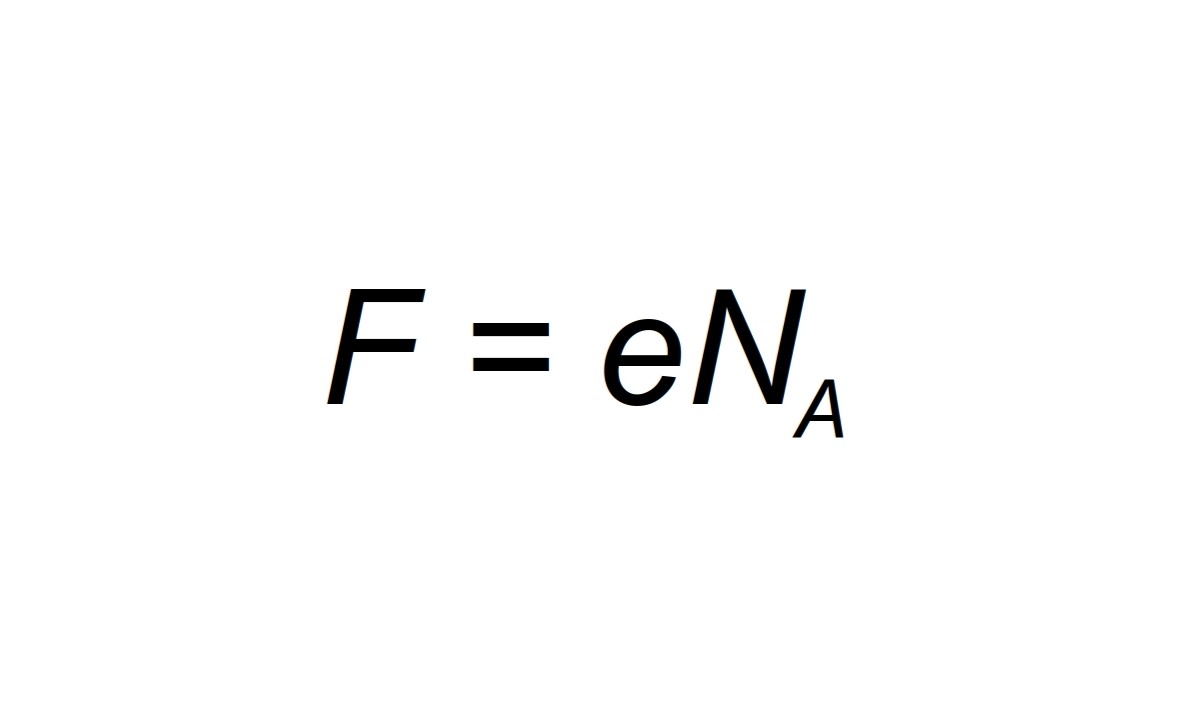
The Faraday constant is a key concept in electrochemistry, representing the charge of one mole of electrons. Named after Michael Faraday, this constant is crucial for understanding reactions in batteries, electrolysis, and more. It’s defined as approximately 96,485 coulombs per mole. Why is it important? Because it helps scientists calculate the amount of substance altered during electrochemical reactions. Imagine trying to figure out how much metal gets plated in an electroplating process without it. Faraday’s work laid the groundwork for modern electrical engineering and chemistry. Ready to dive into 38 fascinating facts about this constant? Let's get started!
What is the Faraday Constant?
The Faraday constant is a fundamental physical constant representing the charge of one mole of electrons. Named after Michael Faraday, it plays a crucial role in electrochemistry and physics. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about this constant.
-
The Faraday constant is approximately 96,485 coulombs per mole (C/mol).
-
It is derived from the charge of a single electron, which is about 1.602 x 10^-19 coulombs.
-
This constant is essential for calculating the amount of substance produced or consumed in electrochemical reactions.
-
Michael Faraday, an English scientist, discovered the principles behind this constant in the 1830s.
