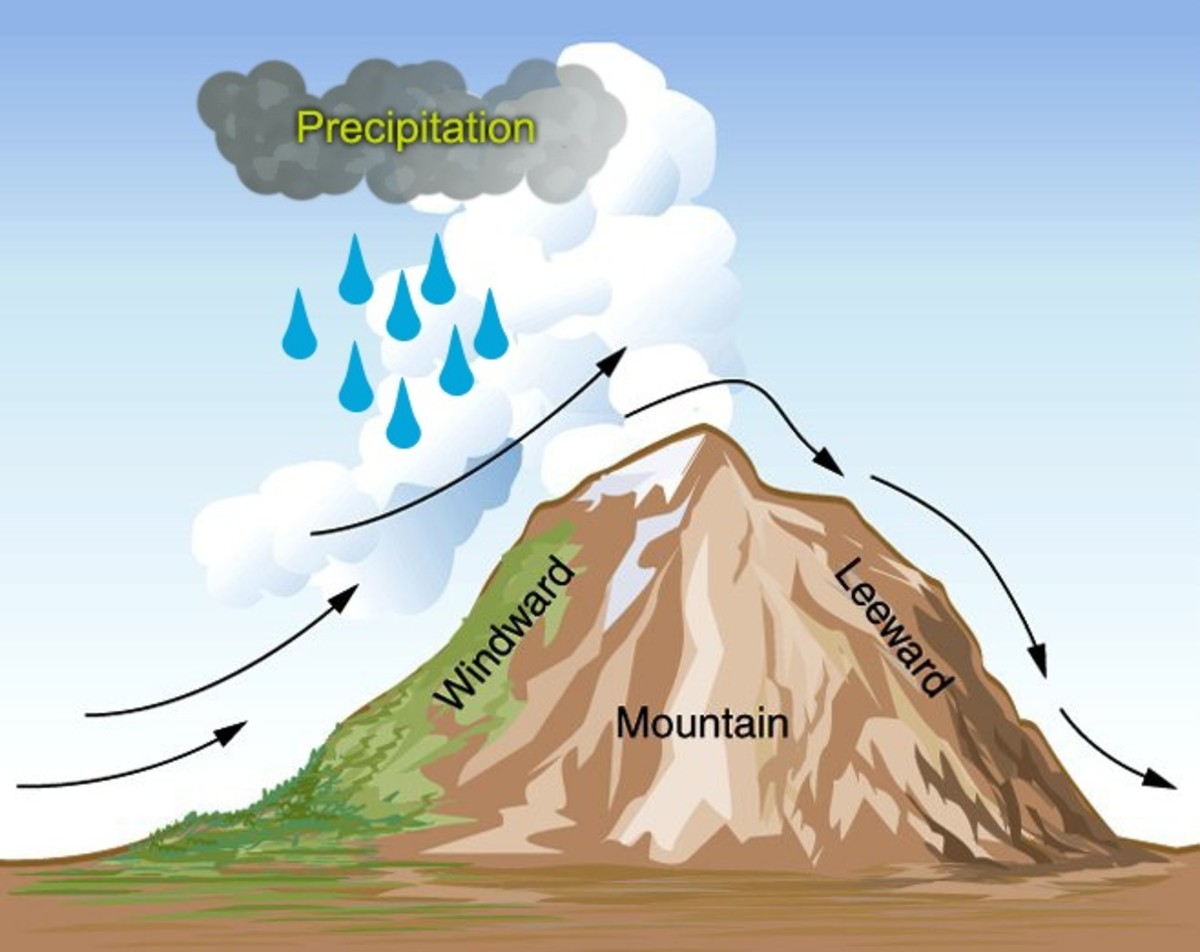
Orographic rainfall is a fascinating natural phenomenon that occurs when moist air is forced upwards by mountains, leading to the formation of clouds and subsequent precipitation on the windward side of the mountain range. This unique type of rainfall has captivated the attention of scientists, meteorologists, and nature enthusiasts alike due to its enigmatic nature and impact on local climate patterns.
In this article, we will delve into the intriguing world of orographic rainfall and uncover 11 fascinating facts about this meteorological phenomenon. From the formation of rain shadows to the role of topography in precipitation distribution, we will explore the various aspects that make orographic rainfall both mysterious and captivating.
So, grab your raincoat and join us on this journey as we unravel the mysteries behind orographic rainfall and gain a deeper understanding of its influence on our planet’s weather patterns.
Key Takeaways:
- Orographic rainfall, caused by mountains, creates different climates on each side, affecting water resources, vegetation, and biodiversity, and contributing to unique geographic features and agricultural benefits.
- Orographic rainfall is essential for water supply, agriculture, and natural beauty, but can also lead to flooding and landslides, and is influenced by climate change.
Orographic rainfall is caused by geographic features.
Orographic rainfall occurs when moist air is forced to rise over mountain ranges or other elevated terrains. As the air rises, it cools, leading to condensation and the formation of clouds. This process is responsible for the orographic rainfall phenomenon.
Orographic rainfall can create distinct climate patterns on different sides of a mountain.
