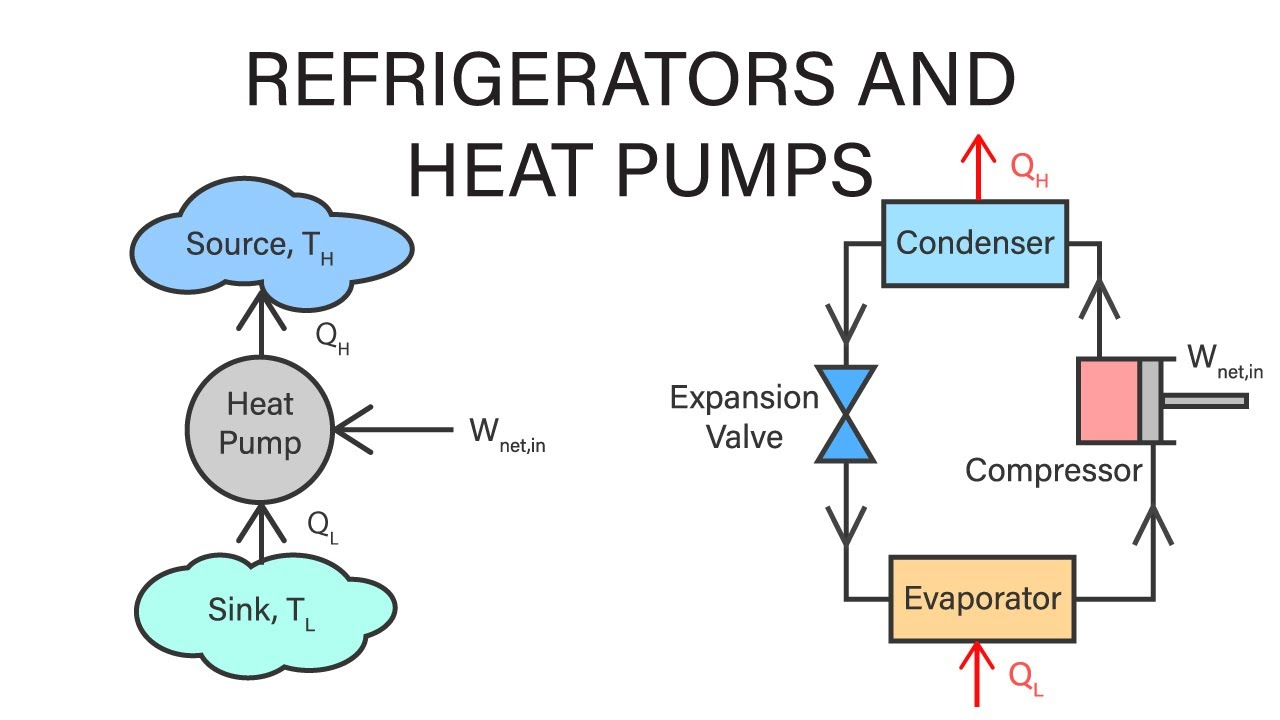
Did you know that your refrigerator and heat pump share a lot in common? Both appliances use similar technology to keep your home comfortable and your food fresh. Refrigerators work by removing heat from inside the unit and releasing it outside, while heat pumps can both heat and cool your home by transferring heat between the indoors and outdoors. These devices are marvels of engineering, making our lives easier and more convenient. From energy efficiency to environmental impact, understanding how they work can help you make better choices for your home. Ready to learn some cool facts about these everyday appliances? Let's dive in!
The Basics of Refrigerators
Refrigerators are essential appliances in modern homes. They keep food fresh and safe by maintaining a cool temperature. Let's dive into some interesting facts about these cooling machines.
-
The first refrigerator for home use was invented in 1913 by Fred W. Wolf. It was called the "Domelre," short for Domestic Electric Refrigerator.
-
Early refrigerators used toxic gases like ammonia and methyl chloride as refrigerants. These were later replaced by safer alternatives.
-
The refrigerator's main component is the compressor, which circulates refrigerant through the system.
-
Modern refrigerators use a refrigerant called HFC-134a, which is less harmful to the environment than older refrigerants.
