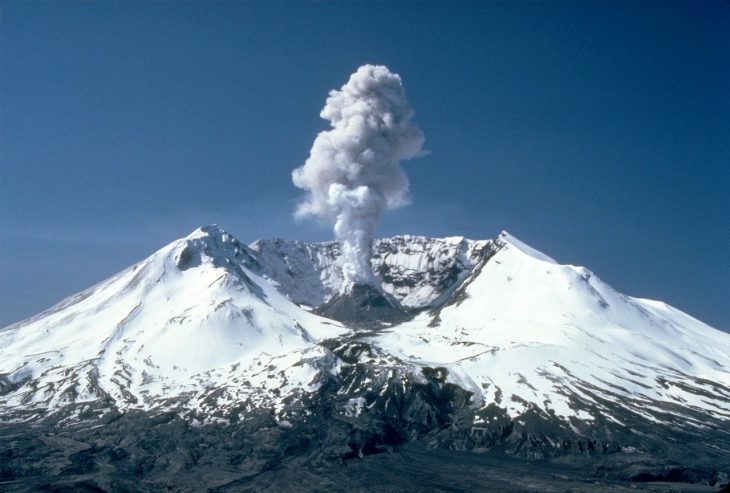

Volcanoes are gorgeous, and yet can be very destructive when they erupt. In numerous instances throughout history, volcanoes have spewed a lethal mix of ash and rain to surrounding cities. If you live near a volcano, and it is showing signs of unrest, you better run!
These magnificent creations of nature are scary by default. They are notorious for their destructive capabilities, and there are only a few natural forces that can match their pure, awesome power. But they aren’t all bad. Think of it this way — volcanic eruptions spread ash over a wide area. This ash contains varying levels of soil nutrients depending on the composition of the magma from which it erupted. While the most abundant elements in magma are silica and oxygen, eruptions also result in the release of water, sulfur dioxide (SO²), carbon dioxide (CO²), hydrogen sulfide (H²S), and hydrogen chloride (HCl), among others.
In addition, volcanoes have done incredible things for us by helping to cool off Earth‘s excess interior heat. Imagine what would happen if that excess interior heat never had an outlet? Did you know, in Naples, Italy there are fertile stretches of land created by volcanic eruptions? The soil in that region is rich because of minerals from a volcanic eruption, minerals broken and weathered down by rain. Once absorbed by the soil, they became a steady supply of nutrients for plant life in that area. Isn’t that amazing?
If you liked the volcano facts we shared here, you’d be glad to know there is more where that came from. Check out the comprehensive list we’ve made of the top 50 cool volcano facts.
- Earth has around 1,500 active volcanoes.
- There are over 10 named volcanoes on Mars. However, unlike Earth, the Red Planet currently has no active volcanoes.
- Venus has at least 30 active volcanoes.
- The planet Mercury has several craters scattered across its land. Its volcano eruptions shaped the planet’s surface about 3.5 billion years ago.
- 56.7°C is the hottest temperature ever recorded on Earth. To compare, volcanic lava’s temperature can reach 1,250°C.
- A volcano is a rupture or opening in the planet’s crust.
- Volcanic ash, hot lava, and gasses can emerge from a volcano.
- Massive volcanic eruptions usually affect atmospheric temperature.
- Lava is a molten rock that comes out from the planet’s interior.
- Magma is formed through the internal heat of the planet and it’s erupted as lava from volcanoes.
- Experts use the word “magma” for molten rock that’s still in the planet’s interior while “lava” for molten rock that comes out through the volcano.
- Created during volcanic eruptions, volcanic ash consists of fragments of rock, volcanic glass, and other minerals.
- Both active and dormant volcanoes can create volcanic gases.
- A magma chamber is a huge pool of liquid rock under the surface of the planet.
- When the magma locates a path to the surface, a volcanic eruption will occur.
- The term “volcano” came from the name Vulcano.
- Vulcano is a volcanic island in the Aeolian Island near Sicily.
- Most of Earth’s active volcanoes are located over magma chambers.
- The gas planets such as Neptune, Uranus, and Saturn have no solid surface. Therefore, these planets do not have volcanoes.
- Io, one of the moons in Jupiter, is the most volcanically active body in our solar system.
A volcanic winter can cause extreme famines.
Volcanic winter can happen after a major volcanic eruption. It’s the decline in global temperatures due to volcanic ash and its droplets. This phenomenon obscures the sun and raises the Earth’s albedo, the measure of the diffuse reflection of solar radiation from the ground back to the space of incidence.
There are plans for "engineering volcanoes."
Scientists have wanted to find a way to manage or even stop volcanic eruptions altogether. Unfortunately, up to this day, there are no successful developments, though theories and other plans are always constant. Experts knew that a regular volcanic eruption can be somewhat manageable, but looking at the bigger picture, a massive eruption can be very catastrophic. It can wipe out a huge population.
Experts are studying how to depressurize the magma chamber.
Although volcanic eruption forecasting is not 100% accurate, the latest technologies we have can reduce the risk of mishaps through evacuation, until an effective “engineered volcano” has transpired. Some of the plans and arguably the most promising include depressurization of the magma chamber and increasing the opening of the vent to reduce the energy of a potential eruption.
The planet Earth has over 1 million underwater volcanoes.