-
The Faraday constant links the macroscopic world of moles to the microscopic world of electrons.
Importance in Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry relies heavily on the Faraday constant for various calculations and processes. Here are some key points highlighting its importance.
-
It helps determine the amount of electric charge needed to deposit or dissolve a substance during electrolysis.
-
The constant is used in Faraday's laws of electrolysis, which quantify the relationship between electric charge and chemical change.
-
It aids in calculating the energy required for electrochemical reactions.
-
The Faraday constant is crucial for understanding battery capacities and efficiencies.
-
It plays a role in determining the stoichiometry of electrochemical reactions.
Applications in Real Life
The Faraday constant isn't just a theoretical concept; it has practical applications in everyday life and technology.
-
It is used in the design and functioning of batteries, including those in smartphones and electric vehicles.
-
The constant helps in the electroplating process, where a thin layer of metal is deposited onto a surface.
-
It is essential for the production of aluminum through the Hall-Héroult process.
-
The Faraday constant is used in the purification of metals like copper and zinc.
-
It aids in the development of fuel cells, which are used in various clean energy applications.
Historical Context
Understanding the historical context of the Faraday constant provides insight into its development and significance.
-
Michael Faraday's experiments in the early 19th century laid the groundwork for modern electrochemistry.
-
Faraday's work on electromagnetism and electrochemistry earned him a place among the greatest scientists of all time.
-
The constant was named in his honor to recognize his contributions to science.
-
Faraday's laws of electrolysis were first published in 1834.
-
His discoveries paved the way for future advancements in electrical engineering and chemistry.
Mathematical Representation
The Faraday constant can be represented mathematically in various ways, making it versatile for different scientific applications.
-
It is often denoted by the symbol F.
-
The constant can be expressed as F = N_A * e, where N_A is Avogadro's number and e is the elementary charge.
-
In terms of units, it is represented as C/mol (coulombs per mole).
-
The value of the Faraday constant is approximately 96,485.33212 C/mol.
-
It can also be used to convert between moles of electrons and coulombs in electrochemical equations.
Relationship with Other Constants
The Faraday constant is interconnected with other fundamental constants in physics and chemistry.
-
It is related to Avogadro's number, which is approximately 6.022 x 10^23 mol^-1.
-
The elementary charge (e) is another related constant, with a value of about 1.602 x 10^-19 coulombs.
-
The Faraday constant can be used to derive the gas constant (R) in certain electrochemical contexts.
-
It is also linked to the Planck constant (h) through the relationship between energy and charge.
-
The constant plays a role in the Nernst equation, which describes the electrochemical potential of a cell.
Fun Facts
Here are some fun and lesser-known facts about the Faraday constant that might surprise you.
-
The Faraday constant is used in the field of biochemistry to study redox reactions in cells.
-
It helps in understanding the principles behind electrocardiograms (ECGs) in medical science.
-
The constant is crucial for the operation of electrochemical sensors used in various industries.
-
It is used in the study of corrosion and the development of anti-corrosion technologies.
-
The Faraday constant is also important in the field of environmental science for monitoring and controlling pollution.
-
It plays a role in the development of new materials through electrochemical synthesis.
-
The constant is used in the study of semiconductor devices and their electrical properties.
-
It helps in the research and development of new energy storage systems, including supercapacitors and advanced batteries.
The Faraday Constant's Impact
The Faraday constant is a cornerstone in electrochemistry. Named after Michael Faraday, it represents the charge of one mole of electrons, about 96,485 coulombs. This number is crucial for calculating reactions in batteries, electroplating, and more. Understanding this constant helps in fields like energy storage and material science.
Faraday's work laid the groundwork for modern electrical engineering. His discoveries continue to influence technologies we use daily. From powering your smartphone to advancing renewable energy, the Faraday constant is at the heart of it all.
Grasping the importance of this constant not only deepens your knowledge of chemistry but also connects you to the broader world of science and technology. So next time you charge your phone or see a shiny new car, remember the Faraday constant's role in making it all possible.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
