The Precambrian Era is a colossal chunk of Earth's history, spanning from the planet's formation about 4.6 billion years ago to roughly 541 million years ago. This era covers nearly 90% of Earth's timeline, yet it often remains shrouded in mystery. Did you know that during this time, the first simple life forms emerged, setting the stage for all future biodiversity? The Precambrian saw the formation of Earth's crust, oceans, and atmosphere, creating the foundation for life as we know it. Intrigued by ancient times? Let's dive into 26 captivating facts that will transport you back to the dawn of our planet.
What is the Precambrian Era?
The Precambrian Era is a vast stretch of time that covers nearly 90% of Earth's history. It spans from the formation of Earth around 4.6 billion years ago to the start of the Cambrian Period, about 541 million years ago. This era is divided into three eons: the Hadean, Archean, and Proterozoic.
- The Precambrian Era lasted for approximately 4 billion years.
- Earth's formation occurred during the Hadean Eon, which is part of the Precambrian Era.
- The Archean Eon saw the formation of the first continental crust.
- The Proterozoic Eon witnessed the rise of oxygen in Earth's atmosphere.
Life in the Precambrian Era
Life during the Precambrian Era was vastly different from what we see today. It was a time of simple organisms and significant evolutionary milestones.
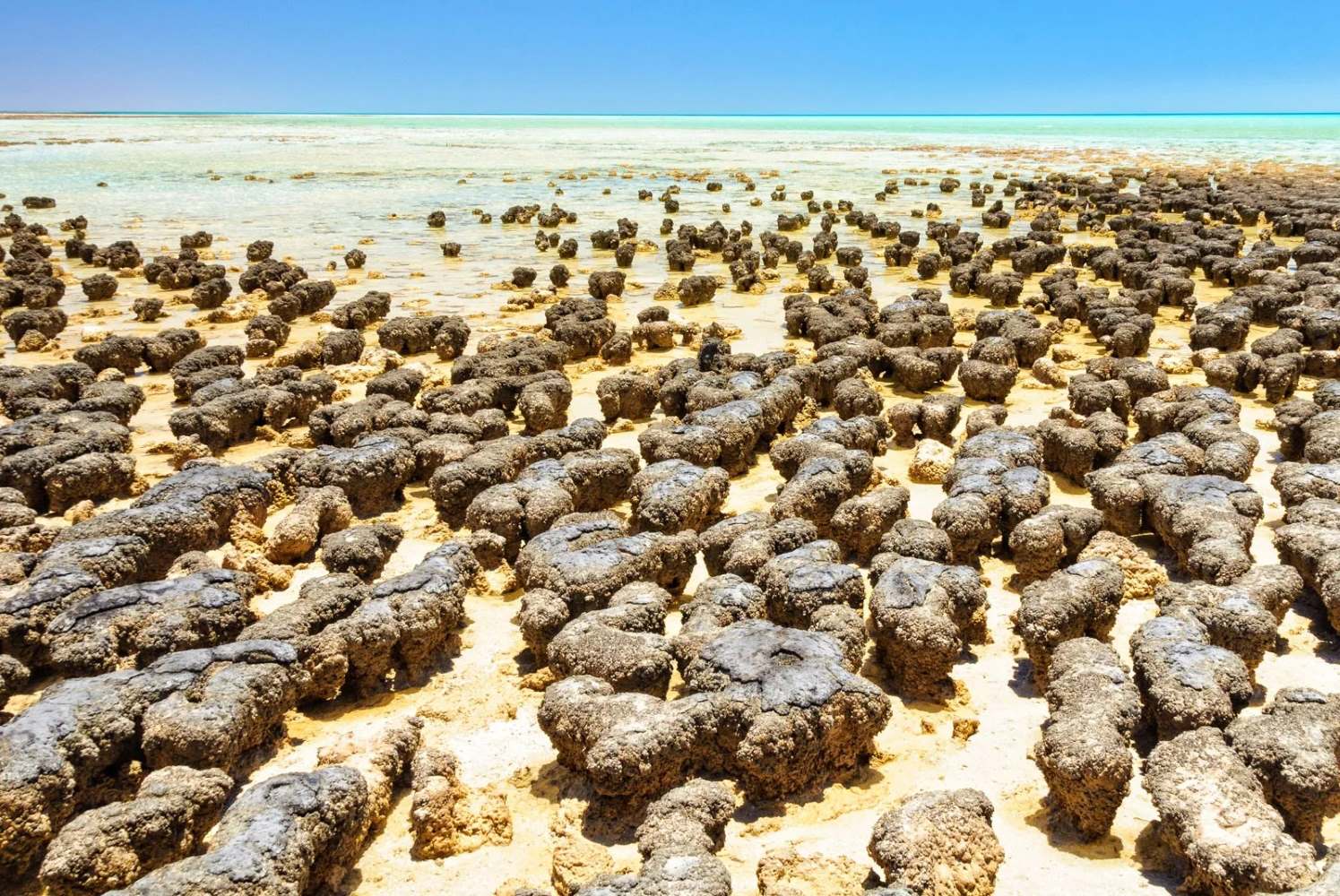
- Stromatolites, layered structures formed by cyanobacteria, are some of the oldest evidence of life.