On our planet, volcanoes often sit in tectonic plates that are converging or diverging, and numerous of them are located underwater. Known as the submarine volcanoes, these underwater vents can also erupt magma like a regular volcano. According to estimates, Earth has over 1 million submarine volcanoes. They are thought to be widespread along the mid-Atlantic ridge located along the floor of the Atlantic Ocean.
There are different kinds of volcanoes.
To a normal person, the most common observation of a volcano is of a “pyramidal mountain,” scattering lava and harmful gases from its crater at the summit. However, this just represents one type of volcano out of the many. Each volcano can have its own unique features and can be more sophisticated than the others. Volcano facts you should take note of!
Geologists had group volcanoes into 4 main kinds.
Geologists have grouped volcanoes into four main kinds: shield volcanoes, lava domes, cinder cones, and composite volcanoes. A shield volcano is normally composed almost entirely of fluid lava flows. Its name, “shield” resembles a shield of a fighter that’s lying on the ground. Furthermore, it’s a wide volcano with a shallowly sloping side.
Lava domes are built by slow eruptions.
Lava domes are built by slow eruptions coming from lava with high viscosity. Normally, lava domes form within the crater of a previous volcanic eruption or can even form independently. Similar to composite volcanoes, lava domes can create powerful eruptions. Although in general, the lava does not flow far from the originating vent.
Mount Fuji is a stratovolcano.
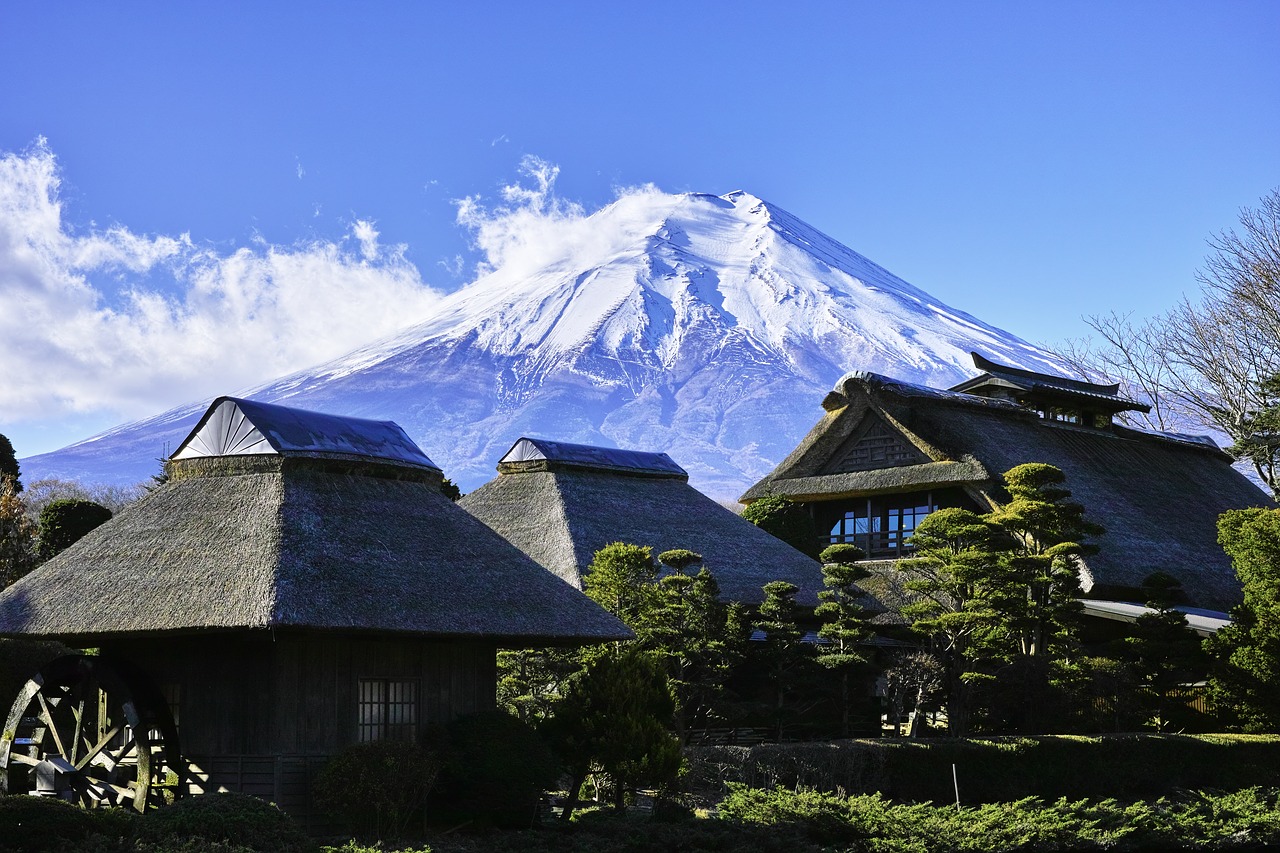

Also known as stratovolcanoes, composite volcanoes are tall cone-shaped mountains. Formed from various kinds of eruptions, the best examples of composite volcanoes are Japan’s Mount Fuji and Italy’s Stromboli. Standing more than 12,000 ft in height, Mount Fuji is the highest mountain in Japan.
Cinder cones came from the eruptions of scoria and pyroclastics.
Cinder cones came from the eruptions of scoria and pyroclastics. They are tiny pieces of highly vesicular dark-colored volcanic rock and clastic rocks made of rock fragments created by explosive volcanism. Arizona’s Sunset Crater and Mexico’s Parícutin are among the world-famous cinder cones.
