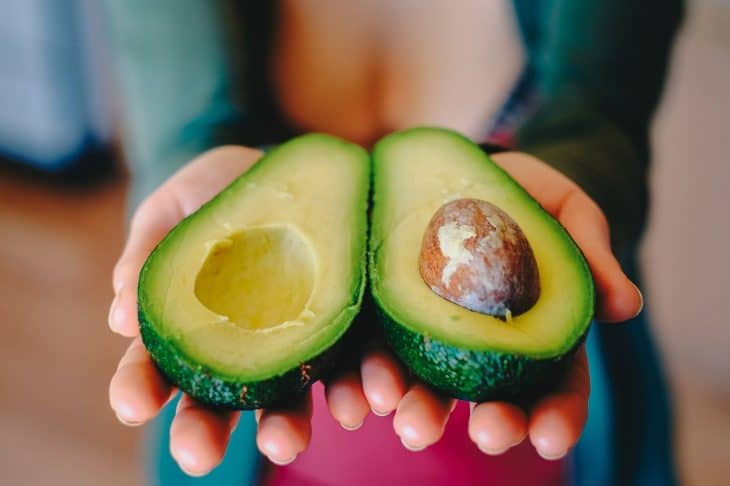

Avocado is no simple food as its nutrient density earned it a spot in the world’s infamous superfoods. Still, there are many things that people do not know about avocado as a fruit, as a tree, and as a food in general. Learn about its origin, symbolization, and more when you read the avocado facts in this article.
- The name ‘avocado’ originated from the Aztec word ‘ahuacatl,’ which means ‘testicle.’
- Other terms used for avocado are ‘alligator pear,’ ‘butter pear,’ ‘vegetable butter,’ and ‘midshipman’s butter.’
- Within an avocado is its edible part characterized by light-green creamy flesh that is not sweet.
- Avocado is the lone edible fruit in the laurel family, Lauraceae.
- Above 95% of the avocado supply in the U.S. comes from Southern California where it stands as the state fruit.
- Avocado is a berry fruit, not a vegetable.
- The fiber in avocado is at 10 g per cup, equivalent to 6.7 g per 100 g.
- Avocado halves have an average of 136-150 calories.
- The tannin content in avocado causes the flesh to taste bitter when cooked.
- Freshly-cut avocado fruit becomes brown in color due to the polyphenol oxidase isoenzymes.
- Avocado joins cinnamon and stinkwood in the same plant family.
- The highest smoke point recorded for avocado oil is 520 degrees F.
- Aztecs perceived avocado as a symbol of love and fertility.
- Ripe avocado can soothe sunburn.
- The greatest avocado producer in the world is Mexico with an average annual export of 1 million tons.
- More than 500 varieties of avocado are worldwide.
- The Aztecs banned virgins from eating avocados because they believed that the fruit is powerful sexually.
- In terms of size, avocado is equivalent to a 16-week old baby inside a womb.
- Factors like lack of pollination can cause avocado to become seedless.
- Some people use avocado as ring boxes in an engagement proposal to partners.
