Elastic potential energy is a fascinating concept that often goes unnoticed in our daily lives. But what exactly is it? Elastic potential energy is the energy stored in objects that can be stretched or compressed, like rubber bands, springs, or even trampolines. When you pull back a slingshot or compress a spring, you're storing energy that can be released to do work. This type of energy plays a crucial role in various fields, from engineering to sports. Understanding it can help you appreciate the mechanics behind everyday objects and even improve your problem-solving skills. Ready to learn more? Let's dive into 29 intriguing facts about elastic potential energy!
What is Elastic Potential Energy?
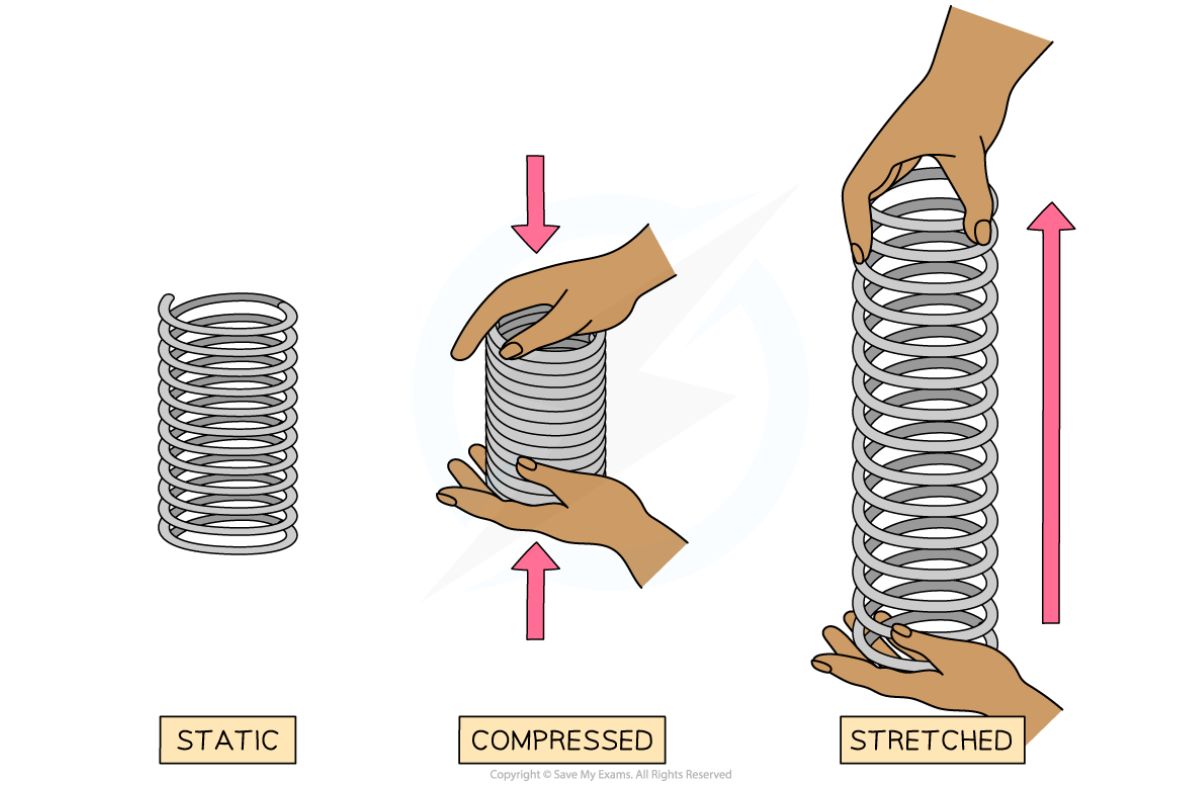
Elastic potential energy is the energy stored in objects when they are stretched or compressed. This type of energy is most commonly associated with materials like springs, rubber bands, and bungee cords. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about elastic potential energy.
-
Elastic potential energy is a form of mechanical energy. It is stored in objects that can be stretched or compressed, such as springs and rubber bands.
-
Hooke's Law describes elastic potential energy. According to Hooke's Law, the force needed to extend or compress a spring by some distance is proportional to that distance.
-
The formula for elastic potential energy is U = 1/2 k x². Here, U represents the elastic potential energy, k is the spring constant, and x is the displacement from the equilibrium position.
-
Elastic potential energy can be converted into kinetic energy. When a stretched or compressed object is released, the stored energy converts into kinetic energy, causing the object to move.
