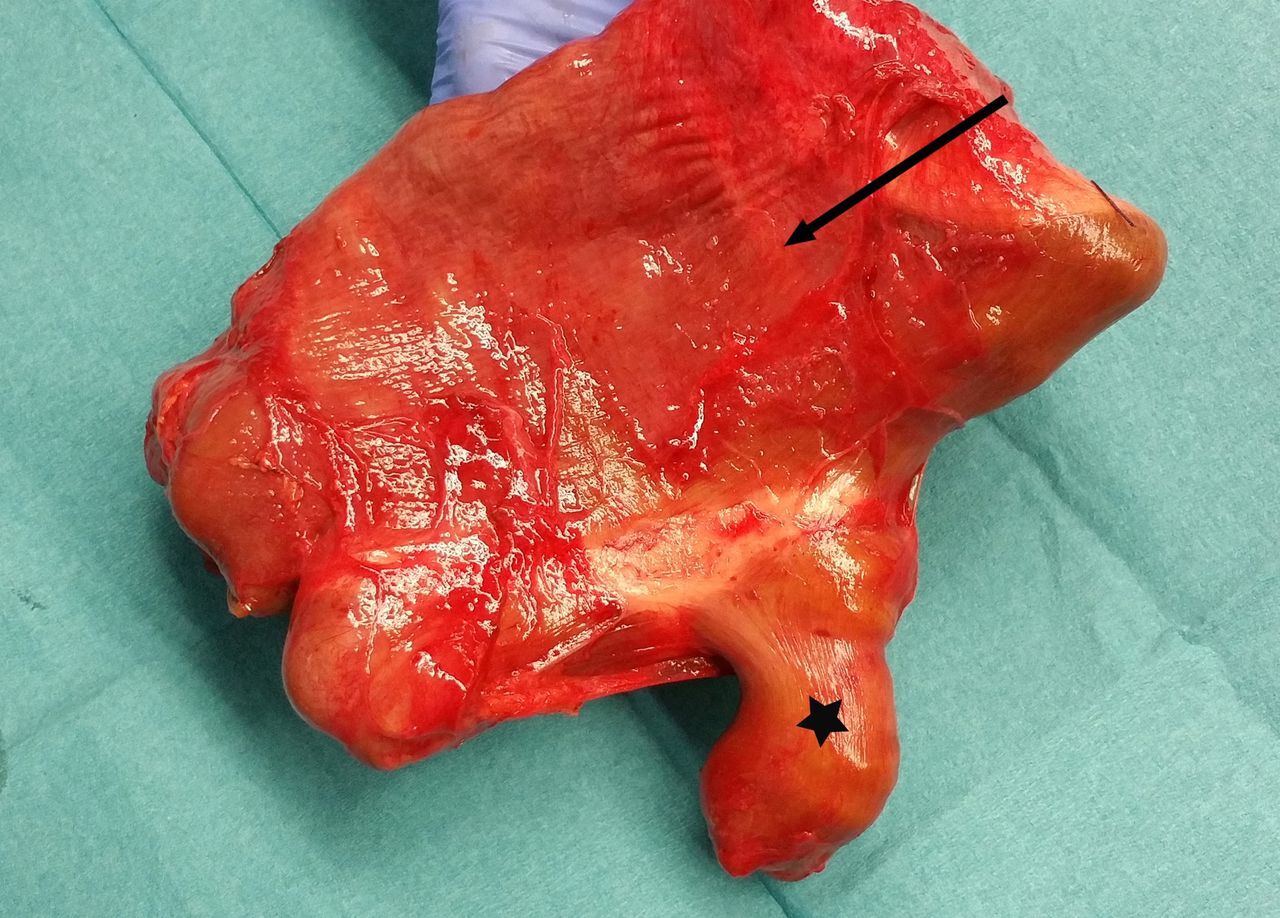
Megaduodenum is a rare condition where the duodenum, the first part of the small intestine, becomes abnormally enlarged. This can lead to various digestive issues and discomfort. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about this condition.
-
Megaduodenum is a condition characterized by the dilation of the duodenum, which can cause significant digestive problems.
-
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine, connecting the stomach to the jejunum. It plays a crucial role in digestion by mixing food with digestive juices.
-
Symptoms of megaduodenum often include abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, vomiting, and sometimes weight loss due to malabsorption of nutrients.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding what leads to megaduodenum can help in managing and preventing the condition. Here are some key causes and risk factors.