When moist air is forced to rise over a mountain, it cools and releases precipitation on the windward side. As the air descends on the leeward side, it warms and becomes drier, resulting in a rain shadow effect. This leads to a stark difference in climate between the two sides of the mountain.
Orographic rainfall plays a crucial role in water resources.
The orographic rainfall is a significant source of water for rivers, lakes, and reservoirs. This water is vital for various purposes such as irrigation, drinking water, and hydroelectric power generation.
Orographic rainfall can result in high precipitation rates.
Due to the natural lifting mechanism caused by mountains, orographic rainfall can lead to intense and prolonged periods of precipitation. This can result in heavy rainfall, causing potential flooding and landslides in affected areas.
Orographic rainfall influences the distribution of vegetation.
The varying levels of precipitation caused by orographic rainfall contribute to the creation of unique ecosystems. The windward side of a mountain experiences more precipitation and favors the growth of lush forests, while the leeward side may have more arid conditions and support different types of vegetation.
Orographic rainfall can contribute to the formation of glaciers.
In regions where orographic rainfall is abundant, excess precipitation can accumulate as snow and eventually transform into glaciers over time. Glaciers then become essential sources of freshwater and can shape the landscape through erosion.
Orographic rainfall can enhance local biodiversity.
The diverse microclimates created by orographic rainfall support a wide range of plant and animal species. This leads to increased biodiversity and ecological richness in mountainous regions.
Orographic rainfall patterns can be influenced by climate change.
As global temperatures rise, changes in atmospheric circulation patterns can impact orographic rainfall. This can have significant consequences for water resources, vegetation distribution, and overall climate patterns in mountainous areas.
Orographic rainfall is a common feature in many mountain ranges around the world.
From the Himalayas to the Andes, orographic rainfall occurs in various mountainous regions worldwide. This phenomenon affects both local climates and the lives of people living in these regions.
Orographic rainfall can contribute to the formation of unique geographic features.
The erosive power of orographic rainfall over time can create stunning geological formations such as deep valleys, steep cliffs, and majestic waterfalls. These natural wonders attract tourists and contribute to the beauty of mountain landscapes.
Orographic rainfall plays an important role in agriculture.
Many agricultural regions located near mountain ranges benefit from orographic rainfall. The reliable water supply promotes plant growth and supports agricultural activities that contribute to local economies.
Conclusion
Orographic rainfall, also known as relief rainfall, is a fascinating natural phenomenon that occurs when moist air is forced to rise over mountainous terrain. This process results in the cooling and condensation of the air, leading to the formation of clouds and subsequent precipitation. Understanding the intricacies of orographic rainfall can provide valuable insights into the unique weather patterns experienced in mountainous regions.
Throughout this article, we’ve explored 11 enigmatic facts about orographic rainfall, from its role in shaping landscapes to its impact on local climates. We’ve learned about rain shadow effects, the importance of wind direction, and the influence of topographic features. By delving into these facts, we can appreciate the complexity and beauty of the natural world.
Next time you find yourself in a mountainous area experiencing rainfall, take a moment to consider the fascinating processes at work. Orographic rainfall is not only a fascinating subject for study, but it also plays a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of ecosystems around the world.
FAQs
Q: What causes orographic rainfall?
A: Orographic rainfall is caused by moist air being forced to rise over mountains, leading to cooling, condensation, and precipitation.
Q: Why does orographic rainfall occur on the windward side of mountains?
A: Orographic rainfall occurs on the windward side of mountains because the air is forced to rise, leading to cooling and condensation of moisture.
Q: What is a rain shadow effect?
A: A rain shadow effect refers to the phenomenon where dry air descends on the leeward side of mountains, leading to reduced rainfall in that area.
Q: How does topography influence orographic rainfall?
A: Topographic features such as slope angle and elevation can affect the intensity and distribution of orographic rainfall.
Q: Are mountains the only factor contributing to orographic rainfall?
A: While mountains play a significant role in orographic rainfall, other factors such as wind speed, air stability, and moisture content also influence its occurrence.
Q: Does orographic rainfall have any ecological significance?
A: Yes, orographic rainfall is crucial for maintaining the biodiversity and ecological balance in mountainous regions by providing water for vegetation and sustaining animal habitats.
Q: Can orographic rainfall lead to flash floods?
A: Yes, in certain cases, intense orographic rainfall can lead to flash floods as the excess precipitation overwhelms the local drainage systems.
Q: Does the intensity of orographic rainfall vary in different mountain ranges?
A: Yes, the intensity of orographic rainfall can vary depending on factors such as the height, shape, and orientation of the mountain range.
Q: Are there any regions in the world known for experiencing significant orographic rainfall?
A: Yes, regions such as the Pacific Northwest in the United States, the Western Ghats in India, and the Andes Mountains in South America are known for their high levels of orographic rainfall.
Q: Can orographic rainfall be predicted accurately?
A: While advancements in weather forecasting have improved the accuracy of predicting orographic rainfall, its complex nature can still make precise predictions challenging.
Q: How does orographic rainfall impact agriculture?
A: Orographic rainfall provides essential water resources for agriculture in mountainous regions, supporting crop growth and sustaining livelihoods.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
