Dholavira, an ancient city of the Indus Valley Civilization, holds many secrets. Located in present-day Gujarat, India, this archaeological site offers a glimpse into a sophisticated urban life that existed over 4,000 years ago. Why is Dholavira significant? It is one of the five largest Harappan sites and showcases advanced water conservation systems, intricate city planning, and a unique script yet to be deciphered. Visitors can marvel at the well-preserved structures, including reservoirs, step wells, and a grand citadel. Dholavira's discovery has provided invaluable insights into early human ingenuity and resilience. Ready to learn more about this ancient marvel? Let's dive into 24 fascinating facts about Dholavira!
Ancient City of Dholavira
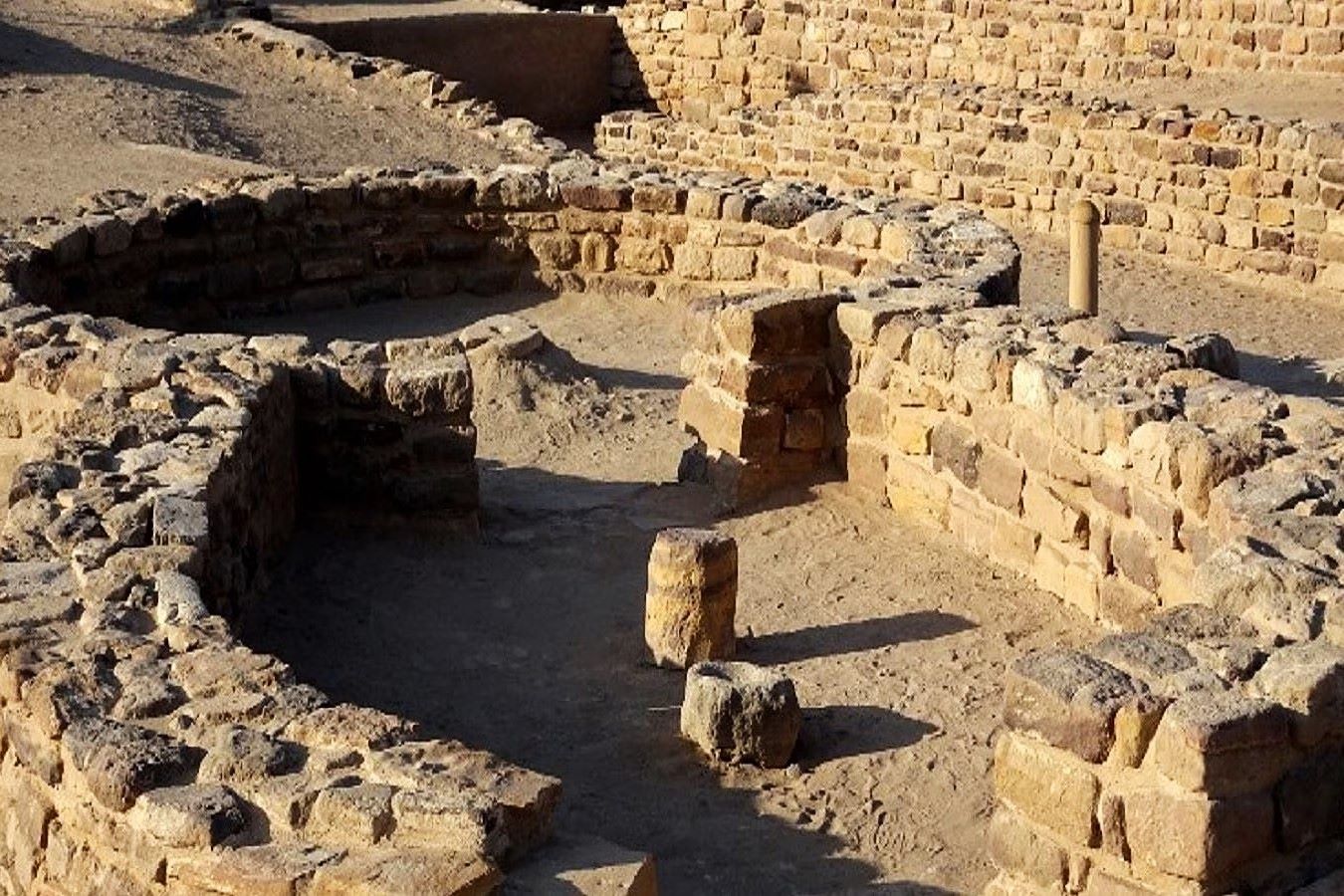
Dholavira, an archaeological site in Gujarat, India, is one of the most remarkable cities of the ancient Indus Valley Civilization. This city offers a glimpse into the life and times of a civilization that thrived thousands of years ago.