Located north of Flagstaff, Arizona, Sunset Crater is the youngest in the group of volcanoes in the San Francisco volcanic field. On the other hand, the Parícutin volcano grew suddenly from the cornfield of local farmer Dionisio Pulido in 1943, bringing numerous scientific attention.
Olympus Mons is around 27 km high.
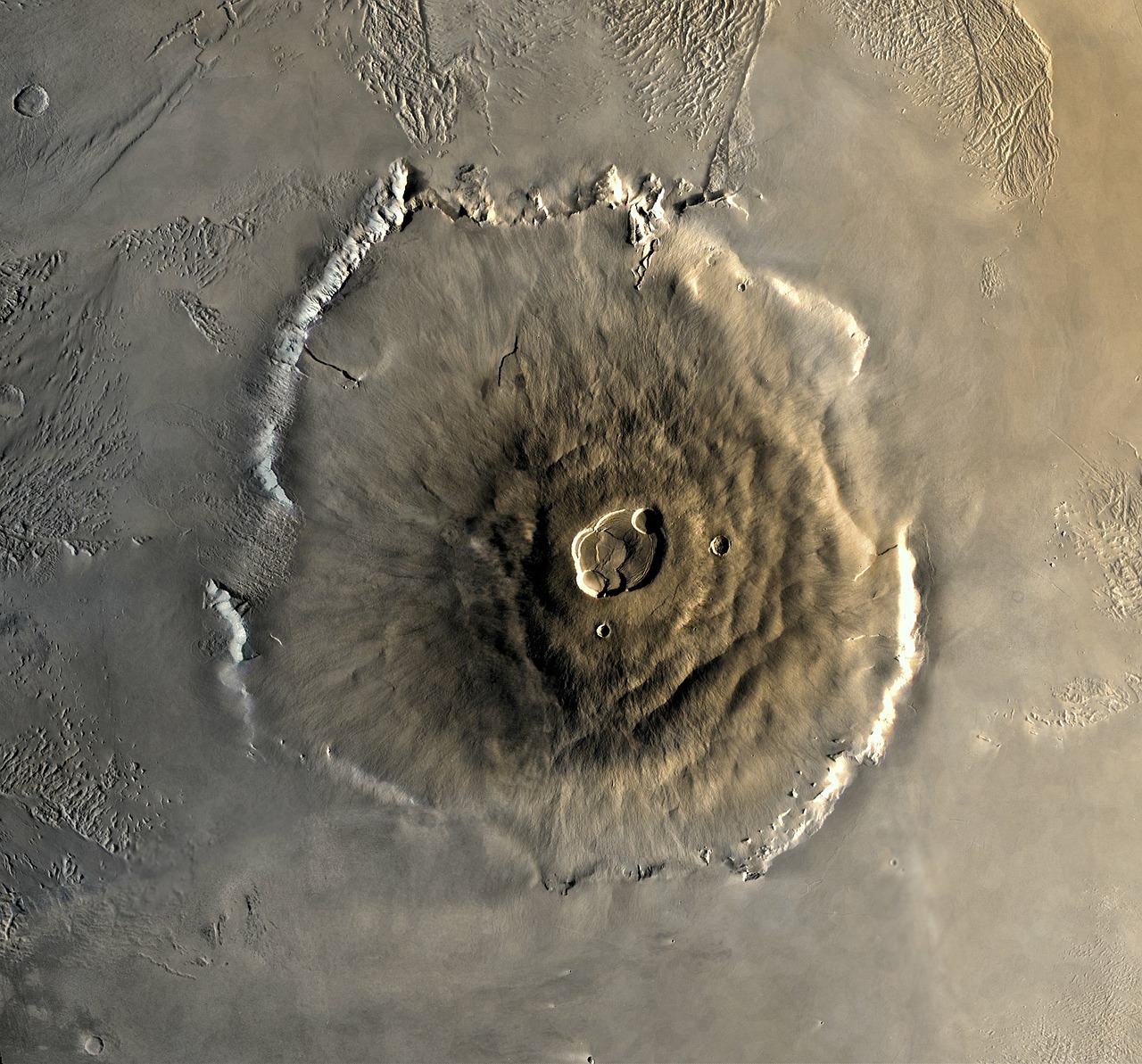
Olympus Mons is the tallest volcano in the known universe. Located on the planet Mars, Olympus Mons stands at 88,583 ft or more than three times the height of Earth’s tallest mountain, Mount Everest. This colossal volcano lies in the Tharsis region of the Red Planet.
Ojos del Salado is the highest active volcano on Earth.
Located in the Andes on Argentina–Chile border, Ojos del Salado is an active composite volcano. It is the highest active volcano on Earth at 22,615 ft. or 6,893 m. The members of the Polish expedition in the Andes, Jan Alfred Szczepański and Justyn Wojsznis, were the first recorded people to reach Ojos del Salado’s summit. Going to Ojos del Salado’s summit requires hiking mostly and the ascent to the top may vary depending on the side you take it from. Tours from Argentina will take approximately 13 to 15 days while the Chilean side takes about nine to 15 days, depending on the hiker’s capabilities.
The Philippines is home to over 250 volcanoes.
