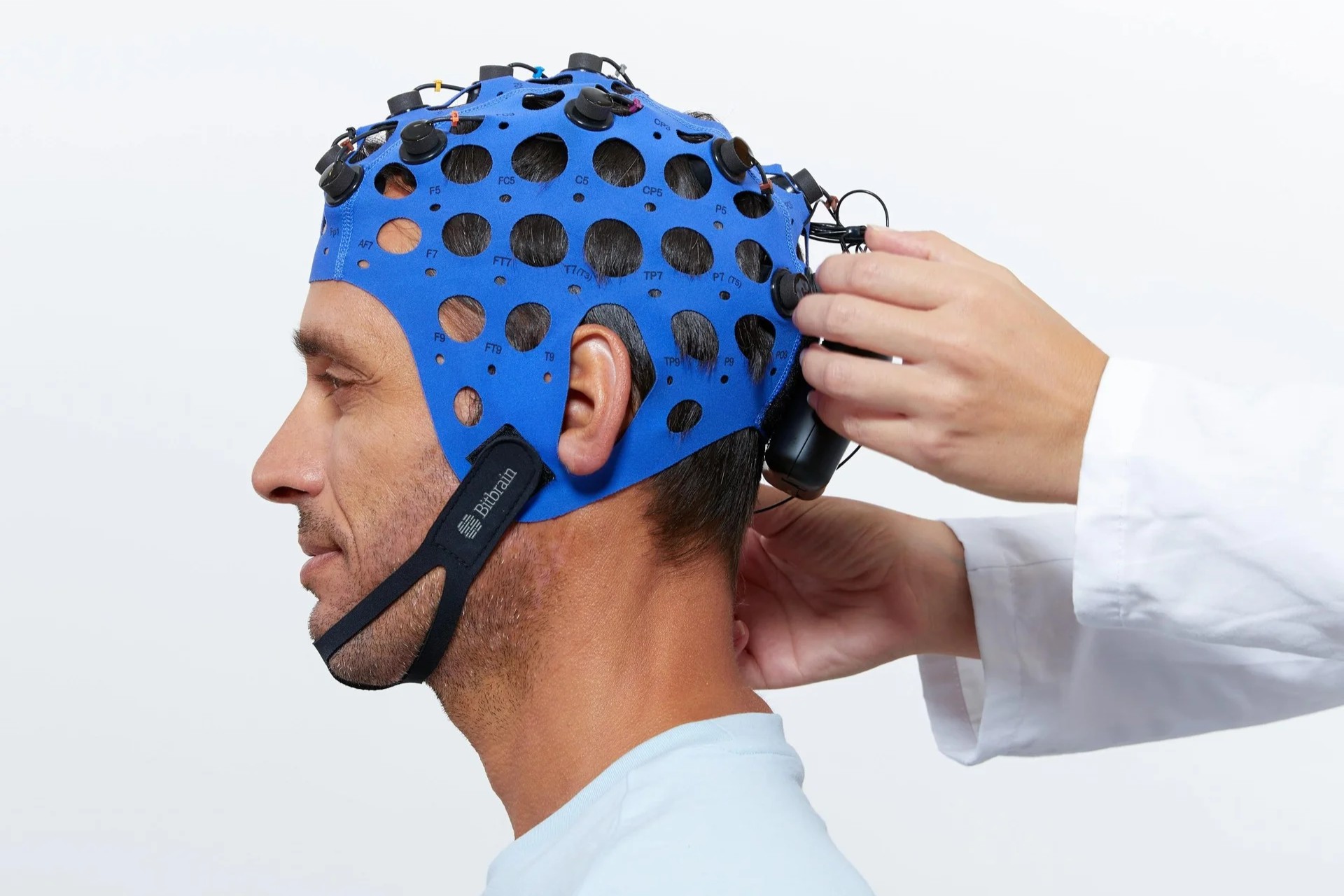
Electroencephalography (EEG) is a fascinating tool used to measure electrical activity in the brain. EEG helps doctors diagnose conditions like epilepsy, sleep disorders, and brain injuries. This non-invasive method involves placing electrodes on the scalp to detect brain waves. Did you know that Hans Berger, a German psychiatrist, invented the EEG in 1924? Since then, it has become a crucial part of neuroscience and medical diagnostics. EEG can even help in understanding cognitive functions like memory and attention. Whether you're a student, a curious mind, or someone interested in medical technology, these 30 facts about EEG will enlighten you on its importance and applications.
What is Electroencephalography (EEG)?
