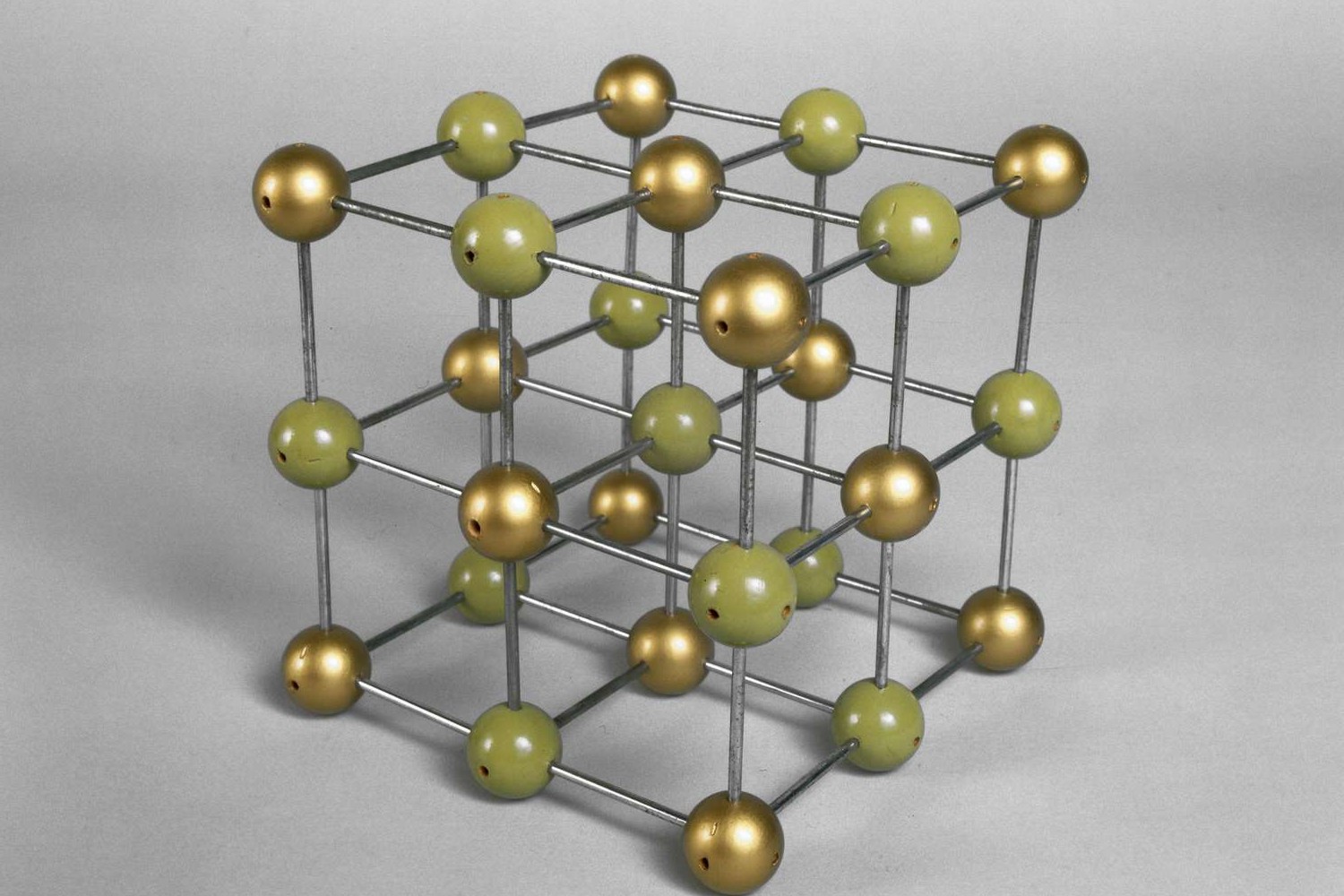
What are ionic compounds? Ionic compounds are formed when atoms transfer electrons to achieve a full outer shell, creating ions. These ions, with opposite charges, attract each other and form a stable compound. Why are they important? They play a crucial role in various fields, from chemistry to everyday life. Where can you find them? Common examples include table salt (sodium chloride) and baking soda (sodium bicarbonate). How do they behave? Ionic compounds typically have high melting and boiling points, conduct electricity when dissolved in water, and form crystalline structures. Why should you care? Understanding ionic compounds helps in grasping fundamental chemistry concepts and their applications in real-world scenarios. Dive into these 39 fascinating facts to learn more about the intriguing world of ionic compounds!
What Are Ionic Compounds?
Ionic compounds are fascinating substances formed by the transfer of electrons between atoms. This process creates ions, which are atoms with a positive or negative charge. These ions then attract each other, forming a stable compound. Let's dive into some intriguing facts about these compounds.
