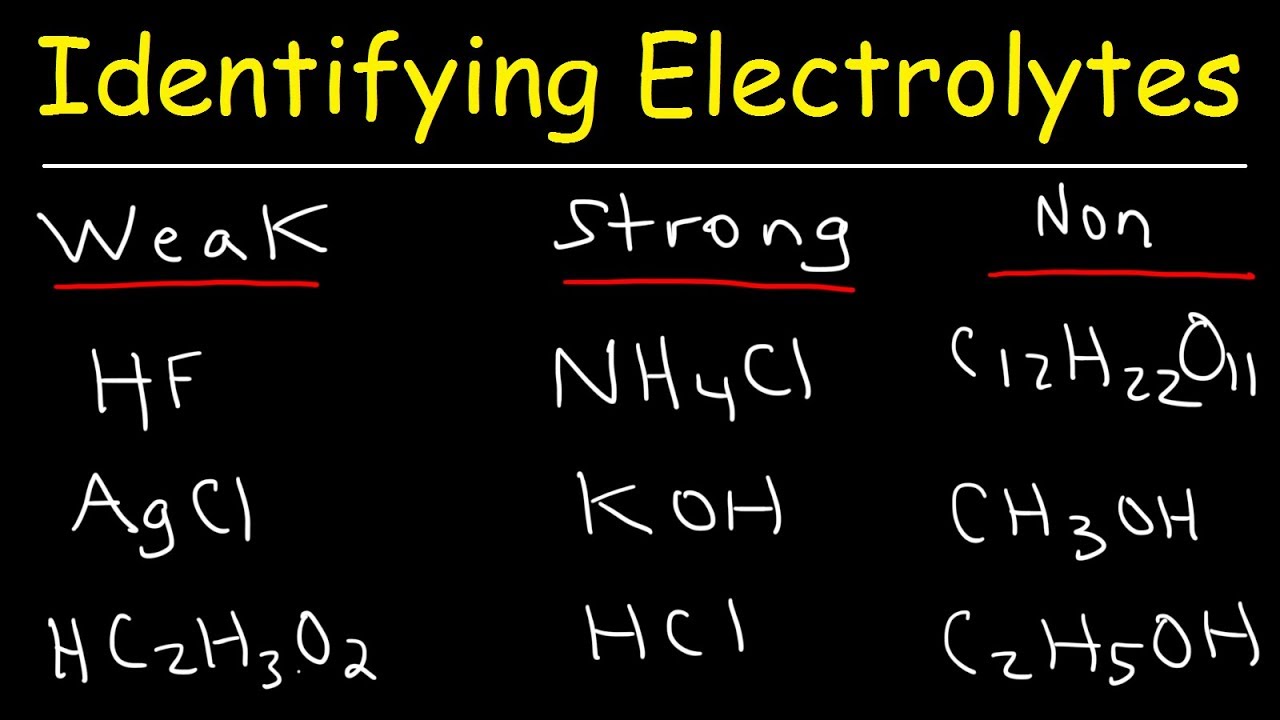
Strong electrolytes play a crucial role in chemistry and everyday life. But what exactly are they? Strong electrolytes are substances that completely dissociate into ions when dissolved in water. This means they conduct electricity very efficiently. Common examples include table salt (sodium chloride), hydrochloric acid, and potassium hydroxide. These substances are vital in various applications, from powering batteries to facilitating biochemical reactions in our bodies. Understanding strong electrolytes can help you grasp essential concepts in science and appreciate their practical uses. Ready to dive into some fascinating facts about these powerful substances? Let's get started!
What Are Strong Electrolytes?
Strong electrolytes are substances that completely dissociate into ions when dissolved in water. This means they conduct electricity very well. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about these powerful compounds.
-
Complete Dissociation: Strong electrolytes fully break apart into ions in solution, unlike weak electrolytes which only partially dissociate.
-
Types of Strong Electrolytes: Common types include strong acids, strong bases, and salts.
-
Strong Acids: Examples of strong acids are hydrochloric acid (HCl), sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄), and nitric acid (HNO₃).
-
Strong Bases: Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and potassium hydroxide (KOH) are well-known strong bases.
-
Salts as Strong Electrolytes: Sodium chloride (NaCl) and potassium nitrate (KNO₃) are typical salts that act as strong electrolytes.
Conductivity and Applications
Strong electrolytes play a crucial role in various applications due to their excellent conductivity.