- Dholavira is located on the Khadir Bet island in the Rann of Kutch.
- The site was discovered in 1967-68 by archaeologist Jagat Pati Joshi.
- Dholavira is one of the five largest Harappan sites and the most prominent archaeological site in India belonging to the Indus Valley Civilization.
- The city covers an area of about 100 hectares.
Unique Urban Planning
Dholavira stands out for its advanced urban planning and architecture. The city's layout reflects a high level of sophistication and organization.
- The city was divided into three main parts: the citadel, the middle town, and the lower town.
- Each part of the city was fortified with massive walls.
- Dholavira had a well-planned drainage system, with channels made of stone and terracotta.
- The city featured large reservoirs for water storage, showcasing advanced hydraulic engineering.
Ingenious Water Management
Water management was a crucial aspect of life in Dholavira, given its arid location. The inhabitants developed innovative methods to collect and store water.
- Dholavira had 16 reservoirs, some of which were as large as modern-day swimming pools.
- The city utilized a series of dams and channels to divert rainwater into these reservoirs.
- Step wells were constructed to access groundwater during dry periods.
- The water management system ensured a stable water supply for the city's population.
Remarkable Artifacts
Excavations at Dholavira have unearthed a wealth of artifacts that provide insights into the culture and daily life of its inhabitants.
- Archaeologists found a large number of seals, which were used for trade and administrative purposes.
- Pottery, beads, and terracotta figurines were discovered, indicating a rich material culture.
- A unique find at Dholavira is a large signboard with ten large symbols, possibly representing an early form of writing.
- Jewelry made of gold, silver, and semi-precious stones was also found, showcasing the craftsmanship of the people.
Trade and Economy
Dholavira was a significant center of trade and commerce in the Indus Valley Civilization. Its strategic location facilitated trade with other regions.
- The city had a thriving economy based on agriculture, animal husbandry, and trade.
- Dholavira's inhabitants traded goods such as beads, pottery, and textiles with other Harappan cities and distant regions.
- The presence of marine shells and semi-precious stones indicates trade with coastal and inland areas.
- The city's economy was supported by a standardized system of weights and measures.
Decline and Abandonment
Like many other Indus Valley Civilization sites, Dholavira eventually declined and was abandoned. Several factors contributed to this decline.
- Climate change and a shift in the course of rivers likely led to water scarcity.
- The decline of trade networks may have weakened the city's economy.
- Archaeological evidence suggests that the city was gradually abandoned rather than destroyed suddenly.
- Despite its decline, Dholavira remains a testament to the ingenuity and resilience of the Indus Valley Civilization.
Final Glimpse of Dholavira
Dholavira, a gem of the ancient Indus Valley Civilization, offers a peek into a world long gone. From its advanced water management system to the intricate city planning, this site showcases human ingenuity from thousands of years ago. The Great Bath, citadel, and lower town reveal a society that valued cleanliness, order, and community. Artifacts like beads, pottery, and seals tell stories of daily life, trade, and culture. Visiting Dholavira isn't just about seeing ruins; it's about connecting with a past that laid the groundwork for future civilizations. Whether you're a history buff or just curious, Dholavira promises a journey through time, highlighting the brilliance of our ancestors. So, next time you're looking for a historical adventure, remember Dholavira – a testament to human achievement and resilience.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.