Avocado Facts Infographics
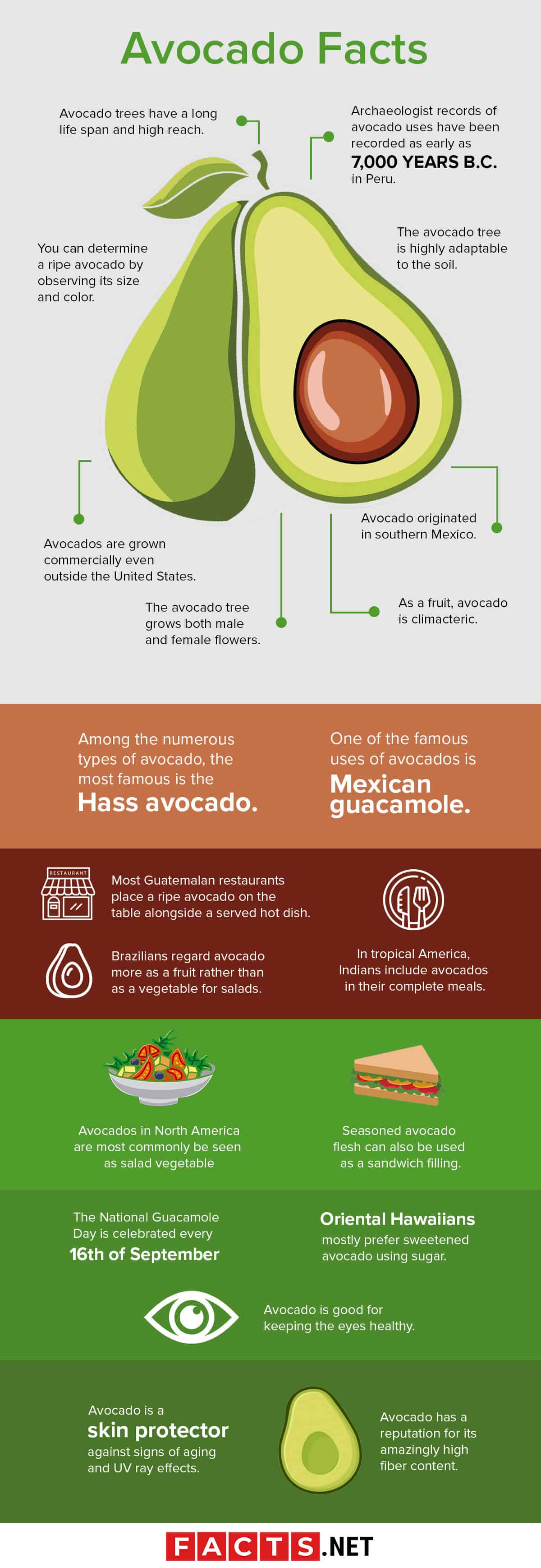
Archaeologist records of avocado uses have been recorded as early as 7,000 years B.C. in Peru.
However, evidence of avocado seeds being buried with Incan mummies was traced going as early as 750 B.C.
Avocado originated in southern Mexico.
Cultivation pushed through from the Rio Grande up to central Peru way before the Europeans arrived. It proves that the fruit was carried to the West Indies and to nearly all tropical and subtropical areas that have suitable environmental conditions.
Avocados are grown commercially even outside the United States.
Other countries that cultivate avocado are Algeria, tropical Africa, South Africa, Australia, the Canary Islands, Crete, Egypt, southern France, Israel, Madagascar, Madeira, Mauritius, New Zealand, Philippines, Sicily, and southern Spain.
As a fruit, avocado is climacteric.
It means that as long as the fruit is attached to the tree, it would not ripen due to a fruit stem inhibitor. Domestic growers consider it pickable when a few mature avocadoes have fallen already.
You can determine a ripe avocado by observing its size and color.
Avocado fruit is already ripe when it feels heavy for its size and it has a dark color. Moreover, you can quicken the ripening process by putting it in a brown paper bag for 2-4 days, and even faster when you add a banana in the bag.
Avocado trees have a long life span and high reach.
They can live up to 400 years and grow to a height of 65-70 feet.