Nicknamed as “Pearl of the Orient Seas,” the Philippines is home to over 250 volcanoes. Its three major islands, Luzon, Visayas, and Mindanao, are flocked by thousands of international and local tourists each year to discover the beauty of its land formations. Located in Mindanao, the stratovolcano, Mount Apo is the highest point in the country at 2,954 m. or 9,692 ft. above sea level. Since Mount Apo’s last eruption is unknown, some call Mount Apo a dormant stratovolcano, while others believe it’s very much active.
You need to ride a boat to reach Taal Volcano.
Arguably the most famous volcano in the Philippines and one of the most beautiful volcanoes in the world, the Taal Volcano is a large caldera surrounded by Taal Lake. To be able to see its natural beauty close up, tourists must ride a boat, then hike up to its summit. If they’re not keen on hiking, tourists can ride a horse and hire a tourist guide.
Taal Volcano already erupted more than 30 times.
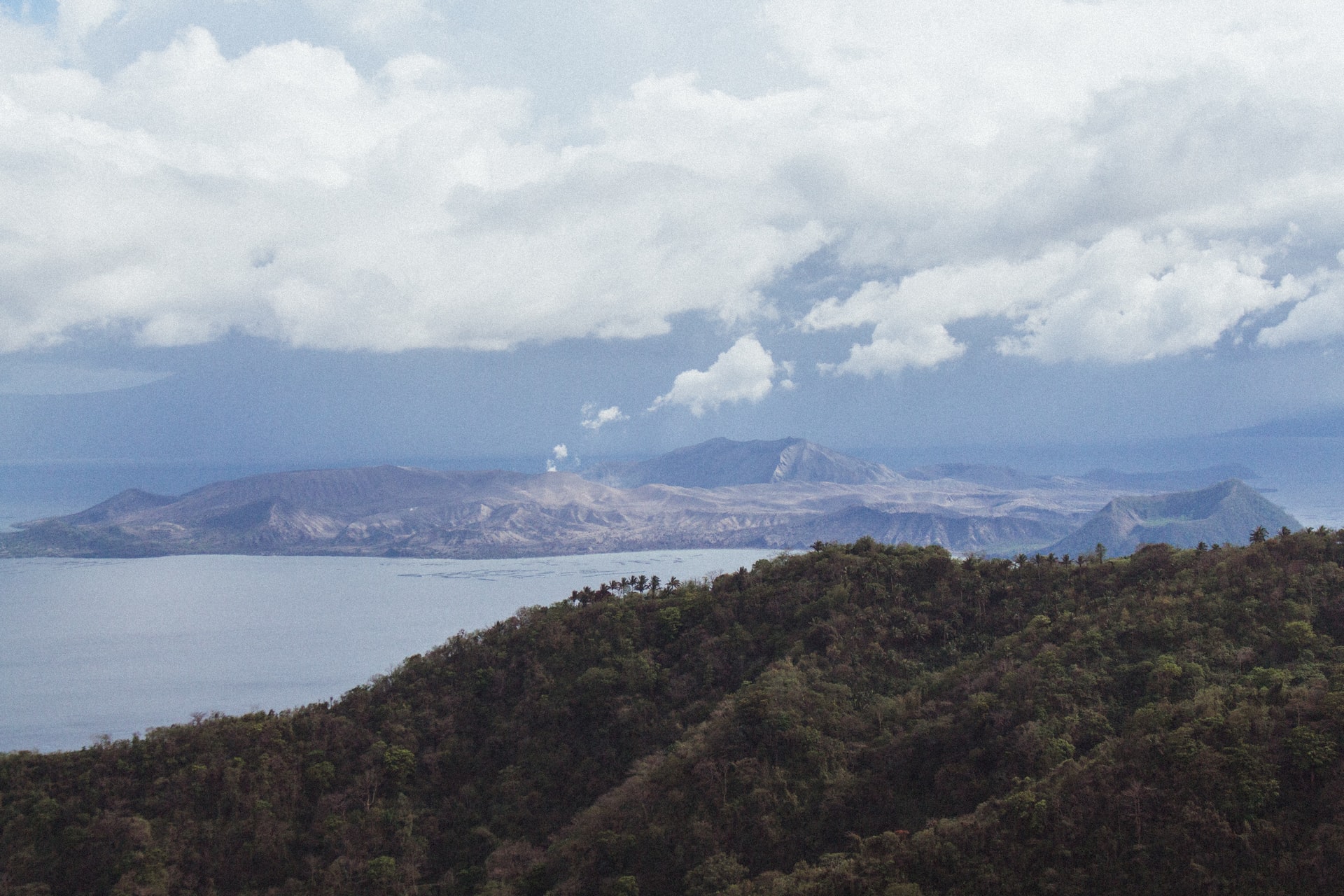

Taal Volcano is also the world’s smallest active volcano. With over 30 recorded historical eruptions since the modern era, its most recent eruption as of this writing was on January 12, 2020, damaging nearby cities and provinces around it. At least $70 million worth of establishments and resources were the amounted losses due to the eruption.
Interestingly and not known to many, you can set up a rare travel tour and swim in the viridian green water of “Taal Volcano’s mouth.” If you’re looking for a one-of-a-kind adventure, then Taal Volcano could be for you!
Mount Pinatubo is the second largest terrestrial eruption of the 20th century.
