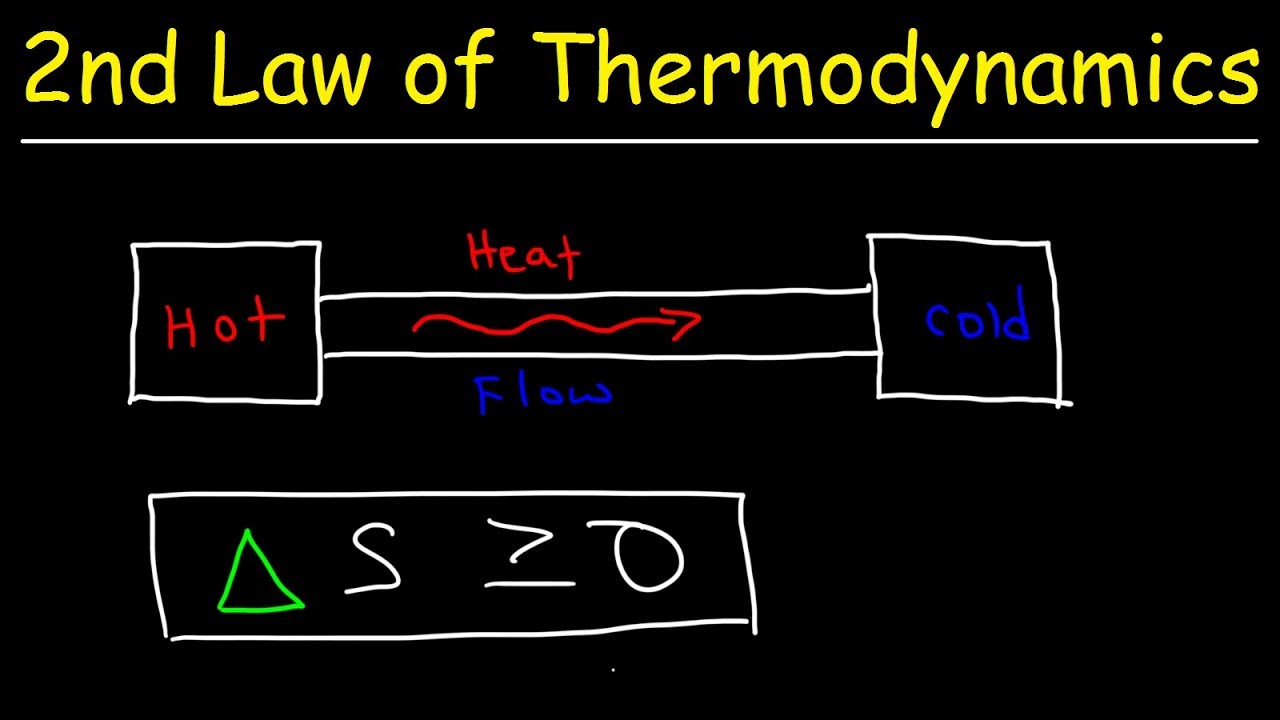
What is the Second Law of Thermodynamics? The Second Law of Thermodynamics states that in any energy transfer or transformation, the total entropy of a closed system will always increase over time. This means energy tends to spread out or disperse, becoming less useful for doing work. Imagine a hot cup of coffee left on a table. Over time, it cools down as heat energy spreads into the surrounding air. This law explains why perpetual motion machines are impossible and why natural processes have a preferred direction. Understanding this principle helps explain everything from why ice melts to how engines work.
Key Takeaways:
- The Second Law of Thermodynamics states that disorder in a closed system always increases, affecting everything from refrigerators to the fate of the universe.
- This law explains why heat can't flow from cold to hot, why ice melts, and even has implications for the fate of the universe.
Understanding the Second Law of Thermodynamics
The Second Law of Thermodynamics is a fundamental principle in physics that governs the direction of energy transfer and the efficiency of energy conversion. It has profound implications in various fields, from engineering to cosmology. Here are some intriguing facts about this essential law.
-
The Second Law of Thermodynamics states that the total entropy of an isolated system can never decrease over time. Entropy is a measure of disorder or randomness.
-
This law implies that natural processes tend to move towards a state of maximum entropy or disorder.
-
The Second Law is often summarized by the phrase, "heat cannot spontaneously flow from a colder body to a hotter body."
