Tetrodotoxin is a potent neurotoxin found in certain marine animals like pufferfish, blue-ringed octopuses, and some newts. This toxin is infamous for its ability to block sodium channels in nerve cells, leading to paralysis and potentially death. Despite its deadly nature, tetrodotoxin has fascinated scientists for years due to its unique properties and potential medical applications. Did you know that just a few milligrams can be lethal to humans? Yet, some cultures consider pufferfish, or fugu, a delicacy, prepared by specially trained chefs to avoid poisoning. Intrigued? Let's dive into 50 facts about tetrodotoxin that will leave you both amazed and cautious.
Key Takeaways:
- Tetrodotoxin, found in pufferfish and other animals, is a highly toxic substance that blocks nerve signals. It has historical, cultural, and medical significance, and plays a crucial role in ecosystems.
- Tetrodotoxin's unique properties make it a subject of extensive research for potential medical applications, including pain management and cancer treatment. Its impact on predator-prey relationships and evolutionary adaptations is also significant.
What is Tetrodotoxin?
Tetrodotoxin (TTX) is a potent neurotoxin found in various marine and terrestrial animals. Known for its deadly effects, it has fascinated scientists and the public alike. Here are some intriguing facts about this powerful substance.
- Tetrodotoxin is named after the Tetraodontidae family of fish, which includes pufferfish, one of its primary sources.
- It is 1,200 times more toxic than cyanide.
- The lethal dose for humans is approximately 2 milligrams.
- TTX blocks sodium channels in nerves, preventing signal transmission.
- Symptoms of TTX poisoning include numbness, paralysis, and respiratory failure.
- There is no known antidote for tetrodotoxin poisoning.
- Pufferfish, also known as fugu, are considered a delicacy in Japan despite the risks.
- Only specially trained and licensed chefs are allowed to prepare fugu in Japan.
- Tetrodotoxin is also found in blue-ringed octopuses, newts, and some frogs.
- The toxin is produced by bacteria that live symbiotically with these animals.
Historical and Cultural Significance
Tetrodotoxin has played a role in various cultures and historical events. Its deadly nature has made it both feared and revered.
- Ancient Egyptians were aware of the toxic properties of pufferfish.
- In Haiti, TTX is believed to be used in voodoo rituals to create "zombies."
- Japanese samurai used to consume small amounts of TTX to build immunity, a practice known as "fugu no jutsu."
- The first recorded case of TTX poisoning dates back to 1774.
- Tetrodotoxin was used as a murder weapon in a famous Japanese case in 1975.
- Some cultures use TTX in traditional medicine, despite its dangers.
- The toxin has been referenced in various works of fiction, including novels and movies.
- In some regions, pufferfish are considered a symbol of bravery and risk-taking.
- The preparation of fugu is often seen as an art form in Japanese cuisine.
- Tetrodotoxin has been studied for its potential use in pain management and medical research.
Biological and Chemical Properties
Understanding the biological and chemical properties of tetrodotoxin helps explain its potency and effects on living organisms.
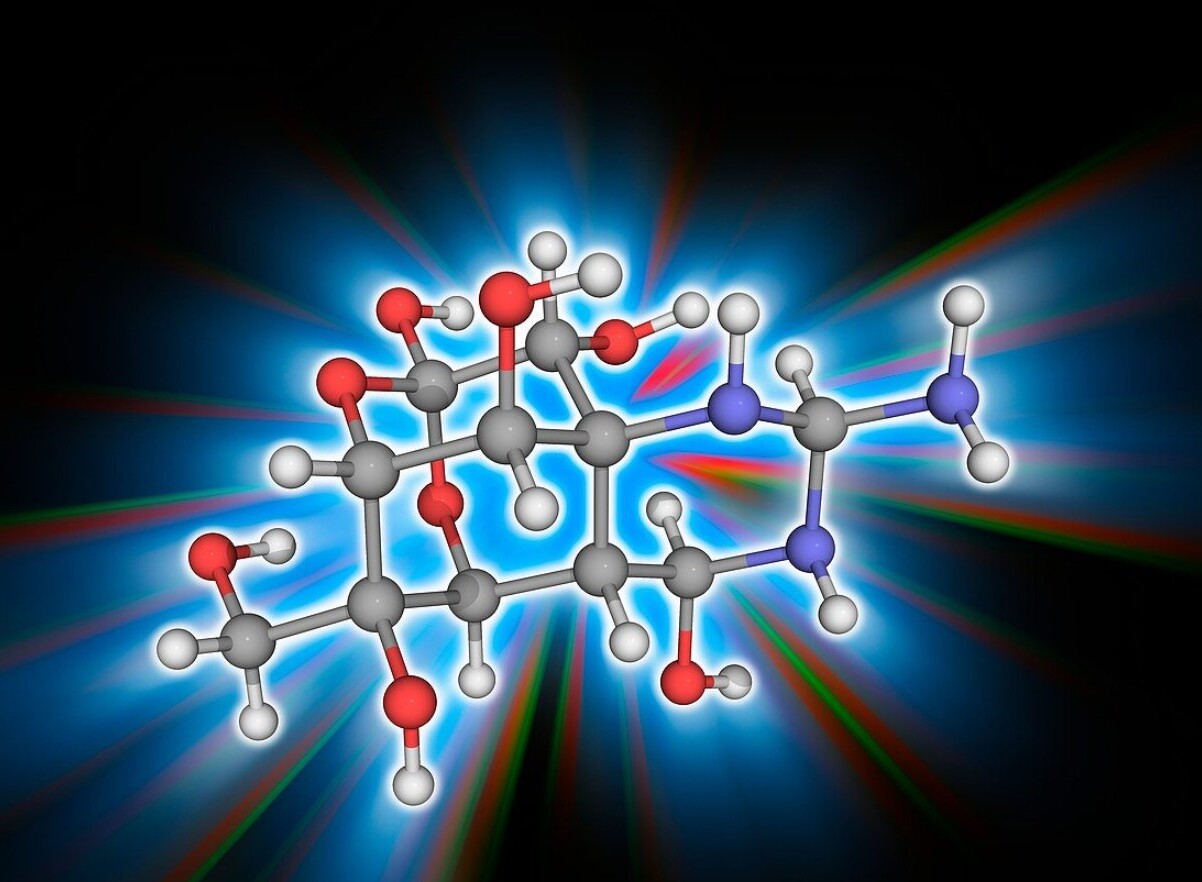
- Tetrodotoxin is a small, non-protein molecule.
- It is heat-stable, meaning cooking does not destroy its toxicity.
- The toxin is water-soluble, making it easily absorbed by the body.
- TTX binds to the voltage-gated sodium channels on nerve cells.