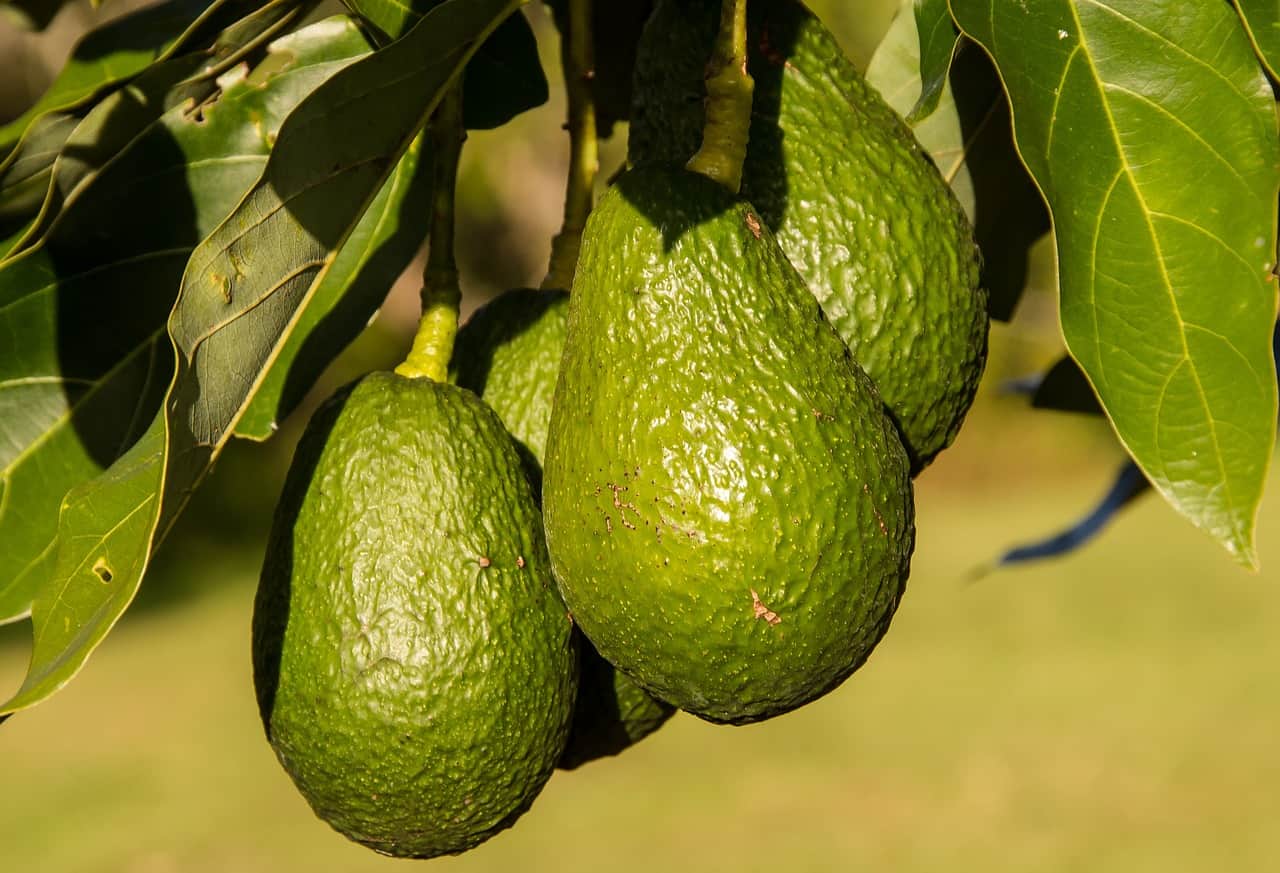

The avocado tree grows both male and female flowers.
In the phenomenon called ‘dichogamy,’ the flowers from different sexes grow at different times to prevent self-pollination.
The avocado tree is highly adaptable to the soil.
Whether it is on lateritic soils, limestone, red clay, sand, or volcanic loam, the avocado tree has proved its versatility.
Among the numerous types of avocado, the most famous is the Hass avocado.
A Californian postman named Rudolph Hass discovered the specific variety in his backyard in California. In 1935, Hass patented it.