-
It introduces the concept of irreversibility in natural processes, meaning certain processes cannot be reversed without external intervention.
-
The Second Law is crucial for understanding why perpetual motion machines of the second kind are impossible. These hypothetical machines would violate the law by creating energy without any input.
Historical Context and Development
The development of the Second Law of Thermodynamics has a rich history, involving many prominent scientists. Understanding its origins helps appreciate its significance.
-
Rudolf Clausius and William Thomson (Lord Kelvin) are credited with formulating the Second Law in the mid-19th century.
-
Clausius introduced the concept of entropy in 1865, providing a mathematical framework for the Second Law.
-
Sadi Carnot, a French engineer, laid the groundwork for the Second Law with his work on heat engines in the 1820s.
-
Carnot's theorem, which describes the maximum efficiency of a heat engine, is a direct consequence of the Second Law.
-
The Second Law was initially controversial but gained acceptance as more experimental evidence supported it.
Applications in Everyday Life
The Second Law of Thermodynamics isn't just a theoretical concept; it has practical applications that impact our daily lives.
-
Refrigerators and air conditioners operate based on the principles of the Second Law, transferring heat from a cooler space to a warmer one using external energy.
-
The efficiency of car engines and power plants is limited by the Second Law, as some energy is always lost as waste heat.
-
The law explains why ice melts in a warm room and why hot coffee cools down over time.
-
It also underlies the concept of thermal equilibrium, where two objects in contact will eventually reach the same temperature.
-
The Second Law is essential for understanding the aging process, as biological systems tend to increase in entropy over time.
Implications in Science and Engineering
The Second Law of Thermodynamics has far-reaching implications in various scientific and engineering disciplines.
-
In chemical reactions, the Second Law helps predict the direction in which reactions will proceed.
-
It is fundamental to the study of statistical mechanics, which describes the behavior of large numbers of particles.
-
The law is crucial for understanding the efficiency of energy conversion processes, such as in batteries and fuel cells.
-
It plays a role in the design of heat exchangers, which transfer heat between fluids in industrial processes.
-
The Second Law is also important in environmental science, as it helps model the flow of energy in ecosystems.
The Universe and the Second Law
The Second Law of Thermodynamics has profound implications for the universe as a whole, influencing our understanding of cosmology and the fate of the universe.
-
The law suggests that the universe is gradually moving towards a state of maximum entropy, known as the "heat death" of the universe.
-
It helps explain the arrow of time, the concept that time has a specific direction from past to future.
-
The Second Law is essential for understanding the formation and evolution of stars and galaxies.
-
Black holes are fascinating objects that obey the Second Law, as they have entropy proportional to their surface area.
-
The law also plays a role in the study of cosmic microwave background radiation, the afterglow of the Big Bang.
Misconceptions and Clarifications
Despite its importance, the Second Law of Thermodynamics is often misunderstood. Here are some common misconceptions and clarifications.
-
The Second Law does not imply that order cannot increase locally; it only states that total entropy must increase in an isolated system.
-
It does not contradict the theory of evolution, as living organisms are not isolated systems and can decrease in entropy by increasing the entropy of their surroundings.
-
The law does not mean that energy is destroyed; it only states that energy quality degrades over time.
-
It is not violated by the existence of life, as life processes increase entropy in the environment.
-
The Second Law is not just about heat; it applies to all forms of energy transfer and conversion.
Fun and Surprising Facts
The Second Law of Thermodynamics can be surprising and even fun when you delve into its nuances.
-
The concept of entropy is used in information theory to measure the amount of uncertainty or information content.
-
Maxwell's demon is a thought experiment that challenges the Second Law by imagining a creature that can sort particles by energy, seemingly decreasing entropy.
-
The Second Law has inspired philosophical discussions about the nature of time, free will, and the ultimate fate of the universe.
The Essence of the Second Law
The Second Law of Thermodynamics isn't just a bunch of fancy words. It tells us that energy naturally flows from hot to cold, and systems tend to move towards disorder or entropy. This principle impacts everything from engines to ice melting. Understanding this law helps us grasp why perpetual motion machines are impossible and why energy efficiency is so crucial.
From the way your refrigerator works to the heat your car engine produces, this law is at play. It’s a fundamental concept that shapes our physical world and technological advancements. So next time you see ice melting or feel the warmth of a campfire, remember, it’s all about the Second Law of Thermodynamics doing its thing.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
