What is sp3 hybridization? sp3 hybridization occurs when one s orbital and three p orbitals in an atom mix to form four equivalent hybrid orbitals. These hybrid orbitals arrange themselves in a tetrahedral geometry, which means they point towards the corners of a tetrahedron. This type of hybridization is common in carbon atoms, especially in organic compounds like methane (CH4). sp3 hybridization allows for the formation of strong sigma bonds, which are essential for the stability and structure of many molecules. Understanding this concept is crucial for grasping how atoms bond and form complex structures in chemistry.
What is sp3 Hybridization?
sp3 hybridization is a concept in chemistry that explains the bonding in molecules where one s orbital and three p orbitals mix to form four equivalent hybrid orbitals. This type of hybridization is crucial for understanding the structure and bonding in organic compounds, especially those involving carbon.
- sp3 hybridization involves the mixing of one s orbital and three p orbitals.
- This hybridization results in four equivalent sp3 hybrid orbitals.
- Each sp3 hybrid orbital has 25% s character and 75% p character.
- The bond angles in sp3 hybridized molecules are approximately 109.5 degrees.
- sp3 hybridization is common in carbon atoms, especially in alkanes.
Characteristics of sp3 Hybrid Orbitals
Understanding the characteristics of sp3 hybrid orbitals helps in predicting the geometry and reactivity of molecules.
- sp3 hybrid orbitals are oriented in a tetrahedral geometry.
- These orbitals are more directional than pure s or p orbitals, leading to stronger sigma bonds.
- The energy of sp3 hybrid orbitals is higher than that of an s orbital but lower than that of a p orbital.
- sp3 hybridization leads to the formation of single bonds (sigma bonds) in molecules.
- The overlap of sp3 hybrid orbitals with other orbitals forms strong covalent bonds.
Examples of sp3 Hybridization
Examples help in visualizing how sp3 hybridization works in real molecules.
- Methane (CH4) is a classic example of sp3 hybridization.
- In methane, the carbon atom forms four sigma bonds with hydrogen atoms.
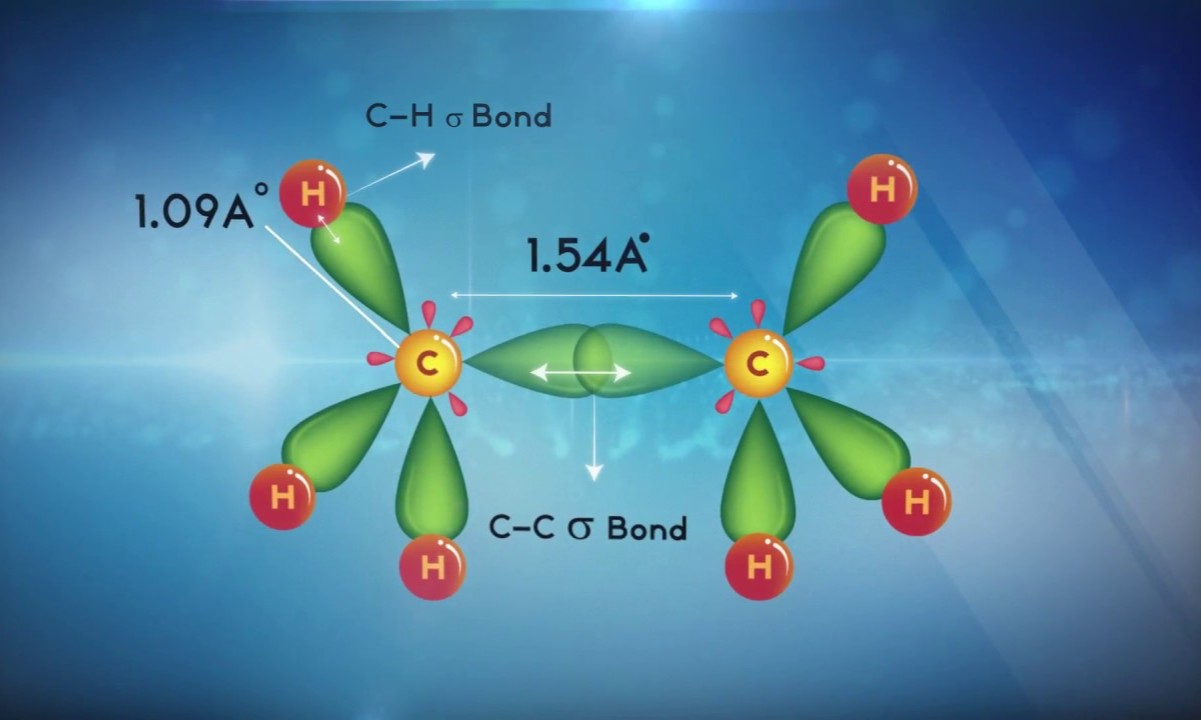
- Ethane (C2H6) also exhibits sp3 hybridization in each carbon atom.
- In ethane, each carbon forms three sigma bonds with hydrogen and one sigma bond with another carbon.
- Ammonia (NH3) shows sp3 hybridization with one lone pair and three sigma bonds.
Importance of sp3 Hybridization in Organic Chemistry
sp3 hybridization is fundamental in organic chemistry, influencing the structure and properties of countless compounds.
- sp3 hybridization explains the tetrahedral geometry of carbon compounds.
- It is essential for understanding the reactivity and stability of alkanes.
- sp3 hybridization is crucial for predicting the three-dimensional structure of organic molecules.
- It helps in explaining the physical properties of organic compounds, such as boiling and melting points.
- sp3 hybridization is also important in biochemistry, particularly in the structure of amino acids and proteins.
sp3 Hybridization in Biological Molecules
Biological molecules often exhibit sp3 hybridization, affecting their function and interaction.
- The carbon atoms in fatty acids are sp3 hybridized.
- In proteins, the carbon atoms in the backbone are sp3 hybridized.
- The tetrahedral geometry of sp3 hybridized carbons in amino acids influences protein folding.
- DNA and RNA contain sp3 hybridized carbon atoms in their sugar-phosphate backbone.
- The sp3 hybridization in biological molecules contributes to their stability and functionality.
sp3 Hybridization and Molecular Geometry
The geometry of molecules with sp3 hybridization is a key aspect of their chemical behavior.
- The tetrahedral geometry minimizes electron pair repulsion, leading to stable structures.
- Deviations from the ideal 109.5-degree bond angle can occur due to lone pairs or multiple bonds.
- The geometry of sp3 hybridized molecules affects their polarity and intermolecular interactions.
- Understanding the geometry helps in predicting the behavior of molecules in chemical reactions.
- The spatial arrangement of atoms in sp3 hybridized molecules is crucial for their biological activity and interaction with other molecules.
The Final Word on sp3 Hybridization
sp3 hybridization is a fascinating concept in chemistry. It explains how atoms form bonds and create the shapes of molecules. This type of hybridization involves the mixing of one s orbital and three p orbitals, resulting in four sp3 hybrid orbitals. These orbitals arrange themselves in a tetrahedral shape, which is crucial for understanding the geometry of many molecules.
Knowing about sp3 hybridization helps in predicting molecular shapes, bond angles, and the behavior of molecules in reactions. It’s a key concept for students and professionals in chemistry, biology, and materials science.
Understanding sp3 hybridization also sheds light on the properties of everyday substances, from water to methane. It’s a building block for more advanced topics in chemistry, making it essential for anyone looking to deepen their knowledge in the field. Keep exploring, and you'll find even more intriguing aspects of molecular geometry.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