-
Ionic bonds form between metals and non-metals. Metals lose electrons to become positively charged ions, while non-metals gain electrons to become negatively charged ions.
-
Sodium chloride (table salt) is a classic example. Sodium (Na) donates an electron to chlorine (Cl), resulting in NaCl.
-
Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points. The strong attraction between ions requires a lot of energy to break.
-
They are usually solid at room temperature. The ionic bonds create a rigid, lattice structure.
-
Ionic compounds dissolve in water. Water molecules surround and separate the ions, allowing them to disperse.
-
They conduct electricity when dissolved or molten. Free-moving ions in solution or liquid state carry electric current.
-
Ionic compounds are often crystalline. The orderly arrangement of ions forms a crystal lattice.
-
They are typically brittle. When struck, the ions shift and repel each other, causing the compound to shatter.
-
Ionic bonds are strong but not the strongest. Covalent bonds, where atoms share electrons, can be stronger.
-
They form through exothermic reactions. The formation of ionic bonds releases energy.
Properties of Ionic Compounds
Understanding the properties of ionic compounds helps in recognizing their applications and behavior in different environments.
-
They have distinct colors. Transition metals in ionic compounds can produce vibrant colors due to electron transitions.
-
They are soluble in polar solvents. Polar solvents like water can dissolve ionic compounds by surrounding the ions.
-
They have high density. The close packing of ions in a lattice structure results in high density.
-
They can form hydrates. Some ionic compounds trap water molecules within their crystal structure.
-
They exhibit lattice energy. This is the energy released when ions form a crystal lattice from gaseous ions.
-
They can be used in electrolysis. Ionic compounds can be broken down into their elements using an electric current.
-
They have low volatility. Ionic compounds do not easily vaporize due to strong ionic bonds.
-
They can form complex ions. Some ionic compounds contain ions that bond with other ions or molecules to form complex structures.
-
They are used in batteries. Ionic compounds like lithium salts are crucial in battery technology.
-
They can act as electrolytes. In solutions, ionic compounds help conduct electricity, essential for biological processes.
Examples of Ionic Compounds
Exploring specific examples of ionic compounds can provide a clearer picture of their diversity and applications.
-
Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) is found in limestone. It is used in construction and as a dietary calcium supplement.
-
Magnesium sulfate (Epsom salt) is used in medicine. It helps relieve muscle aches and is used in bath salts.
-
Potassium nitrate (saltpeter) is used in fertilizers. It provides essential nutrients for plant growth.
-
Sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) is a common household item. It is used in baking, cleaning, and as an antacid.
-
Ammonium chloride is used in dry cells. It acts as an electrolyte in batteries.
-
Copper(II) sulfate is used in agriculture. It is a fungicide and herbicide.
-
Zinc oxide is used in sunscreens. It provides protection against UV rays.
-
Iron(III) chloride is used in water treatment. It helps remove impurities from water.
-
Sodium hypochlorite is used in bleach. It is a powerful disinfectant.
-
Calcium phosphate is found in bones and teeth. It provides structural strength.
Applications of Ionic Compounds
Ionic compounds have a wide range of applications in various fields, from everyday household items to advanced industrial processes.
-
They are used in ceramics. Ionic compounds like aluminum oxide are essential in making ceramics.
-
They play a role in metallurgy. Ionic compounds are used in extracting and refining metals.
-
They are essential in pharmaceuticals. Many medications contain ionic compounds for their therapeutic effects.
-
They are used in food preservation. Sodium chloride and other salts help preserve food by inhibiting microbial growth.
-
They are crucial in agriculture. Fertilizers containing ionic compounds provide essential nutrients to crops.
-
They are used in water softening. Ionic compounds like sodium carbonate help remove hardness from water.
-
They are important in cleaning products. Ionic compounds like sodium lauryl sulfate are used in detergents and soaps.
-
They are used in glass manufacturing. Ionic compounds like sodium carbonate are used to make glass.
-
They are involved in environmental protection. Ionic compounds are used in processes to reduce pollution and treat waste.
Ionic compounds are integral to many aspects of daily life and industry. Their unique properties and diverse applications make them a vital part of modern science and technology.
The Final Word on Ionic Compounds
Ionic compounds are fascinating. They form when atoms transfer electrons, creating charged ions that stick together. These compounds have high melting and boiling points, making them stable. They conduct electricity when dissolved in water or melted, which is why they're used in batteries and electrolysis. Their crystal lattice structure gives them unique properties like brittleness and hardness.
Understanding ionic compounds helps in many fields, from chemistry to engineering. They play a role in everyday items like table salt and baking soda. Knowing their properties can explain why certain materials behave the way they do.
So, next time you see salt or use baking soda, remember the science behind these common items. Ionic compounds are more than just a topic in a textbook; they're a part of our daily lives. Keep exploring and stay curious about the world around you.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