- Microbial mats dominated the Precambrian seas.
- Eukaryotic cells, which have a nucleus, first appeared during this era.
- Multicellular life began to evolve in the late Precambrian.
Geological Features of the Precambrian Era
The Precambrian Era was a time of significant geological activity. The Earth's crust was forming, and the first supercontinents were coming together.
- Cratons, the stable cores of continents, formed during the Archean Eon.
- Rodinia, one of the earliest supercontinents, existed during the Proterozoic Eon.
- Banded iron formations are layers of iron-rich rock that formed in the oceans.
- Greenstone belts are regions of ancient volcanic and sedimentary rocks.
Climate of the Precambrian Era
The climate of the Precambrian Era was harsh and varied greatly over time. From extreme heat to global glaciations, the Earth experienced it all.
- The Hadean Eon was characterized by intense heat and volcanic activity.
- The Archean Eon had a warm climate with little oxygen in the atmosphere.
- The Proterozoic Eon saw the first "Snowball Earth" events, where the planet was covered in ice.
- Oxygenation events during the Proterozoic Eon led to significant climate changes.
Fossils from the Precambrian Era
Fossils from the Precambrian Era are rare but provide crucial insights into early life on Earth. These fossils are often microscopic and found in ancient rocks.
- Acritarchs are some of the oldest known eukaryotic fossils.
- Grypania spiralis is one of the earliest known multicellular fossils.
- Ediacaran biota are the first large, complex organisms found in the fossil record.
- Microfossils from the Precambrian include bacteria and algae.
The Importance of the Precambrian Era
Understanding the Precambrian Era is essential for comprehending the Earth's history and the development of life. This era laid the foundation for the complex ecosystems we see today.
- Plate tectonics began during the Precambrian, shaping the Earth's surface.
- The Great Oxidation Event occurred in the Proterozoic Eon, leading to an oxygen-rich atmosphere.
- Precambrian rocks contain valuable minerals like gold and uranium.
- The first ecosystems were established during this era.
Mysteries of the Precambrian Era
Despite extensive research, many aspects of the Precambrian Era remain shrouded in mystery. Scientists continue to study this period to uncover its secrets.
- The origin of life is still not fully understood.
- The exact causes of the "Snowball Earth" events are still debated.
The Precambrian Era's Legacy
The Precambrian Era laid the groundwork for life as we know it. Spanning over 4 billion years, this era saw the formation of Earth's crust, oceans, and atmosphere. Microbial life began to thrive, setting the stage for more complex organisms. Stromatolites, ancient structures built by cyanobacteria, are some of the oldest fossils, offering a glimpse into early life.
Understanding the Precambrian helps us appreciate the planet's history and the evolution of life. It reminds us of the planet's resilience and the intricate processes that have shaped it. From the formation of the first continents to the rise of oxygen-producing bacteria, the Precambrian Era's legacy is profound.
So, next time you look at a rock or breathe in the air, remember the ancient beginnings that made it all possible. The Precambrian Era truly set the stage for everything that followed.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.