-
The average lifespan of a refrigerator is about 14 years. Regular maintenance can extend this period.
-
The freezer compartment is usually located at the top or bottom of the refrigerator. This design helps in maintaining an even temperature throughout the appliance.
How Refrigerators Work
Understanding how refrigerators work can be fascinating. They use a cycle of evaporation and condensation to remove heat from the interior.
-
Refrigerators operate on the principle of the refrigeration cycle, which involves four main stages: compression, condensation, expansion, and evaporation.
-
The evaporator coil inside the fridge absorbs heat from the food and air, cooling the interior.
-
The condenser coil, usually located at the back or bottom, releases the absorbed heat into the surrounding air.
-
The expansion valve controls the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator, ensuring efficient cooling.
-
A thermostat inside the refrigerator monitors the temperature and controls the compressor's operation.
-
Frost-free refrigerators have a heating element that periodically melts any frost buildup, preventing ice accumulation.
Energy Efficiency and Environmental Impact
Refrigerators have come a long way in terms of energy efficiency and environmental impact. Let's explore some facts about these improvements.
-
Energy-efficient refrigerators use less electricity, saving money on utility bills and reducing carbon footprints.
-
The Energy Star program certifies appliances that meet specific energy efficiency criteria. Look for the Energy Star label when buying a new refrigerator.
-
Modern refrigerators use LED lighting, which consumes less energy and lasts longer than traditional bulbs.
-
Some refrigerators have smart features, like Wi-Fi connectivity and touchscreens, to help monitor energy usage and manage food storage.
-
Inverter technology in compressors allows refrigerators to adjust their cooling capacity based on the load, improving efficiency.
-
Recycling old refrigerators is essential to prevent harmful refrigerants and materials from polluting the environment.
Fun and Unusual Facts
Refrigerators have some quirky and lesser-known aspects. Here are some fun and unusual facts about these appliances.
-
The world's largest refrigerator is located at the Antarctic research station. It stores ice cores for climate research.
-
In Japan, some refrigerators have built-in sake dispensers to keep the traditional drink at the perfect temperature.
-
The first commercial refrigerator was introduced by General Electric in 1927. It was called the "Monitor-Top" because its compressor resembled a ship's monitor turret.
-
Some high-end refrigerators have built-in cameras that let you see the contents without opening the door.
-
The term "fridge" is a shortened form of "Frigidaire," a popular refrigerator brand in the early 20th century.
-
In the 1950s, refrigerators were often marketed as luxury items, with colorful designs and chrome accents.
Heat Pumps: The Unsung Heroes
Heat pumps are versatile devices that can both heat and cool spaces. They work on the same principle as refrigerators but in reverse.
-
Heat pumps transfer heat from one place to another, making them highly efficient for heating and cooling.
-
Air-source heat pumps extract heat from the outside air, even in cold weather, to warm indoor spaces.
-
Ground-source heat pumps, also known as geothermal heat pumps, use the stable temperature of the earth to provide heating and cooling.
-
Heat pumps can be used for water heating, providing an energy-efficient alternative to traditional water heaters.
-
The first heat pump was invented by Peter von Rittinger in 1855. It was used for drying salt in Austria.
-
Modern heat pumps can achieve efficiencies of up to 300%, meaning they produce three units of heat for every unit of electricity consumed.
-
Heat pumps are becoming increasingly popular in regions with mild climates, where they can provide year-round comfort.
-
Some heat pumps have a defrost cycle to prevent ice buildup on the outdoor unit, ensuring efficient operation in cold weather.
Cool Facts to Keep in Mind
Refrigerators and heat pumps are more than just household appliances. They play a crucial role in our daily lives by keeping food fresh and homes warm. From their invention in the 1800s to modern energy-efficient models, these devices have come a long way. Did you know that the first electric refrigerator was introduced in 1913? Or that heat pumps can both heat and cool your home, making them versatile and efficient?
Understanding how these machines work can help you make better choices for your home. Whether you're looking to save on energy bills or reduce your carbon footprint, knowing the facts can guide you. So next time you open your fridge or adjust your thermostat, remember the fascinating history and technology behind these everyday marvels. Keep these cool facts in mind, and you'll appreciate your appliances even more.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