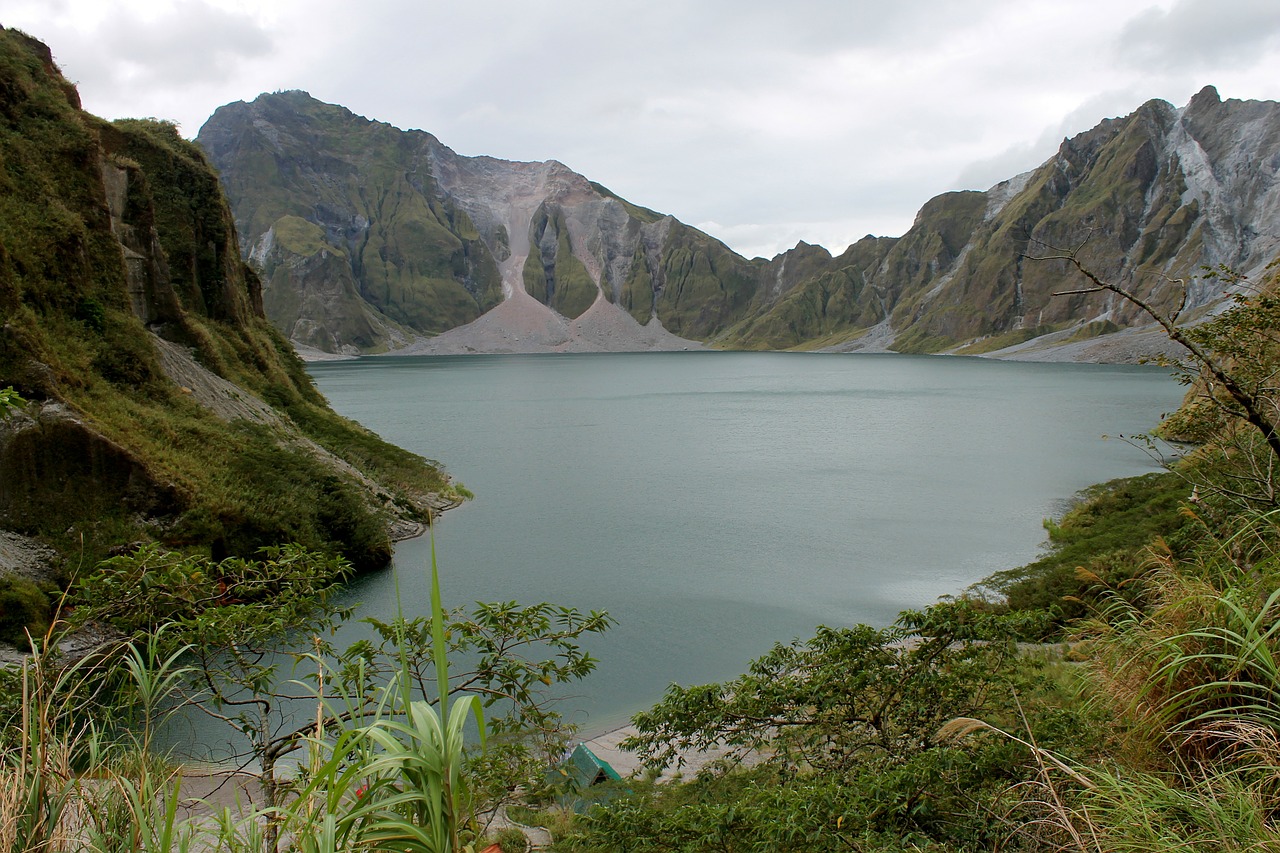

Another volcano from the Philippines, Mount Pinatubo is an active stratovolcano in Luzon. Pinatubo made its name known to the world for its massive eruption on June 15, 1991. It became the second-largest terrestrial eruption of the 20th century next to Alaska’s Novarupta that erupted in 1912.
Hawaii has five five volcanoes.
Hawaii is another beautiful place that’s popular for its volcanoes. The island has five volcanoes and two of those are active, namely Mauna Loa and Kilauea. Moreover, the active shield volcano, Kīlauea is historically the most active of the five volcanoes that together form the magnificent Island of Hawaii. There is an inspiring must-watch I Shouldn’t Be Alive episode titled “Volcano Vacation Hell” where a man survived the volcanic environment of Kilauea.
Mount Vesuvius is one of the most feared volcanoes.
