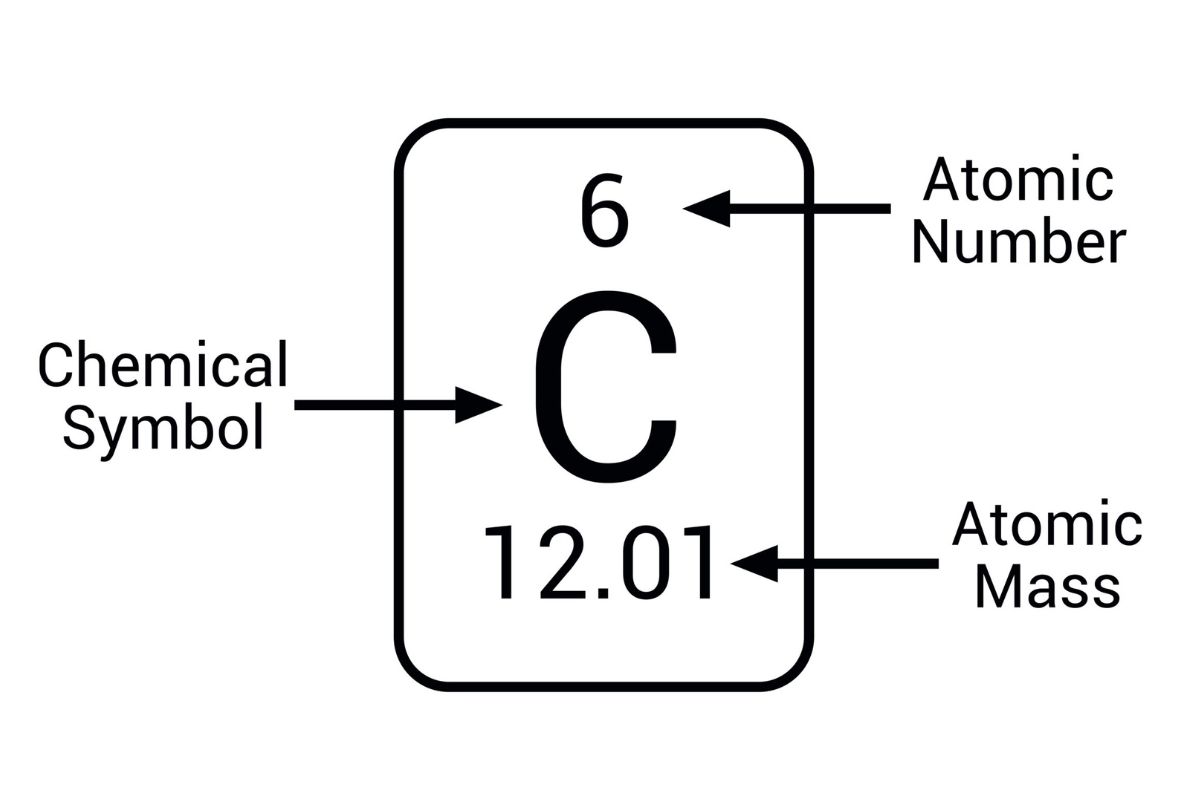
Atomic mass is a fundamental concept in chemistry and physics, but what exactly is it? Atomic mass refers to the mass of an atom, typically measured in atomic mass units (amu). This value is crucial because it helps scientists understand the properties of elements and how they interact. Atomic mass is calculated by adding the number of protons and neutrons in an atom's nucleus. Electrons are so light they barely affect the total mass. Knowing the atomic mass of an element allows chemists to predict how it will behave in reactions, making it a cornerstone of scientific study. Ready to dive into more fascinating facts about atomic mass? Let's get started!
What is Atomic Mass?
Atomic mass, also known as atomic weight, is a fundamental concept in chemistry and physics. It represents the mass of an atom, typically measured in atomic mass units (amu). Understanding atomic mass helps in grasping the properties and behaviors of different elements.
-
Atomic mass is the weighted average of all isotopes of an element. Different isotopes of an element have varying numbers of neutrons, which affects their mass. The atomic mass takes into account the relative abundance of each isotope.
-
Measured in atomic mass units (amu). One atomic mass unit is defined as one-twelfth the mass of a carbon-12 atom. This standard helps scientists compare the masses of different atoms.
