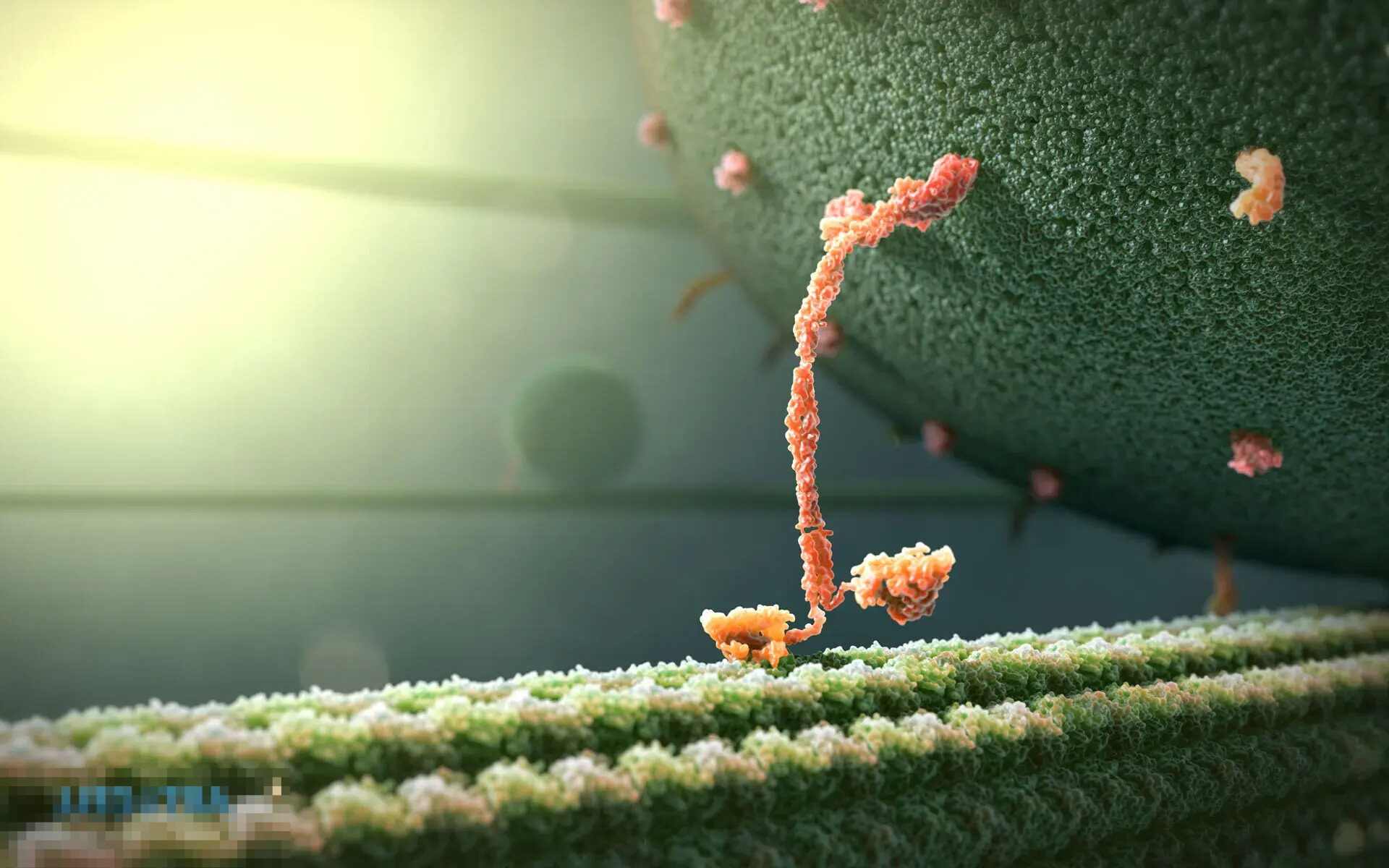
Kinesin is a fascinating molecular motor protein that plays a crucial role in cellular transport. Ever wondered how cells move essential materials like proteins and organelles? Kinesin is the answer. This tiny but mighty protein walks along microtubules, carrying cargo to various parts of the cell. Imagine it as a delivery truck, ensuring everything reaches its destination on time. Without kinesin, cells would struggle to function properly, leading to numerous health issues. From aiding in cell division to supporting nerve cell function, kinesin is indispensable. Ready to learn more? Here are 29 intriguing facts about this cellular powerhouse.
