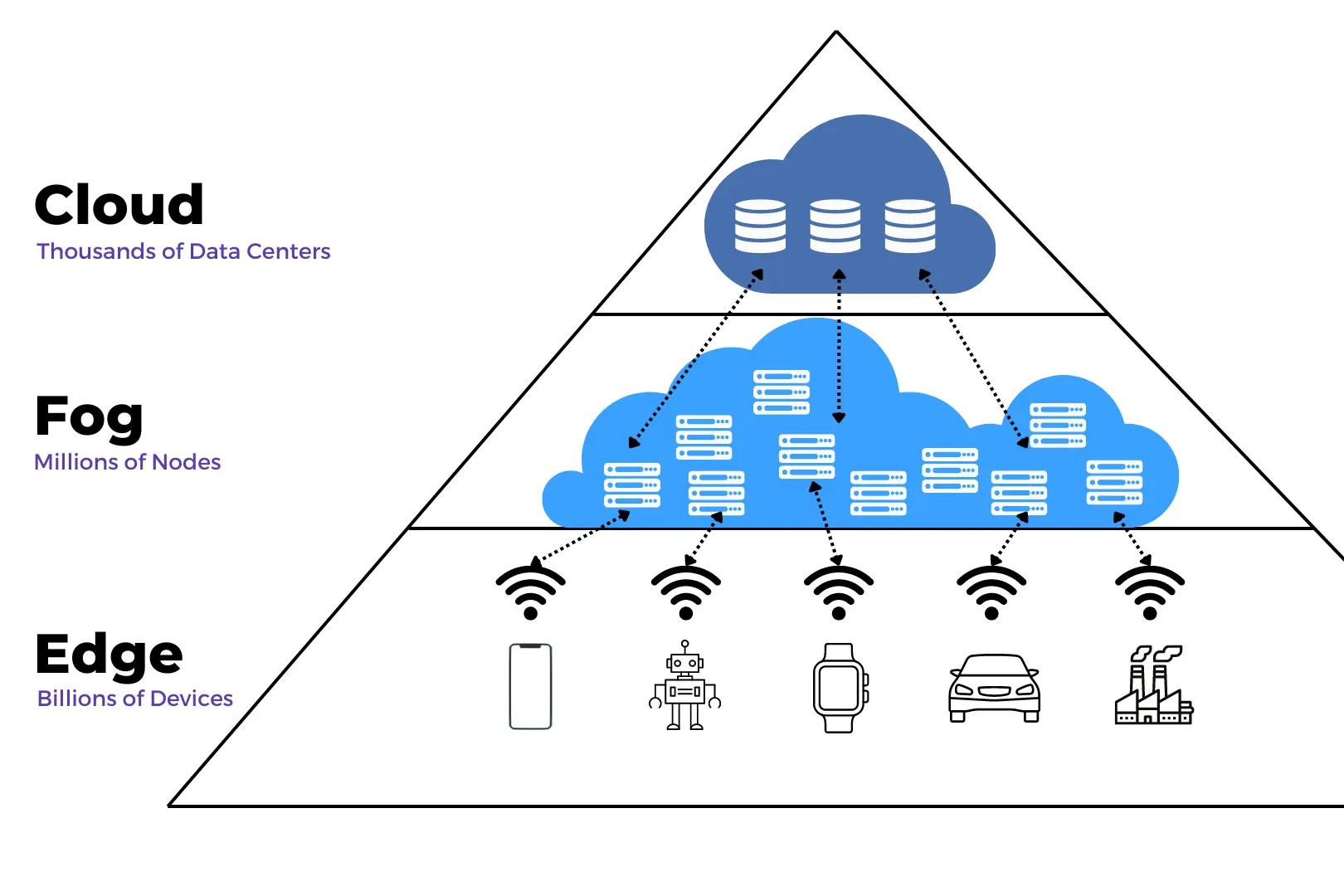
Fog computing is a term that might sound mysterious, but it's actually quite simple. Fog computing extends cloud services to the edge of the network, bringing data processing closer to where it’s generated. This approach reduces latency, enhances security, and improves efficiency. Imagine smart traffic lights that can process data on the spot to manage congestion better. That’s fog computing in action! It’s especially useful for the Internet of Things (IoT), where devices need to make quick decisions. Want to know more? Here are 34 fascinating facts about fog computing that will clear up any confusion and show why it’s becoming so important.
What is Fog Computing?
Fog computing, also known as fogging, extends cloud computing to the edge of an enterprise’s network. It aims to bring data processing closer to the data source, reducing latency and improving efficiency. Here are some fascinating facts about fog computing.