-
Carbon-12 is the reference standard. The atomic mass of carbon-12 is exactly 12 amu, serving as a benchmark for other elements.
-
Protons and neutrons contribute to atomic mass. Electrons have negligible mass compared to protons and neutrons, so they don't significantly affect the atomic mass.
-
Atomic mass is not always a whole number. Due to the presence of isotopes and their varying abundances, the atomic mass of an element is often a decimal value.
Historical Context of Atomic Mass
The concept of atomic mass has evolved over time, with significant contributions from various scientists. Understanding its history provides insight into its current definition and usage.
-
John Dalton's atomic theory laid the groundwork. In the early 19th century, Dalton proposed that atoms of different elements have different masses, leading to the concept of atomic mass.
-
Dmitri Mendeleev's periodic table. Mendeleev arranged elements by increasing atomic mass, which helped predict the properties of undiscovered elements.
-
Discovery of isotopes. In the early 20th century, scientists discovered that elements can have atoms with different masses, leading to the concept of isotopes.
-
Development of mass spectrometry. This technique allowed for precise measurement of atomic masses and the identification of isotopes.
-
Adoption of the carbon-12 standard. In 1961, the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) adopted carbon-12 as the standard for atomic mass.
Importance of Atomic Mass in Chemistry
Atomic mass plays a crucial role in various chemical processes and calculations. It helps scientists understand the behavior of elements and compounds.
-
Molecular mass calculation. The atomic masses of individual atoms in a molecule are summed to determine its molecular mass.
-
Stoichiometry. Atomic mass is essential for balancing chemical equations and determining the proportions of reactants and products.
-
Avogadro's number. This constant (6.022 x 10^23) relates the number of atoms or molecules in a mole to their atomic or molecular mass.
-
Determining molar mass. The molar mass of a substance is the mass of one mole of its atoms or molecules, calculated using atomic mass.
-
Chemical reactions. Understanding atomic mass helps predict the outcomes of chemical reactions and the amounts of products formed.
Atomic Mass and the Periodic Table
The periodic table organizes elements based on their atomic number and atomic mass. This arrangement reveals patterns and trends in element properties.
-
Periodic trends. Atomic mass influences trends such as atomic radius, ionization energy, and electronegativity across periods and groups.
-
Element classification. Elements are classified into metals, nonmetals, and metalloids based on their atomic mass and other properties.
-
Predicting element properties. The periodic table helps predict the physical and chemical properties of elements based on their atomic mass and position.
-
Identifying isotopes. The atomic mass listed on the periodic table is an average value, reflecting the presence of different isotopes.
-
Element discovery. New elements are added to the periodic table based on their atomic number and mass, expanding our understanding of the universe.
Applications of Atomic Mass in Science and Technology
Atomic mass has practical applications in various scientific and technological fields, from medicine to materials science.
-
Radiocarbon dating. This technique uses the atomic mass of carbon isotopes to determine the age of archaeological and geological samples.
-
Nuclear medicine. Isotopes with specific atomic masses are used in medical imaging and cancer treatment.
-
Materials science. Understanding atomic mass helps in designing and developing new materials with desired properties.
-
Environmental science. Atomic mass is used to trace the sources and pathways of pollutants in the environment.
-
Space exploration. Atomic mass helps identify the composition of celestial bodies and the potential for life on other planets.
-
Pharmaceuticals. Atomic mass is crucial in drug design and development, ensuring the correct dosage and efficacy of medications.
-
Forensic science. Atomic mass helps identify substances and trace evidence in criminal investigations.
The Final Word on Atomic Mass
Atomic mass is more than just a number on the periodic table. It’s a key player in understanding elements, their reactions, and how they form compounds. Knowing atomic mass helps scientists predict how substances will behave in different situations. It’s crucial for everything from creating new materials to understanding biological processes.
Remember, atomic mass is the weighted average of all the isotopes of an element. This means it takes into account the different masses and abundances of each isotope. It’s not just a simple average, but a more complex calculation that gives a more accurate picture of an element’s mass.
So, next time you look at the periodic table, take a moment to appreciate the atomic mass. It’s a small number with a big impact on our understanding of the world.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
