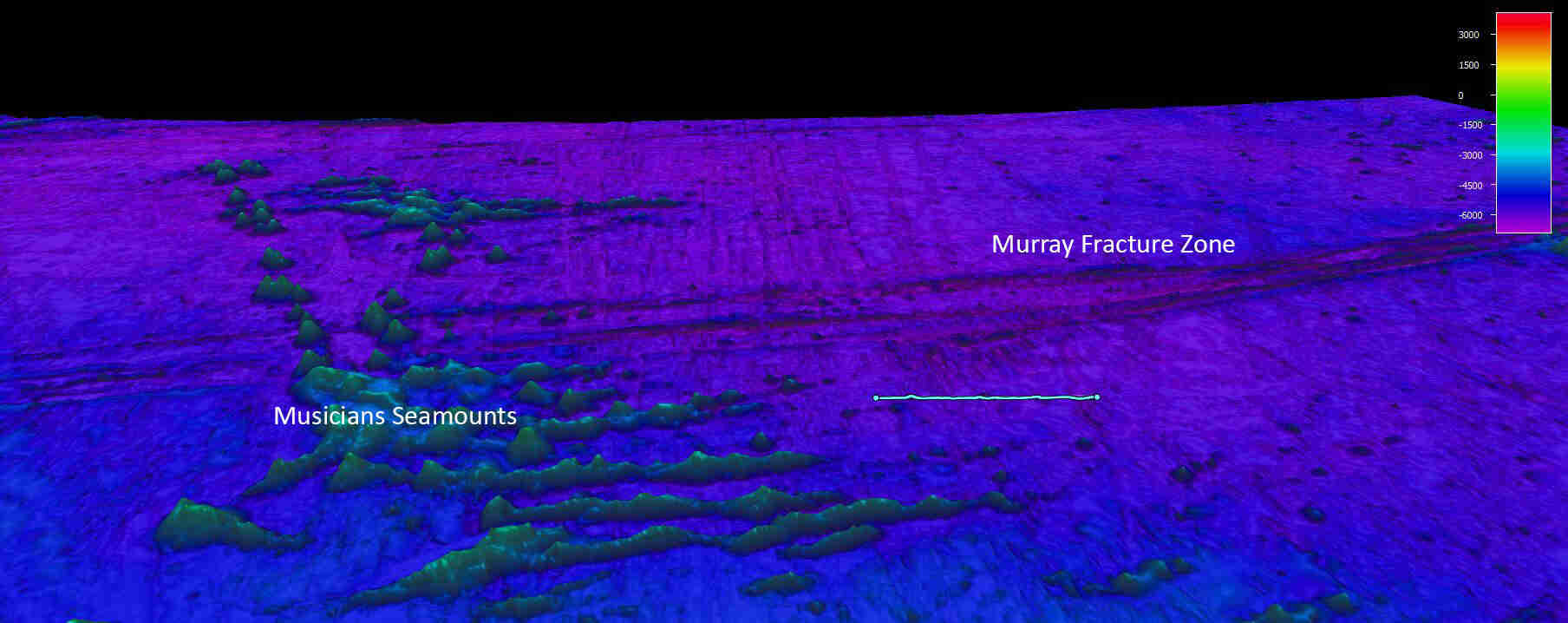
Fracture zones are fascinating geological features that play a crucial role in shaping the Earth’s surface. These zones are known for the fractures and faults that occur in the Earth’s crust, creating significant disruptions in the landscape. From the depths of the oceans to the remote corners of the continents, fracture zones leave an indelible mark on our planet’s geography and geological history. In this article, we will explore 11 intriguing facts about fracture zones that will leave you in awe of their power and significance. From their formation to their impact on the Earth’s tectonic plates, get ready to delve into the world of fracture zones and discover why they are a subject of fascination for both geologists and curious minds alike.
Key Takeaways:
- Fracture zones are dynamic areas of intense seismic activity where tectonic plates interact, impacting ocean currents and supporting unique marine life. They also provide valuable insights into Earth’s geological history and the formation of mineral deposits.
- These fascinating geological features, formed by transform faults, play a crucial role in shaping the Earth’s crust. They are not only home to unique ecosystems and hydrothermal vents but also reveal historical seafloor spreading and the movement of tectonic plates over time.
Fracture zones are tectonic boundaries.
Fracture zones are areas of intense seismic activity where tectonic plates interact. These zones occur along the boundaries of oceanic plates, often marked by deep ocean trenches.
They are formed by transform faults.
Fracture zones are primarily created by transform faults, which result from the lateral movement of tectonic plates. These faults allow for horizontal displacement and can extend for thousands of kilometers.
Fracture zones can cause earthquakes.
Due to the intense tectonic activity, fracture zones are prone to earthquakes. These earthquakes can range in magnitude and have the potential to cause significant damage and tsunamis.
They are home to unique ecosystems.
