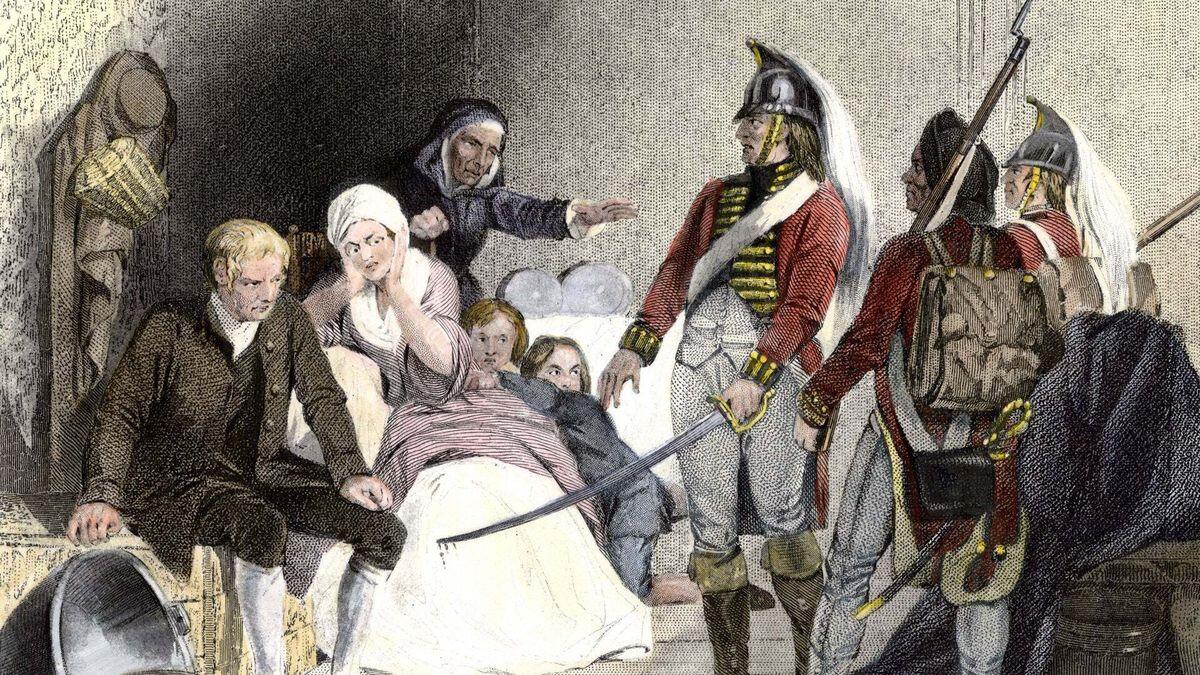
Amendment 3 of the United States Constitution is often overlooked, but it holds a unique place in American history. This amendment states, "No Soldier shall, in time of peace be quartered in any house, without the consent of the Owner, nor in time of war, but in a manner to be prescribed by law." It was a direct response to British practices during the colonial period, where soldiers were housed in private homes without permission. Though rarely cited in modern legal cases, it underscores the importance of privacy and property rights. Understanding Amendment 3 helps us appreciate the broader context of the Bill of Rights and the framers' intent to protect individual freedoms. Ready to learn more? Here are 33 intriguing facts about this often-forgotten amendment.
Key Takeaways:
- Amendment 3 refers to changes in laws and rights. It involves historical context, public opinion, and impacts on society, shaping social, economic, and cultural aspects.
- Amendment 3 influences society through social change, economic effects, and cultural shifts. It involves controversies, legal processes, and notable figures, shaping its future and popular culture.
What is Amendment 3?
Amendment 3 refers to a specific change or addition to a constitution or legal document. These amendments can significantly impact laws, rights, and governance. Let's dive into some intriguing facts about Amendment 3.
-
Historical Context: Amendment 3 often arises in discussions about constitutional changes. Understanding its historical background can provide insight into its significance.
-
Legal Framework: Amendments like this are part of a broader legal framework. They help adapt laws to changing societal needs.
-
Public Opinion: Public opinion plays a crucial role in the adoption of amendments. Voter support or opposition can determine their success.
Key Features of Amendment 3
Amendment 3 usually contains specific provisions that address particular issues. These features can vary widely depending on the context.