-
Fog computing was coined by Cisco. The term "fog computing" was introduced by Cisco in 2014 to describe a decentralized computing infrastructure.
-
It’s not the same as edge computing. Although often used interchangeably, fog computing and edge computing are different. Fog computing involves a broader network that includes edge devices, gateways, and cloud services.
-
Reduces latency significantly. By processing data closer to where it is generated, fog computing can reduce latency to milliseconds.
-
Improves security. Data processed locally is less likely to be intercepted during transmission, enhancing security.
-
Supports IoT devices. Fog computing is crucial for the Internet of Things (IoT), enabling real-time data processing for devices like smart sensors and cameras.
Benefits of Fog Computing
Fog computing offers numerous advantages, making it a popular choice for modern enterprises. Here are some key benefits.
-
Enhances data processing speed. Local data processing means faster response times and improved performance.
-
Reduces bandwidth usage. By processing data locally, fog computing reduces the amount of data sent to the cloud, saving bandwidth.
-
Scalability. Fog computing can easily scale to accommodate more devices and data sources.
-
Cost-effective. Lower bandwidth usage and reduced cloud storage needs can lead to cost savings.
-
Improves reliability. Local processing ensures that even if the cloud connection is lost, critical operations can continue.
Real-World Applications
Fog computing is not just a theoretical concept; it has practical applications in various industries. Here are some examples.
-
Smart cities. Fog computing helps manage traffic, monitor air quality, and enhance public safety in smart cities.
-
Healthcare. Real-time patient monitoring and data analysis are possible with fog computing, improving patient care.
-
Manufacturing. Factories use fog computing for predictive maintenance and real-time quality control.
-
Agriculture. Farmers use fog computing for precision farming, optimizing resource use and crop yields.
-
Retail. Retailers use fog computing for real-time inventory management and personalized customer experiences.
Challenges in Fog Computing
Despite its benefits, fog computing faces several challenges. Here are some of the main issues.
-
Complexity. Implementing fog computing can be complex, requiring specialized knowledge and skills.
-
Interoperability. Ensuring different devices and systems work together seamlessly can be challenging.
-
Security concerns. While fog computing can enhance security, it also introduces new vulnerabilities that need to be addressed.
-
Cost of implementation. Initial setup costs can be high, although long-term savings often offset these expenses.
-
Data management. Managing large volumes of data locally requires robust data management strategies.
Future of Fog Computing
Fog computing is poised to play a significant role in the future of technology. Here are some predictions.
-
Growth in IoT. As IoT devices proliferate, the demand for fog computing will increase.
-
5G integration. Fog computing will complement 5G networks, enhancing their capabilities.
-
AI and machine learning. Fog computing will enable more advanced AI and machine learning applications by providing real-time data processing.
-
Increased adoption. More industries will adopt fog computing as its benefits become more widely recognized.
-
Standardization. Efforts to standardize fog computing protocols and practices will make it more accessible.
Key Players in Fog Computing
Several companies and organizations are leading the way in fog computing. Here are some of the key players.
-
Cisco. As the originator of the term, Cisco continues to be a major player in fog computing.
-
IBM. IBM offers fog computing solutions through its Watson IoT platform.
-
Microsoft. Microsoft’s Azure IoT Edge provides fog computing capabilities.
-
Dell. Dell’s Edge Gateway devices support fog computing.
-
Intel. Intel provides hardware and software solutions for fog computing.
Interesting Tidbits
Here are some lesser-known facts about fog computing that might surprise you.
-
Inspired by meteorology. The term "fog" was chosen because it’s a layer closer to the ground than the "cloud."
-
Energy efficiency. Fog computing can be more energy-efficient than cloud computing by reducing data transmission.
-
Real-time analytics. Fog computing enables real-time analytics, which is crucial for applications like autonomous vehicles.
-
Hybrid models. Many organizations use a hybrid model, combining fog and cloud computing for optimal performance.
Fog Computing: The Future of Data Processing
Fog computing is transforming how data is processed and managed. By bringing data storage and processing closer to the source, it reduces latency, improves efficiency, and enhances security. This technology is especially beneficial for IoT devices, smart cities, and autonomous vehicles, where real-time data processing is crucial.
Businesses adopting fog computing can expect faster decision-making, reduced bandwidth costs, and improved overall performance. As more devices connect to the internet, the demand for efficient data processing will only grow, making fog computing an essential part of our digital future.
Understanding these 34 facts about fog computing gives you a solid foundation to appreciate its potential and impact. Whether you're a tech enthusiast, a business owner, or just curious, fog computing is a game-changer worth keeping an eye on. Embrace this technology and stay ahead in the ever-evolving world of data processing.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