- It prevents the influx of sodium ions, halting nerve signal transmission.
- The molecular structure of TTX includes a guanidinium group, crucial for its binding to sodium channels.
- Tetrodotoxin has a half-life of about 4-6 hours in the human body.
- The toxin can be detected in blood, urine, and tissue samples using specialized tests.
- Some animals have evolved resistance to TTX, allowing them to prey on toxic species.
- Research on TTX has contributed to the development of local anesthetics and other medical applications.
Ecological Impact and Evolution
Tetrodotoxin plays a significant role in the ecosystems where it is found, influencing predator-prey relationships and evolutionary adaptations.
- TTX serves as a defense mechanism for many animals, deterring predators.
- Some predators have developed immunity to TTX, allowing them to consume toxic prey.
- The presence of TTX in an ecosystem can affect the behavior and distribution of species.
- Tetrodotoxin-producing bacteria are found in both marine and terrestrial environments.
- The evolution of TTX resistance in some species is an example of co-evolution.
- TTX can accumulate in the food chain, affecting higher trophic levels.
- Some animals use TTX to capture prey, such as the blue-ringed octopus.
- The distribution of TTX-producing species is influenced by environmental factors like temperature and salinity.
- Tetrodotoxin has been found in some non-toxic species, suggesting horizontal gene transfer.
- The study of TTX and its ecological impact provides insights into the complexity of natural ecosystems.
Medical and Scientific Research
Tetrodotoxin continues to be a subject of extensive research due to its unique properties and potential applications in medicine.
- TTX is being studied for its potential use as a painkiller for chronic pain conditions.
- Researchers are exploring the use of TTX in cancer treatment to target specific cells.
- The toxin has been used to study the function of sodium channels in nerve cells.
- TTX is a valuable tool in neurobiology research for understanding nerve signal transmission.
- Some studies suggest TTX could help treat opioid addiction by reducing withdrawal symptoms.
- The development of synthetic TTX analogs aims to create safer, non-toxic versions for medical use.
- TTX has been used in clinical trials for treating severe pain in cancer patients.
- Research on TTX has led to advancements in the field of toxicology and poison control.
- The study of TTX resistance in animals provides insights into genetic and evolutionary mechanisms.
- Tetrodotoxin remains a fascinating subject for scientists, with ongoing research uncovering new potential applications and understanding of its effects.
The Final Bite
Tetrodotoxin, found in pufferfish, is one of nature's most potent toxins. Despite its deadly nature, it has fascinated scientists and food enthusiasts alike. This toxin blocks sodium channels in nerves, leading to paralysis and, in severe cases, death. Yet, in controlled doses, it shows promise in pain management and other medical applications. The culinary world, particularly in Japan, has turned the preparation of pufferfish into an art form, requiring chefs to undergo rigorous training to ensure safety. Understanding tetrodotoxin's dual nature—both as a deadly poison and a potential medical marvel—highlights the delicate balance between risk and reward. Always approach pufferfish with caution and respect, appreciating the intricate dance between danger and discovery.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