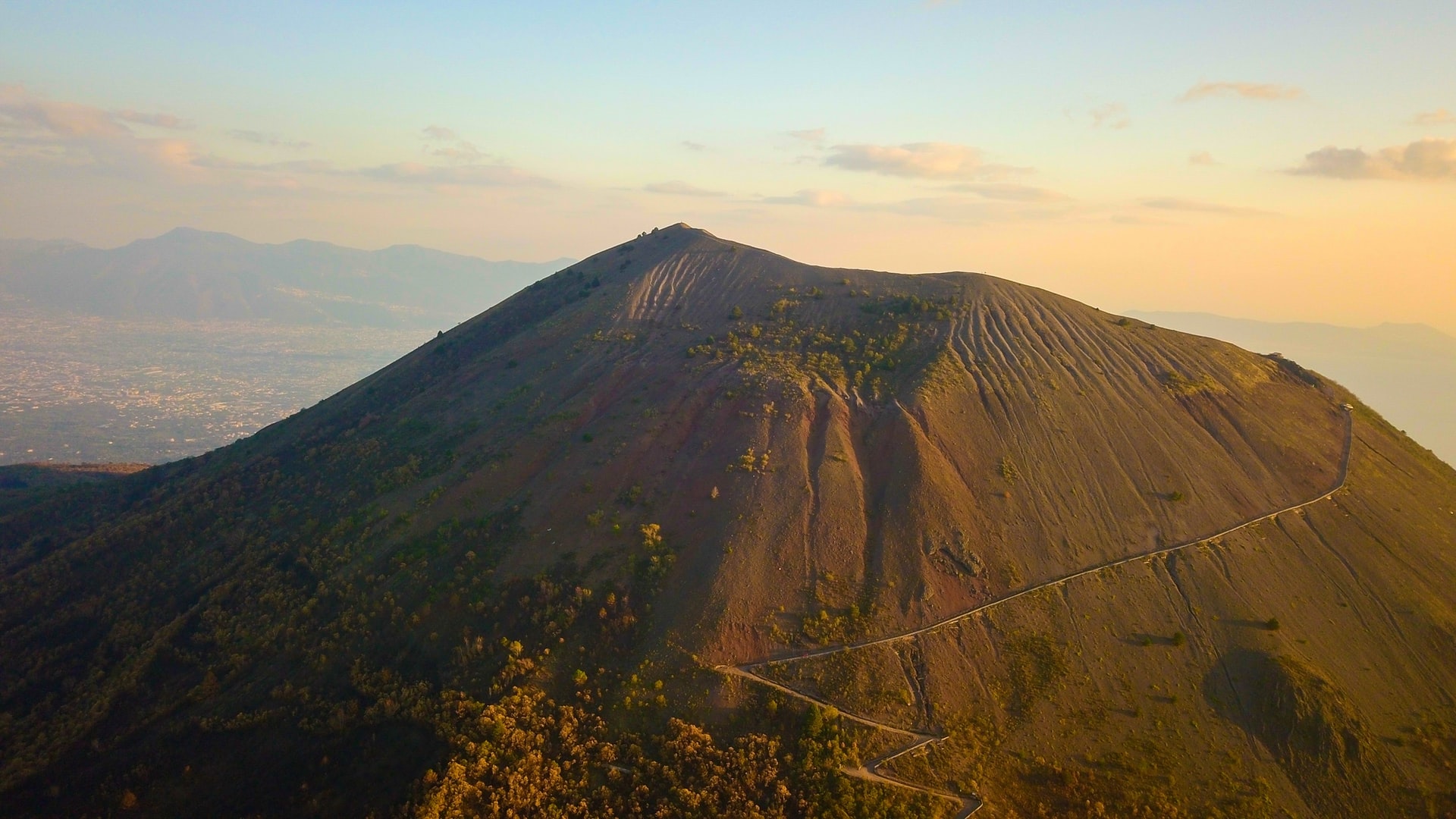

The somma-stratovolcano, Mount Vesuvius (last erupted in March 1944) lies in the Gulf of Naples in Campania, Italy. One of its most historic eruptions dates back to AD 79 that ruined the Roman cities of Pompeii, Herculaneum, Oplontis, and Stabiae, including several other settlements. This volcano is one of the most feared across the globe. Aside from the fact that it’s extremely active and can produce powerful eruptions, it can bury an unbelievable value of infrastructure as well as risking up to 3 million lives within its area.
We create more CO2 emissions than volcanoes.
According to USGS or the United States Geological Survey, both the land and submarine volcanoes of our planet can produce roughly 200 million tons of carbon dioxide (CO2) each year. But compared to our industrial and automotive activities, it’s just a small percentage. Annually, this commercial industry causes over 20 billion tons of CO2 emissions worldwide. Volcano facts that should make you think.
Volcanoes form from rising magma.
Volcanoes on our planet normally form from rising magma. In detail, our Blue Planet’s crust is made of large sections of rock that we call tectonic plates. When a collision between two of Earth’s tectonic plates occurs, the friction created by the plates’ movement produces magma. Thus when the magma approaches the earth’s surface, a volcano is formed.
The hazard area around a volcano covers approximately a 20-mile radius.
In general, the hazard area around a volcano covers approximately a 20-mile radius. However, if a supervolcano such as the Yellowstone Caldera erupts, its ashes can spread hundreds of miles around the western half of the US with an instant devastating impact on the surrounding areas. Thankfully, even though Yellowstone Caldera is still active, experts believe that this volcano will not erupt for at least the next thousand years. And hopefully, future technology will know how to restrain a supervolcano. Yellowstone Caldera’s last eruption was over 600,000 years ago.
A supervolcano has a Volcanic Explosivity Index of 8.
So, what makes a volcano a supervolcano? A supervolcano is a huge volcano that already erupted with a VEI or Volcanic Explosivity Index of 8, and it’s the strongest/largest recorded value on the index. When magma on Earth’s mantle rises into the crust but is unsuccessful to push through, the pressure will build up a massive and growing magma pool until the crust is unable to contain the pressure, then a supervolcano is formed.
Volcanic Explosivity Index starts at 0.
The VEI or Volcanic Explosivity Index has its classifications and description that starts from 0 to 8. The “0 ratings” of VEI is defined as effusive, 1 as gentle, 2 as explosive, and 3 as catastrophic. Furthermore, 4 as cataclysmic, 5 as paroxysmal, 6 as colossal, 7 super-colossal, and finally 8 as mega-colossal such as the Yellowstone Caldera. Volcano facts you need to know!
There's a record of over 10 massive explosive eruptions with VEI 8.
