Magnetic refrigeration might sound like something out of a sci-fi movie, but it's a real technology with some cool facts. Did you know that magnetic refrigeration uses a special material called a magnetocaloric material to cool things down? Unlike traditional fridges that use harmful gases, this method is eco-friendly. How does it work? When the magnetocaloric material is exposed to a magnetic field, it heats up. Remove the magnetic field, and it cools down. This cycle can be repeated to create a cooling effect. Why should you care? Because it could lead to quieter, more efficient, and environmentally friendly refrigerators in the future. Ready to learn more? Let's dive into 37 fascinating facts about this innovative technology!
What is Magnetic Refrigeration?
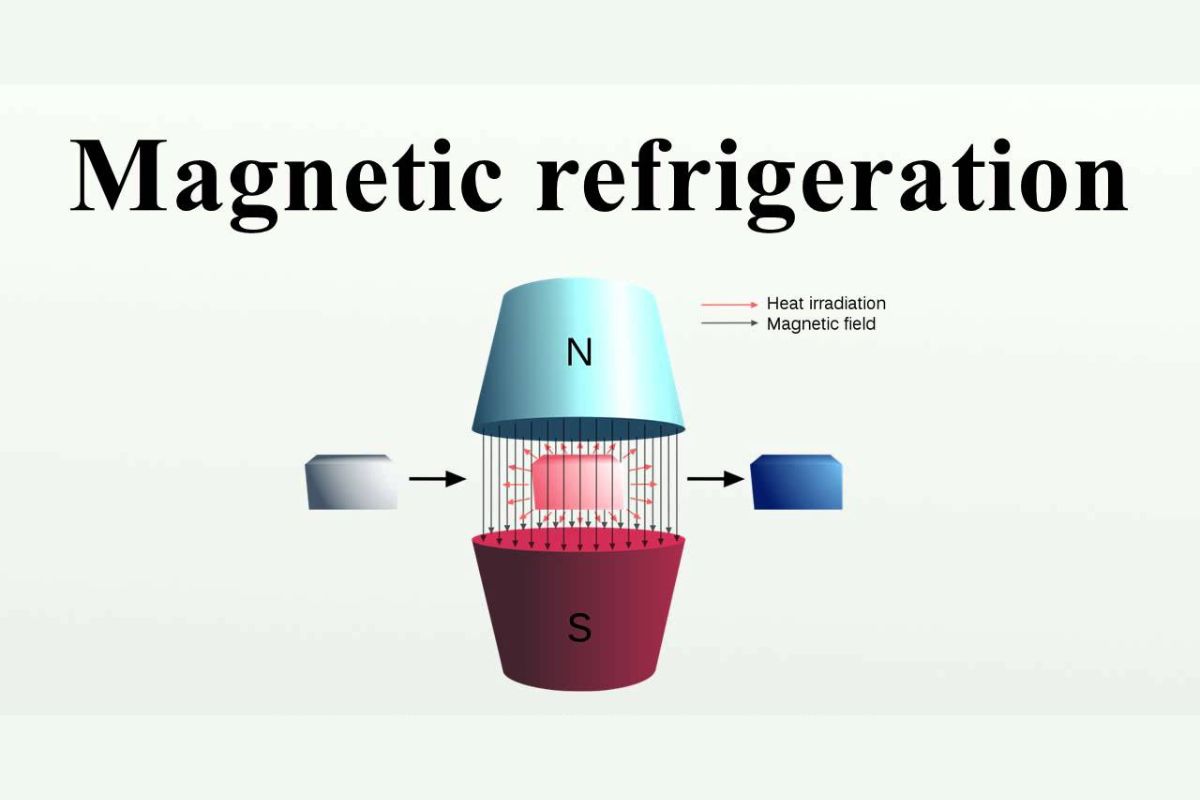
Magnetic refrigeration is a cooling technology that uses the magnetocaloric effect to achieve refrigeration. This method is considered an eco-friendly alternative to traditional gas-compression refrigeration. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about this innovative technology.
-
Magnetic refrigeration relies on the magnetocaloric effect, where certain materials heat up when magnetized and cool down when demagnetized.
-
The concept was first discovered by German physicist Emil Warburg in 1881.
-
Magnetic refrigeration systems use solid refrigerants instead of harmful gases like CFCs or HFCs.
-
This technology can potentially reduce energy consumption by up to 30% compared to conventional refrigeration methods.
