What is Boron Trichloride? Boron Trichloride (BCl₃) is a colorless gas with a pungent odor. It's a chemical compound made of one boron atom and three chlorine atoms. Why is it important? This compound plays a crucial role in various industries, including electronics, pharmaceuticals, and chemical manufacturing. How is it used? In electronics, BCl₃ is used for plasma etching of aluminum, silicon, and other materials. In the pharmaceutical world, it helps synthesize organic compounds. Is it safe? Handling Boron Trichloride requires caution. It reacts violently with water, releasing hydrochloric acid, which can be hazardous. Proper safety measures are essential when working with this compound. Curious to learn more? Dive into these 50 fascinating facts about Boron Trichloride to understand its significance and applications better.
Key Takeaways:
- Boron Trichloride is a versatile compound used in industries, but it requires careful handling due to its toxic and reactive nature. Safety measures and proper disposal are crucial to minimize its environmental impact.
- Understanding Boron Trichloride's chemical properties and applications can lead to safer handling and effective use. From semiconductor industry to cancer treatment, its unique properties make it a valuable compound with diverse applications.
What is Boron Trichloride?
Boron Trichloride (BCl₃) is a chemical compound that combines boron and chlorine. It's a colorless gas with a pungent odor, widely used in various industries. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about this compound.
- Boron Trichloride is a Lewis acid, meaning it can accept an electron pair.
- It has a molecular weight of 117.16 g/mol.
- The compound is highly reactive with water, producing hydrochloric acid and boric acid.
- Boron Trichloride is used in the semiconductor industry for plasma etching.
- It serves as a catalyst in organic synthesis.
- The compound is toxic and can cause severe burns upon contact with skin.
- Boron Trichloride is non-flammable, but it can react violently with water.
- It has a boiling point of 12.6°C (54.7°F).
- The melting point of Boron Trichloride is -107°C (-160.6°F).
- It is often used in the production of high-purity boron.
Applications of Boron Trichloride
Boron Trichloride finds applications in various fields due to its unique properties. Here are some key uses:
- It is used in the manufacture of boron fibers.
- The compound is essential in the production of aluminum boride.
- Boron Trichloride is used to refine aluminum, magnesium, zinc, and copper.
- It acts as a fluxing agent in metallurgy.
- The compound is used in the chemical vapor deposition process.
- It helps in the synthesis of boron-containing compounds.
- Boron Trichloride is used in neutron capture therapy for cancer treatment.
- It is a precursor for the production of boron nitride.
- The compound is used in the manufacture of borosilicate glass.
- It is employed in the production of pharmaceuticals.
Chemical Properties of Boron Trichloride
