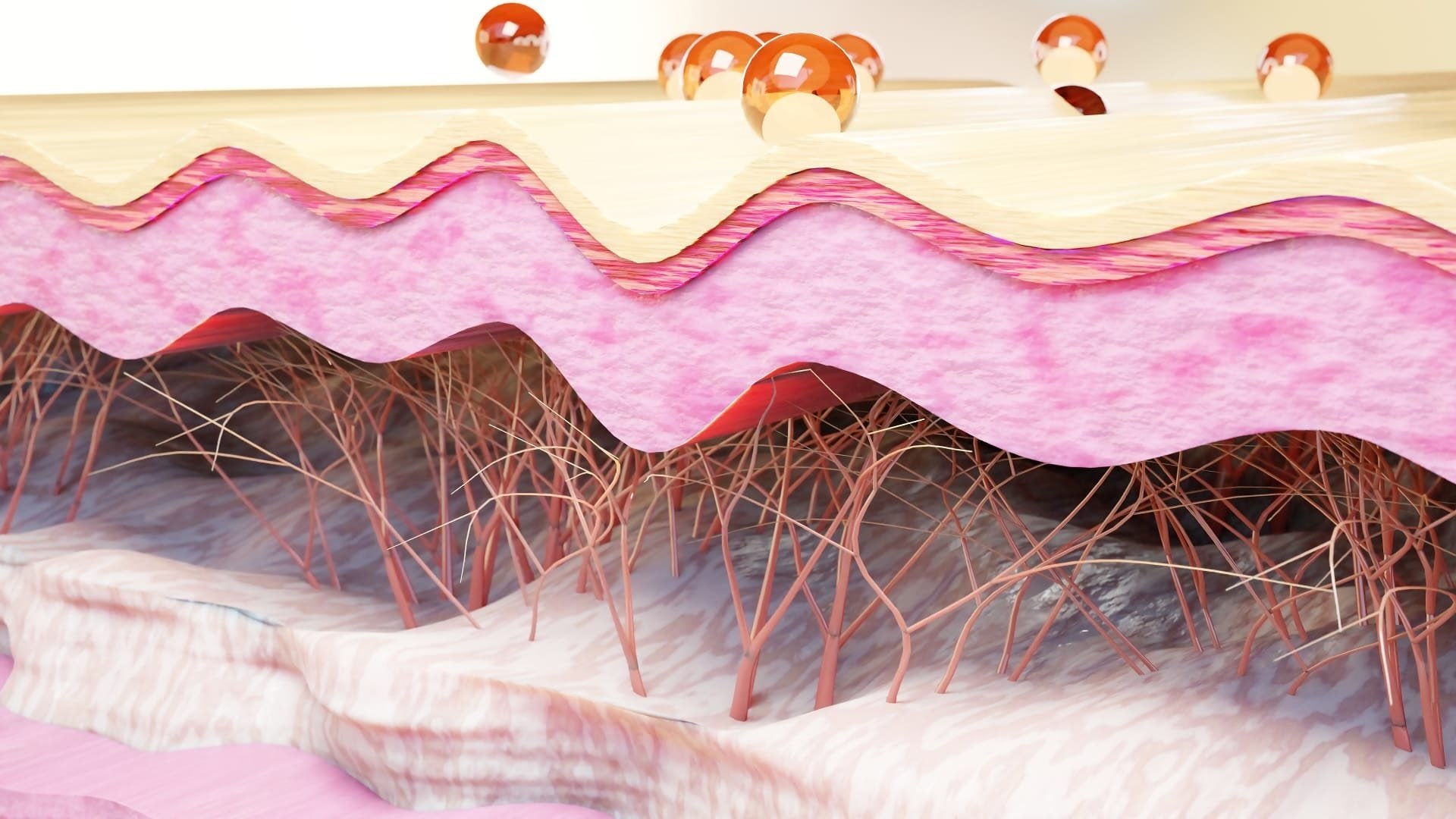
Elastin is a vital protein found in connective tissues, giving skin, blood vessels, and lungs their elasticity. Ever wondered why your skin snaps back after being pinched? That's elastin at work! This stretchy protein allows tissues to resume their shape after stretching or contracting. Unlike collagen, which provides strength, elastin offers flexibility. As we age, elastin production decreases, leading to wrinkles and sagging skin. Understanding elastin's role can help in making informed choices about skincare and health. Dive into these 29 fascinating facts about elastin to learn how it impacts your body and ways to maintain its levels.
What is Elastin?
Elastin is a protein found in connective tissues, giving them the ability to stretch and return to their original shape. It's crucial for skin, lungs, arteries, and other tissues that need to be flexible. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about this incredible protein.
-
Elasticity Powerhouse: Elastin can stretch up to 1.5 times its original length and snap back without damage. This elasticity is essential for tissues that undergo frequent stretching, like skin and blood vessels.