-
Congenital megaduodenum is present at birth and may be due to genetic factors or developmental issues during fetal growth.
-
Acquired megaduodenum can develop later in life due to conditions like chronic duodenal ulcers, tumors, or scarring from previous surgeries.
-
Chronic diseases such as diabetes or scleroderma can increase the risk of developing megaduodenum by affecting the nerves and muscles of the digestive tract.
Diagnosis and Detection
Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Here’s how megaduodenum is typically diagnosed.
-
X-rays are often used to detect the enlargement of the duodenum and assess the extent of the condition.
-
Barium swallow tests involve drinking a barium solution that coats the digestive tract, making it visible on X-rays to highlight abnormalities.
-
Endoscopy allows doctors to view the inside of the duodenum directly and take tissue samples if needed.
Treatment Options
Treatment varies depending on the severity and underlying cause of megaduodenum. Here are some common approaches.
-
Dietary changes can help manage symptoms by reducing the intake of foods that are hard to digest or cause gas and bloating.
-
Medications such as prokinetics can improve gut motility, helping food move through the digestive tract more efficiently.
-
Surgery may be necessary in severe cases to remove obstructions or correct structural abnormalities in the duodenum.
Complications
If left untreated, megaduodenum can lead to several complications. Here’s what you need to know.
-
Malnutrition can occur due to poor absorption of nutrients, leading to weight loss and deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals.
-
Intestinal obstruction is a serious complication where the enlarged duodenum blocks the passage of food, requiring immediate medical attention.
-
Chronic pain and discomfort can significantly impact the quality of life, making daily activities challenging.
Living with Megaduodenum
Managing megaduodenum involves lifestyle adjustments and ongoing medical care. Here are some tips for living with this condition.
-
Regular check-ups with a gastroenterologist are important to monitor the condition and adjust treatment as needed.
-
Small, frequent meals can help reduce symptoms by easing the digestive process and preventing overloading the duodenum.
-
Hydration is crucial, as adequate fluid intake helps maintain digestive health and prevent constipation.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to improve understanding and treatment of megaduodenum. Here are some exciting developments.
-
Genetic studies are exploring the hereditary factors that may contribute to congenital megaduodenum, potentially leading to early detection and intervention.
-
Advanced imaging techniques are being developed to provide more detailed views of the digestive tract, aiding in more accurate diagnosis.
-
New medications are being tested to enhance gut motility and reduce symptoms, offering hope for better management of the condition.
Support and Resources
Support networks and resources can make a big difference for those living with megaduodenum. Here’s where to find help.
-
Patient support groups offer a platform to share experiences, advice, and encouragement with others facing similar challenges.
-
Online forums and communities provide access to information, resources, and support from the comfort of home.
-
Educational materials from reputable health organizations can help patients and families understand the condition and its management.
Interesting Facts
Here are some lesser-known yet intriguing facts about megaduodenum.
-
Rare condition: Megaduodenum is quite rare, making it a topic of interest for medical researchers and specialists.
-
Historical cases: Some of the earliest documented cases of megaduodenum date back to the early 20th century, highlighting the long-standing curiosity about this condition.
-
Animal studies: Research on animals has provided valuable insights into the mechanisms and potential treatments for megaduodenum.
Prevention Tips
While not all cases can be prevented, certain measures can reduce the risk of developing megaduodenum.
-
Healthy diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in fiber can promote digestive health and prevent conditions that may lead to megaduodenum.
-
Regular exercise: Physical activity helps maintain gut motility and overall digestive function, reducing the risk of complications.
-
Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol: These habits can damage the digestive tract and increase the risk of developing conditions that may lead to megaduodenum.
Final Thoughts on Megaduodenum
Megaduodenum, a rare condition, involves the enlargement of the duodenum, the first part of the small intestine. This condition can lead to various symptoms like abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and weight loss. Understanding the causes, which range from congenital defects to chronic diseases, helps in managing it effectively. Diagnosis often requires imaging studies and sometimes endoscopy. Treatment options vary from dietary changes and medications to surgery in severe cases. Early detection and intervention are crucial for better outcomes.
Awareness about megaduodenum is essential for timely medical attention. If you or someone you know experiences persistent digestive issues, consulting a healthcare professional is vital. Knowledge empowers us to seek the right care and improve quality of life. Stay informed, stay healthy!
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