Understanding the chemical properties of Boron Trichloride can help in its safe handling and effective use. Here are some notable properties:
- Boron Trichloride is a covalent compound.
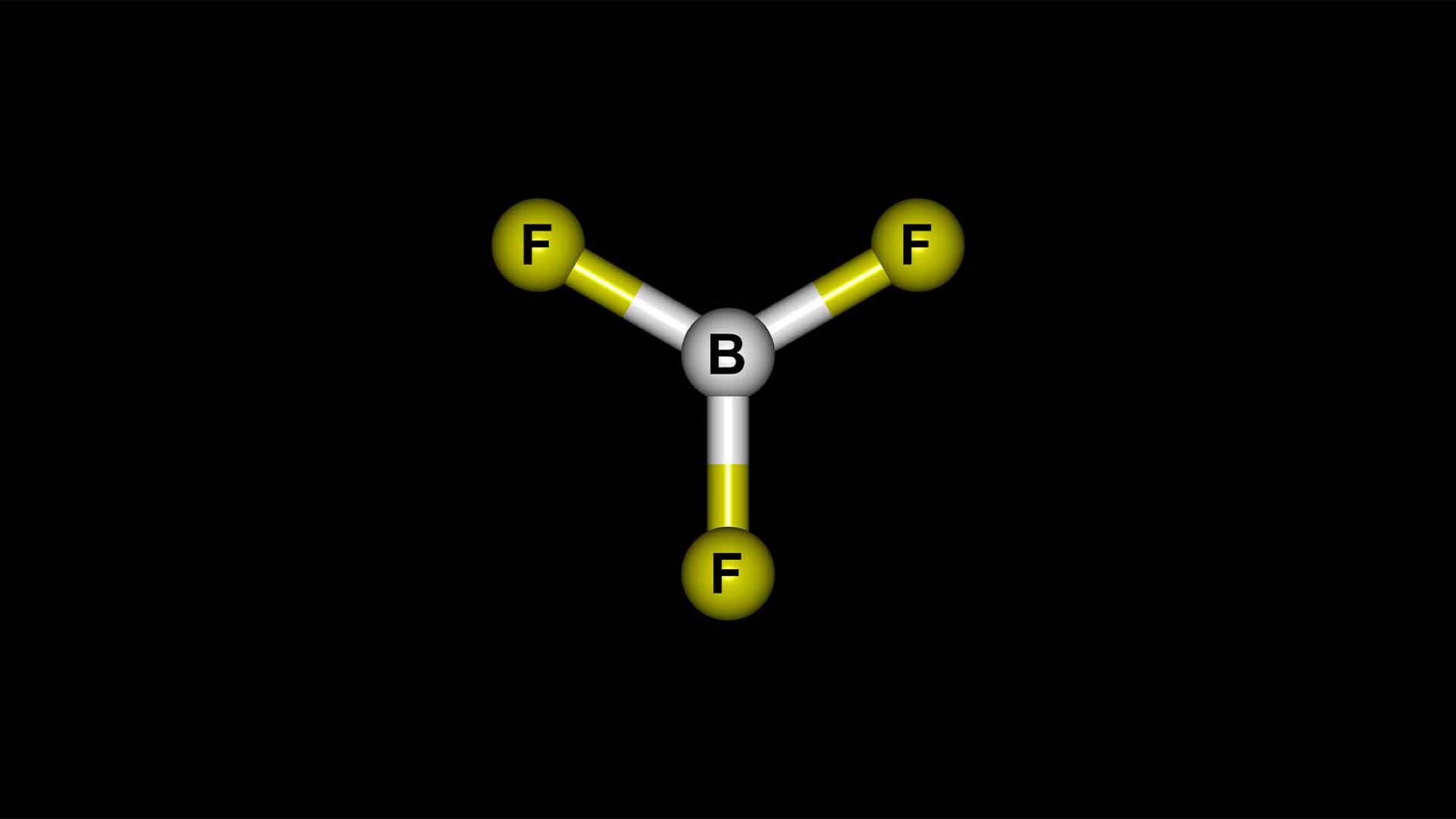
- It has a trigonal planar molecular geometry.
- The compound has a dipole moment of zero.
- It is paramagnetic in nature.
- Boron Trichloride can form adducts with Lewis bases.
- It reacts with alcohols to form borate esters.
- The compound can hydrolyze in the presence of moisture.
- It forms complexes with ethers.
- Boron Trichloride can chlorinate organic compounds.
- It is used in the preparation of boron carbide.
Safety and Handling of Boron Trichloride
Due to its reactive nature, Boron Trichloride requires careful handling. Here are some safety tips and facts:
- Always use protective gear when handling Boron Trichloride.
- Store the compound in airtight containers.
- Ensure proper ventilation in areas where Boron Trichloride is used.
- In case of contact with skin, rinse immediately with plenty of water.
- Avoid inhaling the gas, as it can cause respiratory issues.
- Use fume hoods when working with the compound in a laboratory.
- Boron Trichloride should be stored away from water.
- In case of a spill, use dry sand or earth to contain it.
- Always have a first aid kit nearby when working with Boron Trichloride.
- Dispose of the compound according to local regulations.
Environmental Impact of Boron Trichloride
Boron Trichloride can have significant environmental effects if not managed properly. Here are some facts about its impact:
- It can contaminate water sources if not disposed of correctly.
- The compound can cause acid rain when released into the atmosphere.
- Boron Trichloride can harm aquatic life.
- It contributes to air pollution when released in large quantities.
- Proper disposal methods can minimize environmental impact.
- The compound can degrade soil quality.
- It is important to follow environmental guidelines when using Boron Trichloride.
- Recycling and reusing the compound can reduce waste.
- Boron Trichloride can react with other pollutants, creating hazardous compounds.
- Awareness and education about its environmental impact can lead to better handling practices.
The Final Word on Boron Trichloride
Boron Trichloride, a chemical compound with the formula BCl3, plays a crucial role in various industries. Known for its use in semiconductor manufacturing, it helps in the production of high-purity silicon. This compound also serves as a catalyst in organic synthesis and etching agent in the electronics industry. Despite its benefits, handling BCl3 requires caution due to its corrosive nature and potential health hazards.
Understanding these facts about Boron Trichloride can help you appreciate its importance and the precautions needed when working with it. Whether you're a student, a professional in the field, or just curious, knowing these details can enhance your knowledge and awareness. So, next time you hear about Boron Trichloride, you'll have a solid grasp of what it is and why it matters.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