What is Kinesin?
Kinesin is a motor protein that plays a crucial role in cellular processes. It moves along microtubules, transporting various cellular cargoes. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about this essential protein.
-
Kinesin was first discovered in 1985 by researchers Ronald Vale, Thomas Reese, and Michael Sheetz.
-
It is named after the Greek word "kinesis," which means movement.
-
Kinesin is powered by ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the energy currency of the cell.
-
It moves in a hand-over-hand fashion, similar to how humans walk.
-
Each "step" kinesin takes is approximately 8 nanometers long.
Structure of Kinesin
Understanding the structure of kinesin helps in grasping how it functions. Its unique design allows it to perform its role efficiently.
-
Kinesin consists of two heavy chains and two light chains.
-
The heavy chains form the motor domains, which bind to microtubules and hydrolyze ATP.
-
The light chains are involved in binding to the cargo that kinesin transports.
-
The motor domains are also known as "heads," while the tail region binds to the cargo.
-
The heads of kinesin contain a nucleotide-binding site, crucial for ATP hydrolysis.
Functions of Kinesin
Kinesin is not just a mover; it has several roles within the cell. These functions are vital for cellular health and operation.
-
Kinesin transports organelles like mitochondria and lysosomes within the cell.
-
It plays a role in mitosis by helping to separate chromosomes during cell division.
-
Kinesin is involved in the transport of vesicles, which are small sacs that carry substances within the cell.
-
It helps in the positioning of the Golgi apparatus, an organelle involved in protein and lipid modification.
-
Kinesin also aids in the transport of mRNA, which is crucial for protein synthesis.
Types of Kinesin
There are several types of kinesin, each with specific functions. These types are adapted to meet the diverse needs of the cell.
-
Kinesin-1 is the most well-known type and is involved in the transport of organelles and vesicles.
-
Kinesin-2 is a heterotrimeric motor, meaning it consists of three different subunits.
-
Kinesin-3 is known for its role in the transport of synaptic vesicles in neurons.
-
Kinesin-5 is involved in mitosis, particularly in the separation of spindle poles.
-
Kinesin-13 is unique because it does not transport cargo but instead depolymerizes microtubules.
Kinesin in Neurons
Neurons rely heavily on kinesin for their function. The long distances within neurons make efficient transport systems essential.
-
Kinesin transports neurotransmitter vesicles to the synapse, where they are released to transmit signals.
-
It helps in the maintenance of axonal transport, crucial for neuron survival and function.
-
Mutations in kinesin genes can lead to neurodegenerative diseases like Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease.
-
Kinesin also transports mitochondria to areas of high energy demand within neurons.
-
It plays a role in the development and maintenance of dendrites, the branched extensions of neurons.
Research and Applications
Research on kinesin has led to numerous applications in medicine and biotechnology. Understanding kinesin can lead to breakthroughs in treating diseases.
-
Kinesin inhibitors are being studied as potential cancer treatments, as they can disrupt cell division.
-
Researchers are exploring kinesin's role in Alzheimer's disease, aiming to develop new therapeutic strategies.
-
Kinesin-based nanomachines are being developed for targeted drug delivery within the body.
-
Understanding kinesin's mechanism can lead to advancements in synthetic biology, where engineered proteins perform specific tasks within cells.
The Final Word on Kinesin
Kinesin is a tiny protein with a big job. It moves things around inside cells, acting like a delivery truck on microscopic highways. This protein is crucial for cell division, nerve function, and even wound healing. Without kinesin, cells would struggle to transport essential materials, leading to various health issues.
Understanding kinesin helps scientists develop treatments for diseases like cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. It's fascinating how something so small can have such a significant impact on our health.
Next time you think about the inner workings of your body, remember kinesin. This little protein keeps everything running smoothly, ensuring cells function properly. It's a reminder of the incredible complexity and efficiency of life at the microscopic level. So, keep learning and stay curious about the amazing world inside us all.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