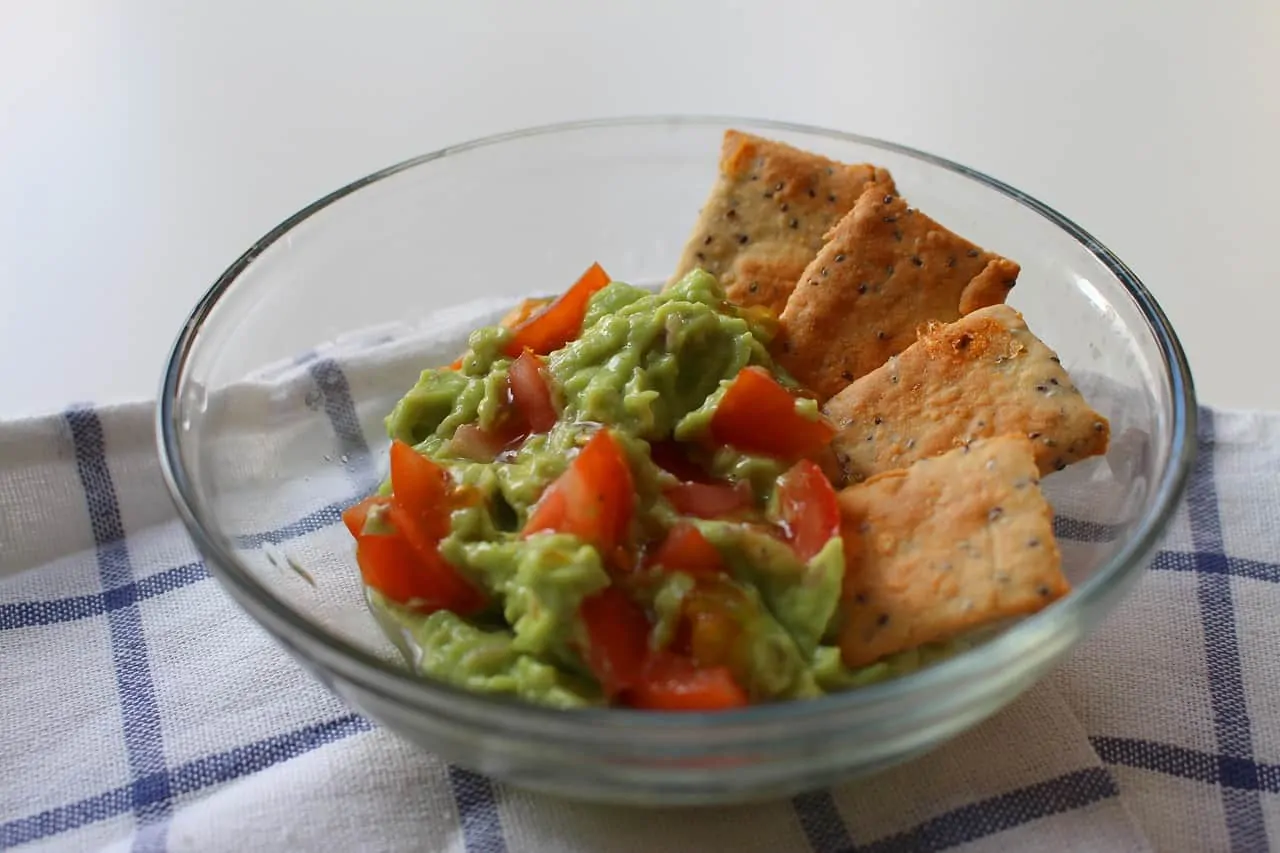
One of the famous uses of avocados is Mexican guacamole.
This food is a mixture of pureed avocado flesh, chili powder, lemon juice, minced garlic, onion juice/powder, salt, and pepper. Variations on the ingredients may include mayonnaise. Eventually, it became a popular dip for snacks like potato chips and crackers.

Most Guatemalan restaurants place a ripe avocado on the table alongside a served hot dish.
Diners can then scoop out the avocado flesh to add it to the dish just before eating. Meanwhile, you can have gourmet avocado for breakfast by warming it at low heat in an oven then topping it with anchovies and scrambled eggs.
Brazilians regard avocado more as a fruit rather than as a vegetable for salads.