To date, there are over 10 massive explosive eruptions that have ever reached the VEI 8 classification. They are Wah Wah Mountains in Utah, United States, (more than 30 million years ago), La Garita Caldera in Colorado, United States, (27 million years ago), La Pacana in Chile (4 million years ago), Taupo Volcano in North Island, New Zealand (340 thousand years ago), and Lake Toba Caldera in Sumatra, Indonesia (74,000 years ago).
Taupo Volcano is the Earth's most recent supereruption.
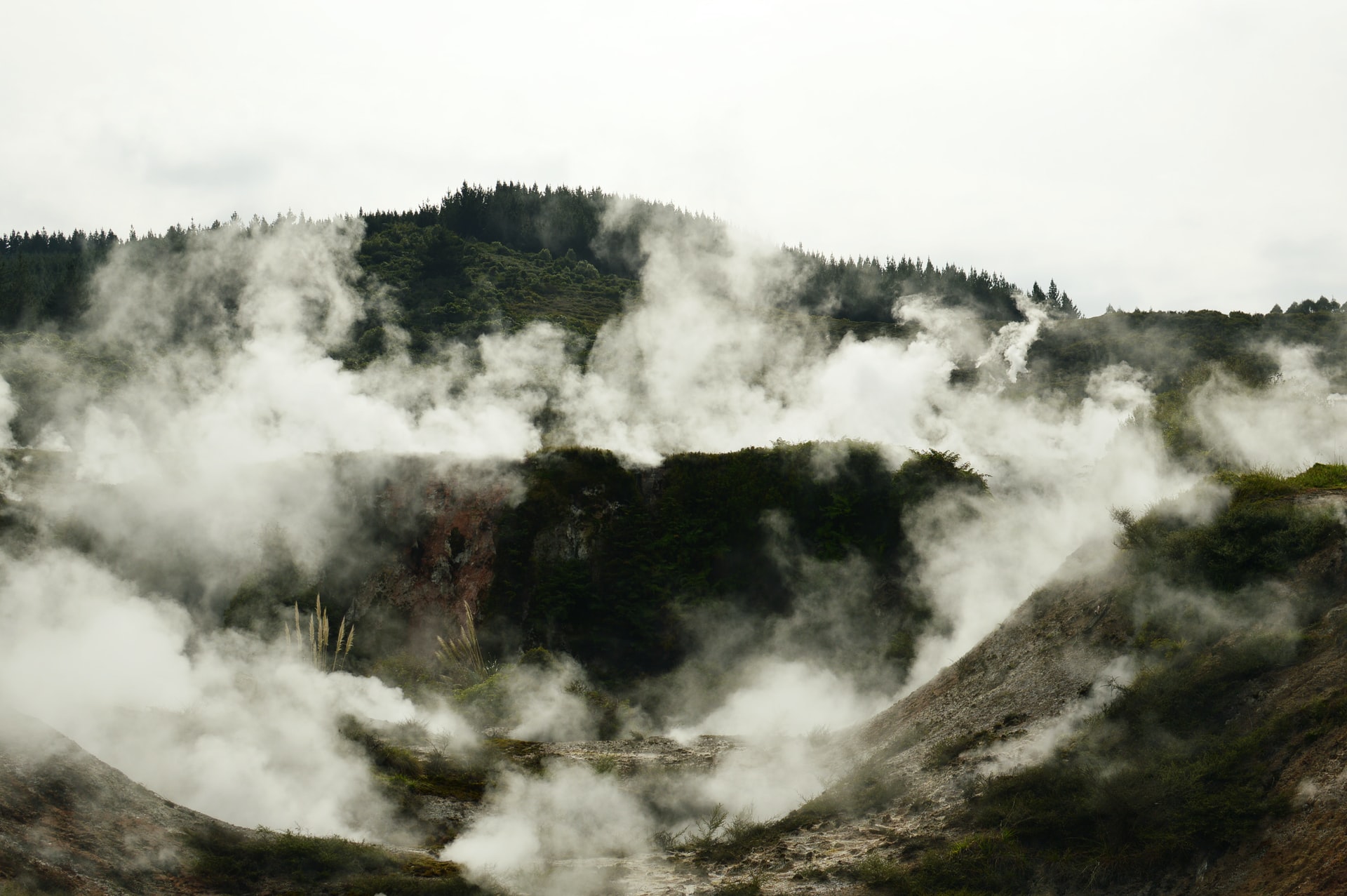

The center of New Zealand’s North Island (Lake Taupo) is a caldera of a large rhyolitic supervolcano. Known as Taupo Volcano, it’s the world’s most up-to-date supereruption and had a Volcanic Explosivity Index of 8 just 26,000 years ago. It is one of the largest eruptions of the world’s history.
Volcanic lighting was observed since 79 AD.
A volcanic eruption can cause volcanic lightning. It’s an electrical discharge coming from the eruption in contrast to the regular thunderstorm. The author, politician, judge, and magistrate of Ancient Rome, ‘Pliny the Younger’ witnessed volcanic lightning in the sky from as early as 79 AD, during the eruption of Mount Vesuvius.
Volcanoes have a loud explosion sound.