-
Magnetic refrigeration operates silently, making it ideal for noise-sensitive environments.
How Does Magnetic Refrigeration Work?
Understanding the working mechanism of magnetic refrigeration can help appreciate its benefits and applications. Here are some key points about its operation.
-
The process begins with a magnetocaloric material placed in a magnetic field.
-
When the material is magnetized, its temperature increases due to the alignment of magnetic dipoles.
-
The material is then cooled by transferring heat to a surrounding medium, usually water or air.
-
Once the material is demagnetized, it cools down further, absorbing heat from the environment.
-
This cycle of magnetization and demagnetization continues, providing continuous cooling.
Advantages of Magnetic Refrigeration
Magnetic refrigeration offers several benefits over traditional cooling methods. Here are some of the most notable advantages.
-
It eliminates the need for harmful refrigerants, reducing environmental impact.
-
The technology is highly energy-efficient, leading to lower electricity bills.
-
Magnetic refrigeration systems have fewer moving parts, resulting in less wear and tear.
-
The absence of compressors and fans makes these systems quieter.
-
They can be used in a wide range of applications, from household refrigerators to industrial cooling systems.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its many advantages, magnetic refrigeration also faces some challenges. Here are a few limitations that need to be addressed.
-
The initial cost of magnetic refrigeration systems is higher than traditional systems.
-
Finding suitable magnetocaloric materials that work efficiently at room temperature is challenging.
-
The technology is still in the experimental stage, with limited commercial availability.
-
Scaling up the technology for large-scale applications remains a hurdle.
-
The efficiency of magnetic refrigeration systems can be affected by external factors like ambient temperature and humidity.
Applications of Magnetic Refrigeration
Magnetic refrigeration has the potential to revolutionize various industries. Here are some areas where this technology can be applied.
-
Household refrigerators and freezers can benefit from the energy efficiency and quiet operation of magnetic refrigeration.
-
Industrial cooling systems can use this technology to reduce energy consumption and environmental impact.
-
Magnetic refrigeration can be used in air conditioning systems for buildings and vehicles.
-
It has potential applications in medical refrigeration, such as cooling MRI machines and preserving biological samples.
-
The technology can be used in cryogenic applications, such as liquefying gases and cooling superconductors.
Future Prospects of Magnetic Refrigeration
The future of magnetic refrigeration looks promising, with ongoing research and development. Here are some potential advancements and trends to watch out for.
-
Researchers are working on developing new magnetocaloric materials that are more efficient and cost-effective.
-
Advances in nanotechnology could lead to the creation of materials with enhanced magnetocaloric properties.
-
Integration with renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, could make magnetic refrigeration even more sustainable.
-
The development of compact and portable magnetic refrigeration units could open up new applications in various fields.
-
Collaboration between academia, industry, and government agencies can accelerate the commercialization of this technology.
Interesting Facts About Magnetic Refrigeration
Here are some additional interesting facts that highlight the uniqueness and potential of magnetic refrigeration.
-
Magnetic refrigeration can achieve temperatures as low as -270°C, making it suitable for extreme cooling applications.
-
The technology has been used in space missions to cool instruments and equipment.
-
Magnetic refrigeration systems can be designed to be modular, allowing for easy scalability and customization.
-
The first prototype of a magnetic refrigerator was built in the early 1990s.
-
Magnetic refrigeration can be combined with other cooling technologies to create hybrid systems with enhanced performance.
-
The technology has the potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions significantly.
-
Magnetic refrigeration could play a crucial role in achieving global sustainability goals by providing an eco-friendly alternative to traditional cooling methods.
The Future of Cooling
Magnetic refrigeration is more than just a cool concept; it's a game-changer. This tech uses magnetic fields to cool things down, making it eco-friendly and efficient. Unlike traditional fridges, it doesn't rely on harmful gases, which means less impact on our planet. Plus, it's quieter and more energy-efficient, saving both money and the environment.
Imagine a world where your fridge is not only keeping your food fresh but also reducing your carbon footprint. That's the promise of magnetic refrigeration. As research continues, we can expect even more advancements, making this technology more accessible and widespread.
So, next time you open your fridge, think about the future. Magnetic refrigeration could soon be the standard, offering a greener, quieter, and more efficient way to keep things cool. It's not just science fiction; it's the future of cooling.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