-
High Conductivity: Because they fully dissociate, strong electrolytes are excellent conductors of electricity.
-
Electrolyte Solutions: These solutions are used in batteries to conduct electricity between the anode and cathode.
-
Medical Uses: Electrolyte solutions are vital in medical treatments, such as intravenous (IV) fluids to restore ion balance in patients.
-
Industrial Applications: Industries use strong electrolytes in processes like electroplating and electrolysis.
-
Electrolyte Drinks: Sports drinks often contain strong electrolytes to help athletes maintain hydration and ion balance.
Chemical Properties
Understanding the chemical properties of strong electrolytes helps in grasping their behavior in different environments.
-
Ionization: Strong electrolytes ionize completely in water, producing a high concentration of ions.
-
pH Levels: Strong acids and bases significantly alter the pH of a solution due to their complete dissociation.
-
Reactivity: These substances are highly reactive, making them useful in various chemical reactions.
-
Neutralization: When strong acids and bases react, they neutralize each other, forming water and a salt.
-
Solubility: Most strong electrolytes are highly soluble in water, which aids in their complete dissociation.
Examples of Strong Electrolytes
Here are some specific examples of strong electrolytes and their unique characteristics.
-
Hydrochloric Acid (HCl): Commonly used in laboratories and industry, it fully dissociates into H⁺ and Cl⁻ ions.
-
Sulfuric Acid (H₂SO₄): Known for its use in car batteries, it dissociates into H⁺ and SO₄²⁻ ions.
-
Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH): A strong base used in soap making, it dissociates into Na⁺ and OH⁻ ions.
-
Potassium Hydroxide (KOH): Used in alkaline batteries, it dissociates into K⁺ and OH⁻ ions.
-
Sodium Chloride (NaCl): Table salt, which dissociates into Na⁺ and Cl⁻ ions in water.
Biological Importance
Strong electrolytes are essential for various biological processes in living organisms.
-
Nerve Function: Ions from strong electrolytes are crucial for nerve impulse transmission.
-
Muscle Contraction: Calcium ions (Ca²⁺) play a key role in muscle contraction.
-
Hydration: Electrolytes help maintain fluid balance within cells and tissues.
-
pH Regulation: They help regulate the pH levels in blood and other bodily fluids.
-
Nutrient Absorption: Electrolytes assist in the absorption of nutrients in the digestive system.
Safety and Handling
Handling strong electrolytes requires caution due to their reactive nature.
-
Corrosive Nature: Many strong electrolytes, like acids and bases, are highly corrosive and can cause burns.
-
Proper Storage: They should be stored in appropriate containers to prevent leaks and reactions.
-
Protective Gear: Using gloves and goggles is essential when handling these substances.
-
Ventilation: Working in a well-ventilated area helps avoid inhaling harmful fumes.
-
Neutralization Spills: Spills should be neutralized immediately to prevent damage and injury.
Environmental Impact
Strong electrolytes can have significant effects on the environment if not managed properly.
-
Water Pollution: Improper disposal can lead to water contamination, harming aquatic life.
-
Soil Contamination: Spills can alter soil pH, affecting plant growth and soil health.
-
Air Quality: Fumes from strong acids and bases can contribute to air pollution.
-
Waste Management: Proper disposal methods are crucial to minimize environmental impact.
-
Regulations: Many countries have strict regulations for the disposal and handling of strong electrolytes to protect the environment.
Interesting Tidbits
Here are some lesser-known facts about strong electrolytes that might surprise you.
-
Historical Use: Ancient civilizations used natural strong electrolytes like salt for preservation and medicinal purposes.
-
Everyday Products: Many household cleaning products contain strong electrolytes for their effectiveness in breaking down grime.
-
Scientific Research: Ongoing research explores new applications and safer handling methods for strong electrolytes.
Final Thoughts on Strong Electrolytes
Strong electrolytes play a crucial role in various chemical processes and everyday applications. They completely dissociate into ions in water, making them excellent conductors of electricity. This property is essential in fields like medicine, where electrolytes help maintain bodily functions, and in industries that rely on electrochemical reactions. Understanding strong electrolytes can also aid in grasping fundamental concepts in chemistry, such as acid-base reactions and solution conductivity.
Whether you're a student, a professional, or just curious, knowing about strong electrolytes enriches your knowledge and appreciation of the chemical world. From table salt to battery acid, these substances are all around us, influencing countless aspects of our daily lives. Keep exploring and experimenting to see the fascinating effects of strong electrolytes in action.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
