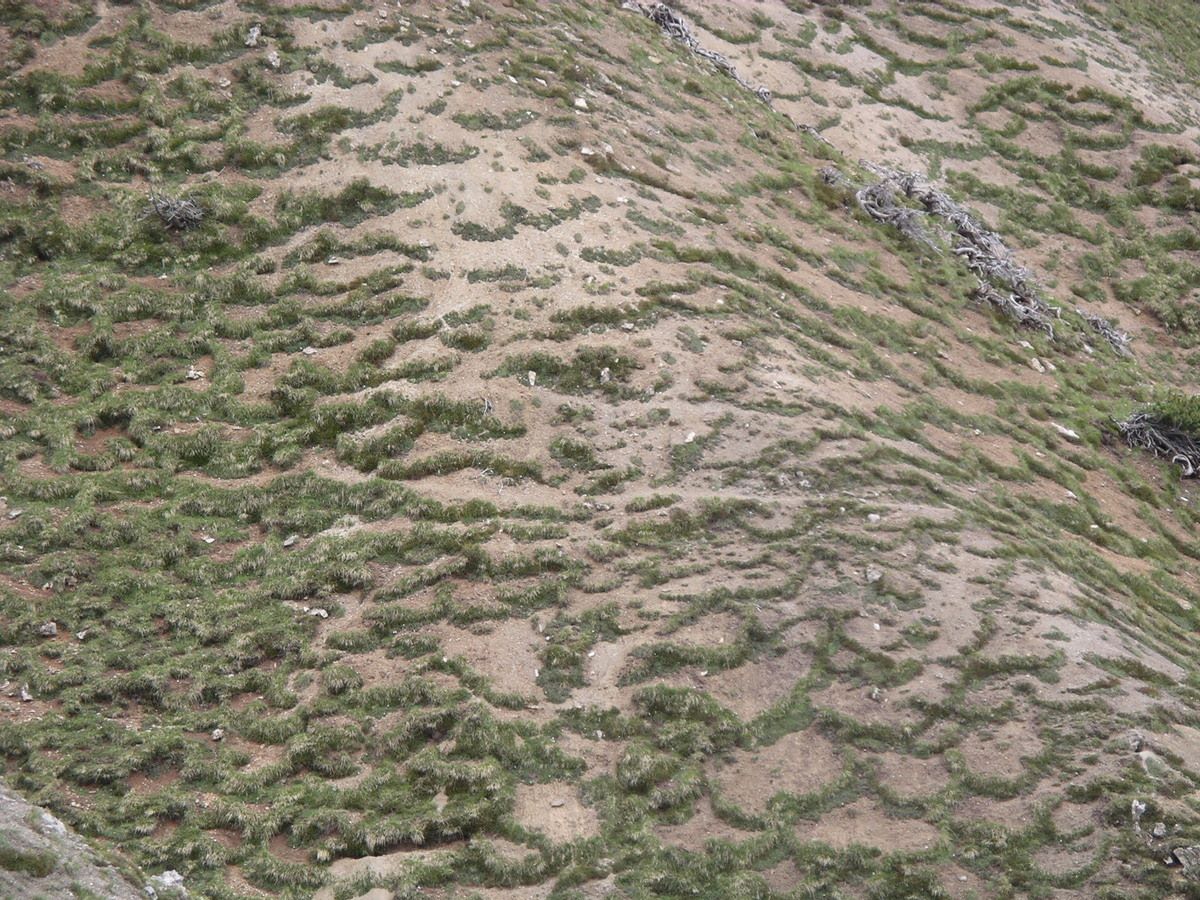
What are solifluction lobes? These fascinating landforms occur in cold regions where the ground is often frozen. Solifluction lobes form when soil and rock slowly move downhill due to repeated freezing and thawing cycles. Imagine a slow-motion landslide, but instead of a sudden collapse, the earth creeps down the slope over time. This process creates distinctive, tongue-shaped features on the landscape. Solifluction is essential for understanding soil movement in periglacial environments. These lobes can tell us a lot about past climates and how landscapes evolve. Ready to learn more? Let's dig into 14 intriguing facts about these unique geological formations!
What Are Solifluction Lobes?
Solifluction lobes are fascinating geological formations found in cold environments. They form due to the slow, downslope movement of water-saturated soil and sediment. Let's dive into some intriguing facts about these unique features.
-
Solifluction lobes typically form in periglacial environments. These areas are found near glaciers or ice sheets where the ground is subject to freeze-thaw cycles.
-
The term "solifluction" comes from Latin. It combines "solum" (soil) and "fluctio" (flow), literally meaning "soil flow."
-
They are often found on slopes. The gradient of the slope influences the speed and extent of the soil movement.
How Do Solifluction Lobes Form?
Understanding the formation process of solifluction lobes can help us appreciate their unique characteristics. Here are some key points about their formation.
-
Freeze-thaw cycles play a crucial role. Water in the soil freezes and expands, causing the soil to lift. When it thaws, the soil contracts and moves downslope.
-
They form in layers. Each freeze-thaw cycle adds a new layer of soil to the lobe, creating a stepped appearance.
-
Vegetation can influence their formation. Plants can stabilize the soil, slowing down the movement and affecting the shape of the lobes.
Characteristics of Solifluction Lobes
Solifluction lobes have distinct features that set them apart from other geological formations. Here are some characteristics to look out for.
-
They have a tongue-like shape. The lobes often appear as elongated, tongue-like protrusions on the slope.
-
Size varies widely. They can range from a few meters to several hundred meters in length.
-
Surface texture is unique. The surface of solifluction lobes is often rough and uneven due to the movement of soil and rocks.
Where Can You Find Solifluction Lobes?
These geological features are not limited to one specific region. They can be found in various parts of the world.
-
Common in Arctic and Antarctic regions. The cold climates in these areas provide ideal conditions for solifluction lobes to form.
-
Also found in mountainous regions. High-altitude areas with periglacial conditions, such as the Alps or the Rockies, also host these formations.
-
Present in temperate regions. Even some temperate regions with seasonal freeze-thaw cycles can have solifluction lobes.
Why Study Solifluction Lobes?
Studying solifluction lobes can provide valuable insights into past and present environmental conditions. Here are some reasons why they are important.
-
They indicate climate conditions. The presence of solifluction lobes can reveal information about past climates and freeze-thaw cycles.
-
Help in understanding soil movement. Studying these lobes can improve our understanding of soil dynamics and erosion processes in cold environments.
The Final Scoop on Solifluction Lobes
Solifluction lobes, fascinating features of cold climates, form through the slow, downslope movement of waterlogged soil. These lobes, often found in permafrost regions, reveal much about past and present climate conditions. They help scientists understand soil dynamics and landscape evolution. Recognizing their patterns can aid in predicting future environmental changes.
These natural formations also highlight the delicate balance within ecosystems. Human activities, like construction and deforestation, can disrupt this balance, leading to increased erosion and other environmental impacts. By studying solifluction lobes, we gain insights into preserving these fragile environments.
So, next time you see a solifluction lobe, remember its story. It's not just a pile of dirt; it's a testament to the Earth's dynamic processes. Understanding these features helps us appreciate and protect our planet's unique landscapes.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.