-
Specific Provisions: Each Amendment 3 has unique provisions tailored to address specific legal or social issues.
-
Implementation: The process of implementing an amendment can be complex, involving multiple steps and stakeholders.
-
Impact on Rights: Amendments often impact individual or collective rights, either expanding or restricting them.
Historical Examples of Amendment 3
Throughout history, various Amendment 3s have been proposed and adopted. These examples highlight their diverse applications.
-
U.S. Constitution: The Third Amendment to the U.S. Constitution prohibits the quartering of soldiers in private homes without the owner's consent.
-
State Constitutions: Many U.S. states have their own Amendment 3s addressing issues like taxation, education, or governance.
-
International Examples: Other countries also have amendments labeled as Amendment 3, each with unique contexts and implications.
The Process of Amending Constitutions
Amending a constitution is a rigorous process that involves multiple steps and stakeholders. Understanding this process can shed light on the significance of Amendment 3.
-
Proposal Stage: Amendments are typically proposed by legislators or through citizen initiatives.
-
Debate and Revision: Proposed amendments undergo extensive debate and revision before being finalized.
-
Ratification: Ratification often requires approval by a supermajority of legislators or a public vote.
The Role of Judiciary in Amendment 3
The judiciary plays a crucial role in interpreting and enforcing amendments. Their decisions can shape the practical impact of Amendment 3.
-
Judicial Review: Courts have the power to review amendments and determine their constitutionality.
-
Case Law: Judicial decisions create case law that guides the application of amendments.
-
Enforcement: Courts also play a role in enforcing amendments, ensuring compliance with their provisions.
Controversies Surrounding Amendment 3
Amendments can be controversial, sparking debates and disagreements. Amendment 3 is no exception.
-
Political Disputes: Political parties often have differing views on amendments, leading to heated debates.
-
Public Protests: Controversial amendments can lead to public protests and activism.
-
Legal Challenges: Amendments may face legal challenges that question their validity or implementation.
The Impact of Amendment 3 on Society
Amendments can have far-reaching impacts on society, influencing various aspects of life.
-
Social Change: Amendments can drive significant social change, addressing issues like civil rights or public policy.
-
Economic Effects: Economic policies and regulations can be shaped by constitutional amendments.
-
Cultural Shifts: Amendments can reflect and influence cultural values and norms.
Future Prospects of Amendment 3
Looking ahead, the future of Amendment 3 will depend on evolving societal needs and legal developments.
-
Potential Revisions: Future revisions or new amendments may build on the foundations of Amendment 3.
-
Technological Advances: Technological changes can create new issues that amendments need to address.
-
Global Trends: Global trends and international developments can influence the direction of constitutional amendments.
Notable Figures Involved in Amendment 3
Key individuals often play significant roles in the development and adoption of amendments.
-
Legislators: Lawmakers who propose and advocate for amendments are crucial to their success.
-
Activists: Activists and advocacy groups can drive public support for amendments.
-
Legal Experts: Legal scholars and experts provide essential analysis and interpretation of amendments.
Educational Resources on Amendment 3
For those interested in learning more, various educational resources are available.
-
Books: Numerous books provide in-depth analysis of constitutional amendments.
-
Online Courses: Online courses offer accessible education on legal and constitutional topics.
-
Documentaries: Documentaries can provide visual and narrative insights into the history and impact of amendments.
Amendment 3 in Popular Culture
Amendments can also find their way into popular culture, influencing media and entertainment.
-
Movies: Films often explore themes related to constitutional rights and amendments.
-
TV Shows: Television series can dramatize legal and political battles over amendments.
-
Literature: Novels and other literary works may incorporate themes related to constitutional changes.
The Final Word on Amendment 3
Amendment 3, part of the U.S. Constitution, protects citizens from being forced to house soldiers during peacetime. This amendment, born from the grievances of the American Revolution, ensures privacy and property rights. Though rarely cited in modern court cases, it remains a vital part of the Bill of Rights, symbolizing the importance of personal freedom and government limits.
Understanding Amendment 3 helps grasp the broader context of American liberties. It reminds us of the historical struggles that shaped today's legal landscape. While not often in the spotlight, its presence reinforces the balance between individual rights and governmental power.
So, next time you think about constitutional rights, remember Amendment 3. It’s a small but significant piece of the puzzle that protects our freedoms.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