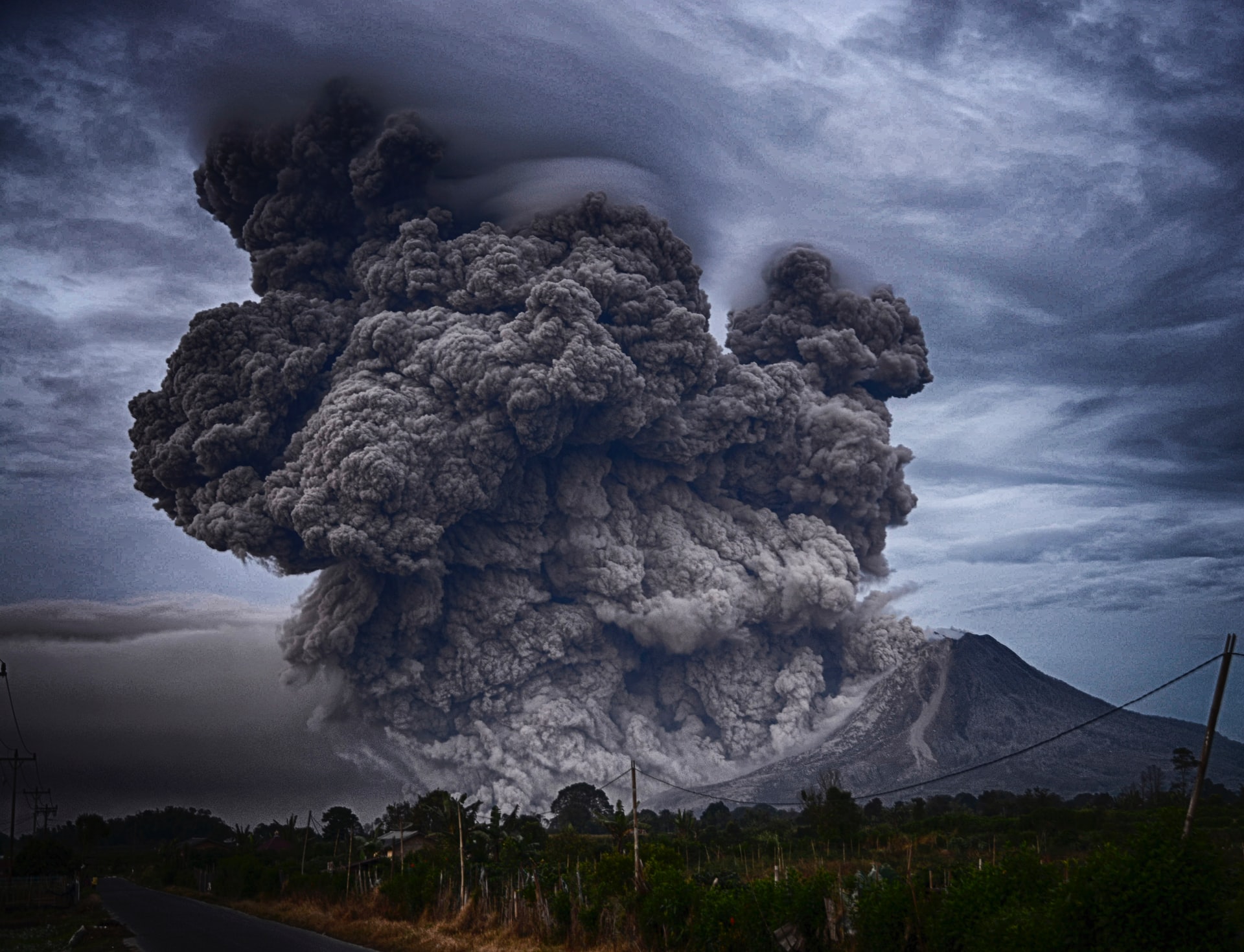

A volcano eruption’s sound is described as loud explosions, hissing, rumbling, bursting bubbles, and a “screaming jet engine.” Each volcano around the world can have a unique sound as there are reports of some eruption to be relatively quiet. Though the loudest ones, their booming sounds can travel hundreds of kilometers and do certain damages such as injuring the sense of hearing and shatter glass.
Volcanic explosion can reach over 150 decibels.
To illustrate thoroughly how loud can a volcanic explosion can be, humans, in general, can tolerate up to 130 decibels. When Krakatoa, a caldera in Indonesia, erupted in 1883, it had recorded 172 decibels at over 100 kilometers from its place. Loud volcano facts!
The 1883 eruption of Krakatoa was a VEI 6.
The 1883 eruption of Krakatoa was massive. Heard from as far as 3,000 kilometers away, its eruption produced a 120-foot tsunami and killed at least 30,000 people. The eruption released more than 15 million tons of sulfur from August 26 to August 27, 1883. Its eruption was heard up to Perth, Western Australia. Thus, it’s one of the deadliest and most colossal volcanic events in recorded history reaching as high as a Volcanic Explosivity Index 6, or VEI 6.
Indonesia is amongst the riskiest countries to experience a volcanic eruption.
According to the experts, the top 10 countries that have the most at risk of a deadly volcanic eruption are:
- Indonesia
- Japan
- Philippines
- Ethiopia
- Mexico
- Ecuador
- Guatemala
- Kenya
- El Salvador
- Italy
There's a difference between an extinct and dormant volcano.
An extinct volcano is a particular volcano that has not erupted. It has never erupted! An example of this would be Mount Thielsen in Oregon, United States. Meanwhile, dormant volcanoes are the ones that have not erupted in thousands of years but have a tendency to erupt again in the far or near future.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
