What are logic gates? Logic gates are the building blocks of digital circuits. They perform basic logical functions essential for computer operations. Why are they important? Without logic gates, computers wouldn't process information or execute commands. How do they work? Each gate takes one or more binary inputs and produces a single binary output. Types of logic gates include AND, OR, NOT, NAND, NOR, XOR, and XNOR. Applications range from simple calculators to complex microprocessors. Fun fact: The first logic gates were mechanical switches! Ready to learn more? Let's dive into 38 fascinating facts about these tiny yet powerful components.
What Are Logic Gates?
Logic gates are the building blocks of digital circuits. They perform basic logical functions essential for digital computing. Here are some fascinating facts about them:
-
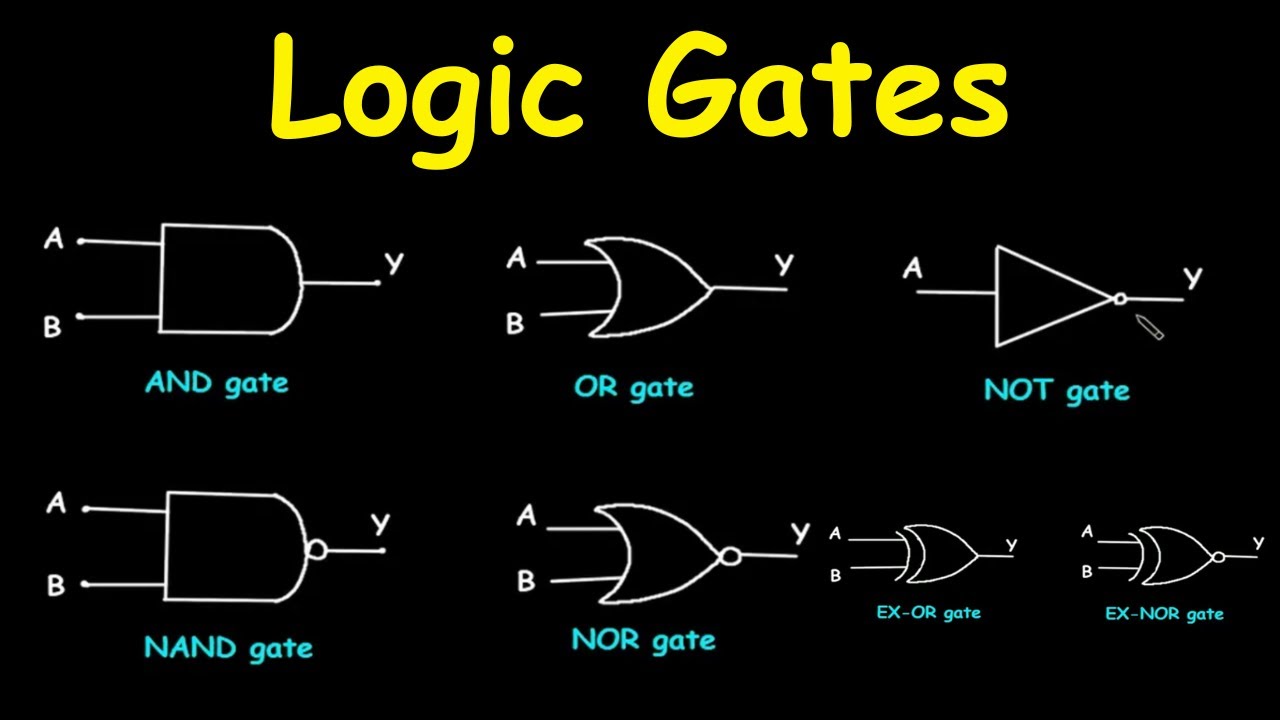
Basic Types: The three fundamental logic gates are AND, OR, and NOT. These gates form the basis of more complex circuits.
-
Binary Inputs: Logic gates operate using binary inputs, which means they only understand 0s and 1s.
-
Truth Tables: Each gate has a truth table that shows all possible input combinations and their corresponding outputs.
-
AND Gate: This gate outputs 1 only if all its inputs are 1. Otherwise, it outputs 0.
-
OR Gate: The OR gate outputs 1 if at least one of its inputs is 1. If all inputs are 0, it outputs 0.
-
NOT Gate: Also known as an inverter, the NOT gate outputs the opposite of its input. If the input is 1, the output is 0, and vice versa.