-
Skin's Best Friend: Elastin works alongside collagen to keep skin firm and elastic. While collagen provides strength, elastin allows the skin to stretch and move.
-
Aging Effects: As we age, elastin production decreases, leading to wrinkles and sagging skin. This reduction is a significant factor in the visible signs of aging.
-
Lung Function: Elastin is vital for lung function, allowing the lungs to expand and contract with each breath. Without elastin, breathing would be much more difficult.
-
Arterial Health: Arteries rely on elastin to maintain their shape and flexibility. This helps them withstand the pressure of blood flow and prevents them from becoming rigid.
How Elastin is Produced
Understanding how elastin is produced can shed light on its importance and potential for medical advancements.
-
Fibroblasts Role: Fibroblasts, a type of cell in connective tissues, produce elastin. These cells are also responsible for producing collagen and other essential proteins.
-
Tropoelastin: The precursor to elastin is called tropoelastin. This soluble protein is secreted by cells and then assembled into elastin fibers outside the cell.
-
Cross-Linking: Elastin fibers are formed through a process called cross-linking, where tropoelastin molecules bond together. This process gives elastin its unique elastic properties.
-
Genetic Influence: The production of elastin is controlled by the ELN gene. Mutations in this gene can lead to disorders affecting connective tissues.
-
Developmental Peak: Elastin production peaks during fetal development and early childhood. After this period, the body's ability to produce elastin significantly decreases.
Medical and Cosmetic Applications
Elastin's unique properties make it valuable in various medical and cosmetic fields.
-
Wound Healing: Elastin can aid in wound healing by promoting tissue regeneration and reducing scarring. Its elastic properties help the skin recover its original shape.
-
Anti-Aging Products: Many anti-aging creams and treatments aim to boost elastin production or mimic its effects to reduce wrinkles and improve skin elasticity.
-
Tissue Engineering: Researchers are exploring ways to use elastin in tissue engineering to create artificial organs and tissues that can stretch and function like natural ones.
-
Vascular Grafts: Elastin-based materials are being developed for vascular grafts, which can replace damaged blood vessels and restore normal blood flow.
-
Drug Delivery: Elastin-like peptides are being studied for use in drug delivery systems, where their elastic properties can help control the release of medications.
Elastin in Animals
Elastin isn't just important for humans; it's crucial for many animals as well.
-
Animal Skins: Many animals, including mammals, birds, and reptiles, have elastin in their skin, allowing them to move and stretch without injury.
-
Bird Flight: Birds rely on elastin in their wings for flight. The protein helps their wings stretch and contract efficiently during flight.
-
Fish Flexibility: Fish have elastin in their skin and connective tissues, allowing them to swim with fluid, flexible movements.
-
Insect Exoskeletons: Some insects have elastin-like proteins in their exoskeletons, providing flexibility and strength.
-
Mammalian Tendons: In mammals, tendons contain elastin, which helps them withstand the stress of muscle contractions and maintain flexibility.
Fun and Surprising Facts
Here are some lesser-known and surprising facts about elastin that highlight its versatility and importance.
-
Stretchy Ligaments: Ligaments, which connect bones to other bones, contain elastin. This allows them to stretch and provide stability to joints.
-
Ear Flexibility: The outer ear contains elastin, which helps it maintain its shape and flexibility, allowing it to bend without breaking.
-
Voice Box: Elastin is present in the vocal cords, enabling them to stretch and produce a wide range of sounds.
-
Eye Health: The elastic fibers in the eye's lens capsule contain elastin, helping the lens change shape for focusing.
-
Elastic Arteries: The aorta, the largest artery in the body, has a high concentration of elastin, allowing it to stretch and accommodate blood flow from the heart.
-
Skin Elasticity: Stretch marks occur when the skin is stretched beyond its elastin capacity, causing the fibers to break.
-
Genetic Disorders: Williams syndrome, a genetic disorder, is caused by a deletion of the ELN gene, leading to cardiovascular problems and distinctive facial features.
-
Marine Mammals: Whales and dolphins have high levels of elastin in their skin and blubber, allowing them to move efficiently through water.
-
Elastin Supplements: Some dietary supplements claim to boost elastin production, though their effectiveness is still under research.
The Final Stretch
Elastin is a fascinating protein that plays a crucial role in our body's flexibility and resilience. Found in connective tissues, it helps skin, blood vessels, and lungs maintain their shape after stretching or contracting. Unlike collagen, which provides strength, elastin offers elasticity, making it essential for various bodily functions. As we age, elastin production decreases, leading to wrinkles and less flexible tissues. Understanding elastin's role can help in developing treatments for aging and certain medical conditions.
From its unique properties to its vital functions, elastin is more than just a protein; it's a key player in maintaining our body's youthful and functional state. Whether you're interested in skincare, medical research, or just curious about how your body works, knowing about elastin gives you a deeper appreciation for the complex mechanisms that keep us moving and thriving.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