-
Springs are common examples of objects that store elastic potential energy. When a spring is compressed or stretched, it stores energy that can be released later.
Everyday Examples of Elastic Potential Energy
Elastic potential energy is all around us, often in everyday objects and activities. Here are some examples you might encounter daily.
-
Rubber bands store elastic potential energy. When stretched, rubber bands store energy that can be used to propel objects or hold items together.
-
Trampolines use elastic potential energy. The springs in trampolines store energy when compressed and release it to propel jumpers into the air.
-
Bungee cords rely on elastic potential energy. When stretched, bungee cords store energy that helps them snap back to their original length.
-
Archery bows store elastic potential energy. When an archer pulls back the bowstring, the bow stores energy that is transferred to the arrow when released.
-
Exercise resistance bands use elastic potential energy. These bands store energy when stretched, providing resistance for strength training exercises.
Scientific Principles Behind Elastic Potential Energy
Understanding the scientific principles behind elastic potential energy can help explain how it works and why it's important.
-
Elastic potential energy depends on the material's properties. Different materials have varying abilities to store and release energy based on their elasticity.
-
The spring constant (k) is crucial. A higher spring constant means a stiffer spring, which requires more force to stretch or compress and stores more energy.
-
Elastic potential energy is a conservative force. This means the total mechanical energy (kinetic + potential) in a closed system remains constant.
-
Energy conservation applies to elastic potential energy. When an object with stored elastic potential energy is released, the energy converts to kinetic energy, following the law of conservation of energy.
-
Elastic potential energy can be calculated for various shapes. While springs are common, other shapes like rubber sheets or elastic bands also store energy, and their potential energy can be calculated using similar principles.
Applications of Elastic Potential Energy
Elastic potential energy has numerous applications in technology, sports, and everyday life. Here are some interesting uses.
-
Catapults use elastic potential energy. Ancient and modern catapults store energy in stretched bands or twisted ropes to launch projectiles.
-
Mechanical watches rely on elastic potential energy. The mainspring in a mechanical watch stores energy when wound and releases it to power the watch's movement.
-
Shock absorbers in vehicles use elastic potential energy. Springs in shock absorbers compress and store energy to cushion the ride and improve vehicle handling.
-
Toys like wind-up cars use elastic potential energy. When wound up, these toys store energy in a spring that is released to power their movement.
-
Medical devices like braces use elastic potential energy. Orthodontic braces apply force to teeth using elastic bands, gradually moving them into the desired position.
Fun Facts About Elastic Potential Energy
Elastic potential energy isn't just useful; it can also be fun and surprising. Here are some fun facts to ponder.
-
Slinkies demonstrate elastic potential energy. When stretched and released, a Slinky stores and releases energy, allowing it to "walk" down stairs.
-
Elastic potential energy can be found in nature. Some plants, like the Venus flytrap, use stored energy to snap shut and capture prey.
-
Bungee jumping relies on elastic potential energy. The bungee cord stretches and stores energy, then releases it to bounce the jumper back up.
-
Elastic potential energy is used in sports equipment. Tennis rackets, golf clubs, and other sports gear use materials that store and release energy to enhance performance.
-
Muscles store elastic potential energy. When muscles stretch, they store energy that can be used for quick, powerful movements.
Historical Context of Elastic Potential Energy
The concept of elastic potential energy has been understood and utilized for centuries. Here are some historical insights.
-
Ancient Greeks understood elastic potential energy. They used it in devices like catapults and ballistae for warfare.
-
Leonardo da Vinci studied elastic potential energy. His sketches and designs often included mechanisms that stored and released energy.
-
The Industrial Revolution harnessed elastic potential energy. Springs and other elastic materials became essential components in machinery and tools.
-
Modern engineering continues to innovate with elastic potential energy. Advances in materials science have led to new applications and more efficient energy storage solutions.
The Power of Elastic Potential Energy
Elastic potential energy is more than just a scientific concept. It’s a part of everyday life, from the springs in your mattress to the rubber bands holding things together. Understanding how it works can help you see the world differently. It’s all about how objects store and release energy. This energy can be harnessed in countless ways, making it a key player in both simple toys and complex machinery.
Knowing these facts can spark curiosity and inspire innovation. Whether you're a student, a teacher, or just someone who loves learning, there's always more to explore. Keep asking questions and seeking answers. The world of physics is vast and fascinating, and elastic potential energy is just one piece of the puzzle. Dive in, experiment, and see what you can discover next.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