Advanced Logic Gates
Beyond the basic gates, there are more advanced types that perform specific functions. These gates are crucial for more complex operations.
-
NAND Gate: This gate is the opposite of the AND gate. It outputs 0 only if all its inputs are 1.
-
NOR Gate: The NOR gate outputs 1 only if all its inputs are 0. Otherwise, it outputs 0.
-
XOR Gate: The XOR (exclusive OR) gate outputs 1 if an odd number of its inputs are 1. If the number of 1s is even, it outputs 0.
-
XNOR Gate: This gate is the opposite of the XOR gate. It outputs 1 if an even number of its inputs are 1.
Applications of Logic Gates
Logic gates are not just theoretical concepts; they have practical applications in various fields. Here are some examples:
-
Computers: Logic gates are the foundation of computer processors. They perform arithmetic and logical operations.
-
Digital Clocks: These devices use logic gates to keep accurate time.
-
Calculators: Logic gates help perform basic arithmetic operations in calculators.
-
Traffic Lights: Logic gates control the sequence of traffic lights to ensure smooth traffic flow.
-
Robotics: Robots use logic gates to make decisions based on sensor inputs.
Historical Facts
The history of logic gates is rich and fascinating. Here are some historical tidbits:
-
George Boole: The concept of logic gates is based on Boolean algebra, developed by George Boole in the 19th century.
-
Claude Shannon: In 1937, Claude Shannon applied Boolean algebra to electrical circuits, laying the groundwork for digital circuits.
-
First Computer: The first electronic computer, ENIAC, used thousands of vacuum tubes as logic gates.
-
Transistors: The invention of the transistor in 1947 revolutionized logic gates, making them smaller and more efficient.
-
Integrated Circuits: In the 1960s, integrated circuits allowed multiple logic gates to be placed on a single chip.
Fun Facts
Logic gates can be fun too! Here are some interesting and quirky facts:
-
Minecraft: Players can build logic gates in the game Minecraft using redstone.
-
DNA Computing: Scientists have created logic gates using DNA molecules.
-
Quantum Gates: In quantum computing, logic gates operate on quantum bits, or qubits, which can be both 0 and 1 simultaneously.
-
Light Gates: Researchers are developing logic gates that use light instead of electricity for faster processing.
-
Biological Gates: Some researchers are exploring the use of biological cells to create logic gates.
Real-World Examples
Logic gates are everywhere, even if you don't see them. Here are some real-world examples:
-
Smartphones: Your smartphone's processor uses millions of logic gates to function.
-
Home Appliances: Devices like microwaves and washing machines use logic gates for their control systems.
-
Automobiles: Modern cars use logic gates in their electronic control units (ECUs) for various functions.
-
Telecommunications: Logic gates are essential in the functioning of telecommunication networks.
-
Gaming Consoles: Consoles like the PlayStation and Xbox use logic gates in their processors.
Educational Uses
Logic gates are also important in education. Here are some ways they are used:
-
Teaching Tool: Logic gates are used to teach basic concepts of digital electronics and computer science.
-
Simulations: Students use software to simulate logic gate circuits and understand their behavior.
-
Hands-On Projects: Building simple circuits with logic gates helps students grasp their practical applications.
-
Competitions: Robotics competitions often involve creating logic gate circuits to solve problems.
Future of Logic Gates
The future holds exciting possibilities for logic gates. Here are some trends and predictions:
-
Smaller Gates: As technology advances, logic gates will continue to shrink, allowing for more powerful and compact devices.
-
Faster Processing: Innovations like optical and quantum gates promise faster processing speeds.
-
Energy Efficiency: Future logic gates will likely be more energy-efficient, reducing the power consumption of electronic devices.
-
New Materials: Researchers are exploring new materials, like graphene, to create more efficient logic gates.
The Final Word on Logic Gates
Logic gates are the building blocks of digital circuits. They control how devices like computers, smartphones, and even microwaves process information. Understanding AND, OR, NOT, NAND, NOR, XOR, and XNOR gates can help you grasp how complex operations are performed using simple binary inputs. These gates form the foundation of Boolean algebra, which is crucial for designing and troubleshooting digital systems.
Whether you're a student, hobbyist, or professional, knowing how these gates work can open doors to new opportunities in electronics and computer science. From creating basic circuits to developing advanced algorithms, logic gates are everywhere. So next time you use any digital device, remember the tiny but mighty logic gates making it all possible. Keep exploring, keep learning, and who knows? You might just invent the next big thing in tech!
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