Fracture zones create diverse habitats for marine life. The deep trenches and nutrient-rich waters support a wide range of organisms, including deep-sea fish, corals, and other species that have adapted to extreme conditions.
Fracture zones provide valuable research opportunities.
Scientists study fracture zones to gain insights into plate tectonics, earthquake dynamics, and the geologic history of the Earth. These areas serve as natural laboratories for investigating the processes that shape our planet.
They can impact oceanic circulation patterns.
The presence of fracture zones can influence ocean currents, affecting the global circulation patterns. These zones can create barriers or channels that alter the flow of water, impacting climate systems on a global scale.
Fracture zones are associated with hydrothermal vents.
Hydrothermal vents, rich in minerals and chemicals, often occur in fracture zones. These vents support unique ecosystems and have been a subject of great interest for scientists exploring the possibilities of extraterrestrial life.
They play a role in the formation of mineral deposits.
Fracture zones act as conduits for mineral-rich fluids, contributing to the formation of valuable mineral deposits such as gold, silver, and copper. These deposits can be economically significant and drive mining activities.
Some fracture zones are named after significant explorers or pioneering scientists.
Fracture zones have been named to honor influential figures in the field of geology and oceanography. These names serve as reminders of the contributions made by these individuals to the understanding of our planet.
Fracture zones can reveal historical seafloor spreading.
By studying fracture zones, scientists can gain insights into the process of seafloor spreading and the movement of tectonic plates over time. This information provides crucial evidence for plate tectonics theory.
Fracture zones are constantly evolving.
Fracture zones, like the Earth’s crust, are not static. They continue to evolve through tectonic forces, shaping the landscapes and seafloor features we see today. Constant monitoring and research help us understand these dynamic processes better.
These 11 intriguing facts about fracture zones shed light on the geological wonders that shape our planet. From their role in plate tectonics to their influence on marine ecosystems, fracture zones showcase the incredible forces at work beneath our feet. As we continue to explore and unravel the mysteries of our Earth, fracture zones remain a captivating field of study.
Conclusion
In conclusion, fracture zones are fascinating geological phenomena that play a significant role in shaping the Earth’s crust. From their formation along tectonic plate boundaries to the unique ecosystems they support, fracture zones hold many intriguing facts that can captivate anyone interested in geology. With their deep ocean trenches, volcanic activity, and seismic activity, fracture zones highlight the dynamic nature of our planet. Understanding these fracture zones is crucial for scientists to comprehend plate tectonics, earthquake occurrences, and the distribution of resources. Moreover, they provide valuable insights into the geologic history of the Earth.Exploring the various fracture zones around the world can lead to new discoveries and advancements in our understanding of the Earth’s interior. The continued research and exploration of these zones will undoubtedly unveil more intriguing facts, enriching our knowledge and deepening our appreciation for the dynamic processes that have shaped our planet over millions of years.
FAQs
1. What exactly is a fracture zone?
A fracture zone is a linear oceanic feature characterized by a series of faults and fractures that occur along the boundary of tectonic plates.
2. How are fracture zones formed?
Fracture zones are formed as a result of the stress and movement between tectonic plates. These stressors cause the crust to crack and form faults, creating distinct fracture zones.
3. Are fracture zones dangerous?
In general, fracture zones themselves are not dangerous. However, they can be associated with tectonic activity, such as earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, which can pose risks to nearby areas.
4. Do fracture zones have any biological significance?
Yes, fracture zones are known to create unique habitats for marine organisms. These areas often support diverse ecosystems due to the availability of nutrients and the presence of hydrothermal vents.
5. Can fracture zones be explored?
Fracture zones can be explored using remote sensing technologies and deep-sea research vessels. Scientists use various tools to study the geological features and organisms associated with these zones.
6. Are all fracture zones located in the ocean?
While most well-known fracture zones are found in the ocean, there are also fracture zones on land. These terrestrial fracture zones can be observed along fault lines and are often associated with earthquakes.
7. How deep are fracture zones?
Fracture zones in the ocean can extend several kilometers below the water surface. The depth of fracture zones on land can vary depending on the specific geologic conditions in the area.
8. Can fracture zones be used as a source of natural resources?
Fracture zones can be rich in mineral deposits, hydrocarbon reserves, and other valuable resources. However, extracting these resources from such deep and remote areas poses significant challenges.
9. Do fracture zones affect climate patterns?
Fracture zones themselves do not directly affect climate patterns. However, the volcanic activity associated with certain fracture zones can release gases and aerosols into the atmosphere, which may have an impact on climate.
10. Are all fracture zones connected?
No, fracture zones are not always connected. While some fracture zones may intersect or overlap, each fracture zone is distinct and has unique characteristics.
11. Can fracture zones be used to study plate tectonics?
Yes, fracture zones provide crucial evidence for studying plate tectonics. By examining the patterns and orientations of fractures, scientists can gain insights into the movement and interaction of tectonic plates over time.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