Electroencephalography, commonly known as EEG, is a technique used to measure electrical activity in the brain. It involves placing electrodes on the scalp to detect brain waves. This method has been instrumental in understanding brain functions and diagnosing various neurological conditions.
-
EEG measures brain waves. These waves are electrical impulses generated by neurons communicating with each other.
-
Hans Berger invented EEG. In 1924, German psychiatrist Hans Berger recorded the first human EEG, revolutionizing neuroscience.
-
EEG is non-invasive. Unlike some other brain imaging techniques, EEG does not require surgery or injections.
-
EEG can detect epilepsy. One of its primary uses is diagnosing epilepsy by identifying abnormal brain wave patterns.
-
EEG helps in sleep studies. It monitors brain activity during sleep to diagnose disorders like sleep apnea and narcolepsy.
How Does EEG Work?
Understanding how EEG works can demystify its applications and importance. The process involves several steps, from electrode placement to data interpretation.
-
Electrodes are placed on the scalp. These small sensors detect electrical activity in the brain.
-
EEG records brain waves. The electrical signals are amplified and recorded as wave patterns on a computer.
-
Different brain waves indicate different states. For example, alpha waves are associated with relaxation, while beta waves indicate alertness.
-
EEG data is analyzed by specialists. Neurologists and other experts interpret the wave patterns to diagnose conditions.
-
EEG can be done in various settings. It can be performed in hospitals, clinics, or even at home with portable devices.
Applications of EEG
EEG has a wide range of applications, from medical diagnostics to research and beyond. Its versatility makes it a valuable tool in many fields.
-
EEG is used in research. Scientists use it to study brain functions and cognitive processes.
-
EEG aids in brain-computer interfaces. It helps develop systems that allow people to control devices with their thoughts.
-
EEG monitors anesthesia depth. During surgery, it ensures patients remain unconscious and pain-free.
-
EEG assists in diagnosing brain injuries. It can detect abnormalities caused by trauma or stroke.
-
EEG is used in neurofeedback therapy. This technique helps people learn to control their brain waves to improve mental health.
EEG in Everyday Life
Beyond clinical and research settings, EEG technology is making its way into everyday life, offering new possibilities for personal health and entertainment.
-
EEG headsets for gaming. Some video games use EEG to create immersive experiences controlled by brain waves.
-
EEG in meditation apps. These apps use EEG to monitor brain activity and provide feedback for better meditation practices.
-
EEG for stress management. Devices track brain waves to help users manage stress and improve relaxation.
-
EEG in education. It helps understand how students learn and can tailor teaching methods to individual needs.
-
EEG in sports. Athletes use it to enhance focus and performance by training their brain waves.
Future of EEG
The future of EEG looks promising with advancements in technology and new applications emerging. This section explores what lies ahead for EEG.
-
Wireless EEG systems. Future devices will be more portable and user-friendly, allowing for continuous monitoring.
-
EEG and artificial intelligence. AI will enhance data analysis, making it faster and more accurate.
-
EEG in virtual reality. Combining EEG with VR could create more immersive and interactive experiences.
-
EEG for mental health. It will play a bigger role in diagnosing and treating mental health conditions.
-
EEG in personalized medicine. Tailoring treatments based on individual brain wave patterns will become more common.
Interesting Facts About EEG
Here are some lesser-known yet fascinating facts about EEG that highlight its uniqueness and versatility.
-
EEG can detect brain death. It helps determine if a person has lost all brain activity.
-
EEG is used in lie detection. Some lie detectors incorporate EEG to measure brain responses.
-
EEG can study animal brains. Researchers use it to understand brain functions in various species.
-
EEG helps in biofeedback. This technique trains people to control physiological functions by monitoring brain waves.
-
EEG in art. Artists use EEG to create interactive installations that respond to viewers' brain activity.
The Power of EEG
Electroencephalography (EEG) is a fascinating tool that has transformed our understanding of the brain. From diagnosing epilepsy to aiding in sleep studies, EEG provides invaluable insights into brain activity. Its non-invasive nature makes it a preferred choice for both medical professionals and researchers.
EEG's ability to monitor brain waves in real-time helps in understanding various neurological conditions and mental states. This technology has also paved the way for advancements in brain-computer interfaces, offering hope for individuals with severe disabilities.
As we continue to explore the brain's complexities, EEG remains a cornerstone in neuroscience. Its applications are vast, and its potential is still being unlocked. Whether you're a student, a researcher, or just curious about the brain, understanding EEG can open up a world of knowledge.
Stay curious, and keep exploring the wonders of the human brain!
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