Mainly, they mash the fruit and mix into ice cream, milkshakes, and sherbet. They only add the avocado flesh once the heated ice cream mixes were cooled.
In tropical America, Indians include avocados in their complete meals.
They would half the avocados, add some salt, and then eat it alongside tortillas and a cup of coffee.
Avocados in North America are most commonly be seen as salad vegetables.
Locals would just half it and garnish with seasonings, mayonnaise, lemon juice, lime juice, mayonnaise, or other types of dressings. Sometimes, they would stuff the halves with crab, shrimp or other seafood. To serve as a salad, slice or dice some avocado flesh to pair with cucumbers, tomatoes, or other vegetables.

Seasoned avocado flesh can also be used as a sandwich filling.
When mixed with pineapple juice and cream cheese, it is then added to fruit salads as creamy dressings.
Oriental Hawaiians mostly prefer sweetened avocado using sugar.
Then, they would combine it with fruits like banana, dates, grapefruit, orange, and pineapple. Meanwhile, in Java, locals would thoroughly mix avocado flesh with strong black coffee wherein it would then be sweetened and consumed as a dessert.
The National Guacamole Day is celebrated every 16th of September.
The name itself ‘guacamole’ originated from the Aztec word “āhuacamolli,” meaning “avocado sauce.”
Avocado is good for keeping the eyes healthy.
Its lutein content is a powerful antioxidant that is capable of protecting eyes from high energy light waves.
Avocado is a skin protector against signs of aging and UV ray effects.
Moreover, avocado oil can alleviate plaque psoriasis. Two organic compounds in avocado namely beta-carotene and lycopene can improve skin tone and health and eliminate premature aging signs.
Avocado has a reputation for its amazingly high fiber content.
It involves both soluble and insoluble fiber that the body needs equitably to aid in proper digestion and prevent gastrointestinal diseases.

Avocado has the potential to alleviate cancer.
Its carotenoid and monounsaturated fat content is associated with cancer reduction, especially when blended with the phytochemicals content of the diet. The fruit contains glutathione as well, an antioxidant that serves as cell protection from cancer and the dangerous effects of free radicals.
Avocado is toxic to horses.
The persin content found in the fruit can cause respiratory distress in horses that may lead to heart failure and death.
Unripe avocado was also found to have toxic effects.
Two resins were observed from avocado skin and are toxic to guinea pigs by subcutaneous and peritoneal injection. Aside from that, the leaves of avocado trees were found to contain dopamine while its oil also has methyl chavicol content.
The extra-large seed of the avocado is an evolved feature.
It was from the time of the now-dead megafauna which involves the giant armadillo. Avocado fruit had to be big enough to be able to attract such large animals. Hence, the seed also needed to be firm enough to withstand the animals’ digestive systems.

A major disease found in avocado trees is fungus-caused root-rot.
Phytophthora cinnamomi can be fought off by using strict sanitary methods and resistant rootstocks like ‘Duke.’ This disease is found among trees in Central America, South America, California, West Indies, and Hawaii, among others.
Avocado oil is richly filled with vitamins A, B, E, and G.
Its digestibility coefficient is 93.8%. However, it is still too costly to be regularly used as salad oil despite the stated avocado nutrition facts.
Avocado is famous for its less calorie content as that of butter.
It supports the fact that the fruit has a high-level healthy fat that is efficient in reducing cholesterol. This quality is what sets it apart from the other dietary items with high-calorie content.
Avocado is 73% water.
Fat makes up 15%, carbohydrates that are mostly fibers are at 8.5%, while protein is at 2%.

Avocado beats banana in potassium content.
Banana may have been best known as the potassium king in fruits, but it only has 487 mg of the minerals. Meanwhile, avocado has a whopping 975 mg per piece.
The heaviest recorded avocado in the world weighed 2.19 kg or 4.83 lbs.
Guinness World Records recognized the fruit from Venezuela on January 28, 2009, where the owner Gabriel Ramirez Nahim grew it.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
