Gene transcription factors are one of the most fascinating components of the biological world. They play a crucial role in regulating gene expression, acting as the “conductors” of the cellular orchestra. These proteins bind to specific DNA sequences and initiate or inhibit the transcription of genes, thereby controlling the production of proteins essential for various cellular processes.
In this article, we will delve into the extraordinary world of gene transcription factors and unravel some mind-blowing facts about their functions and mechanisms. From their pivotal role in embryonic development to their involvement in diseases, these remarkable proteins have left scientists in awe. So, fasten your seatbelts as we embark on a journey to explore the intricate workings of gene transcription factors and discover why they are the superheroes of the biological realm.
Key Takeaways:
- Gene transcription factors are like the master controllers of a genetic orchestra, directing which genes are played and when. They can either turn genes on or off, influencing everything from development to disease.
- Transcription factors are like the conductors of a genetic symphony, orchestrating the expression of genes in response to environmental cues. They play a vital role in evolution and offer potential targets for treating diseases.
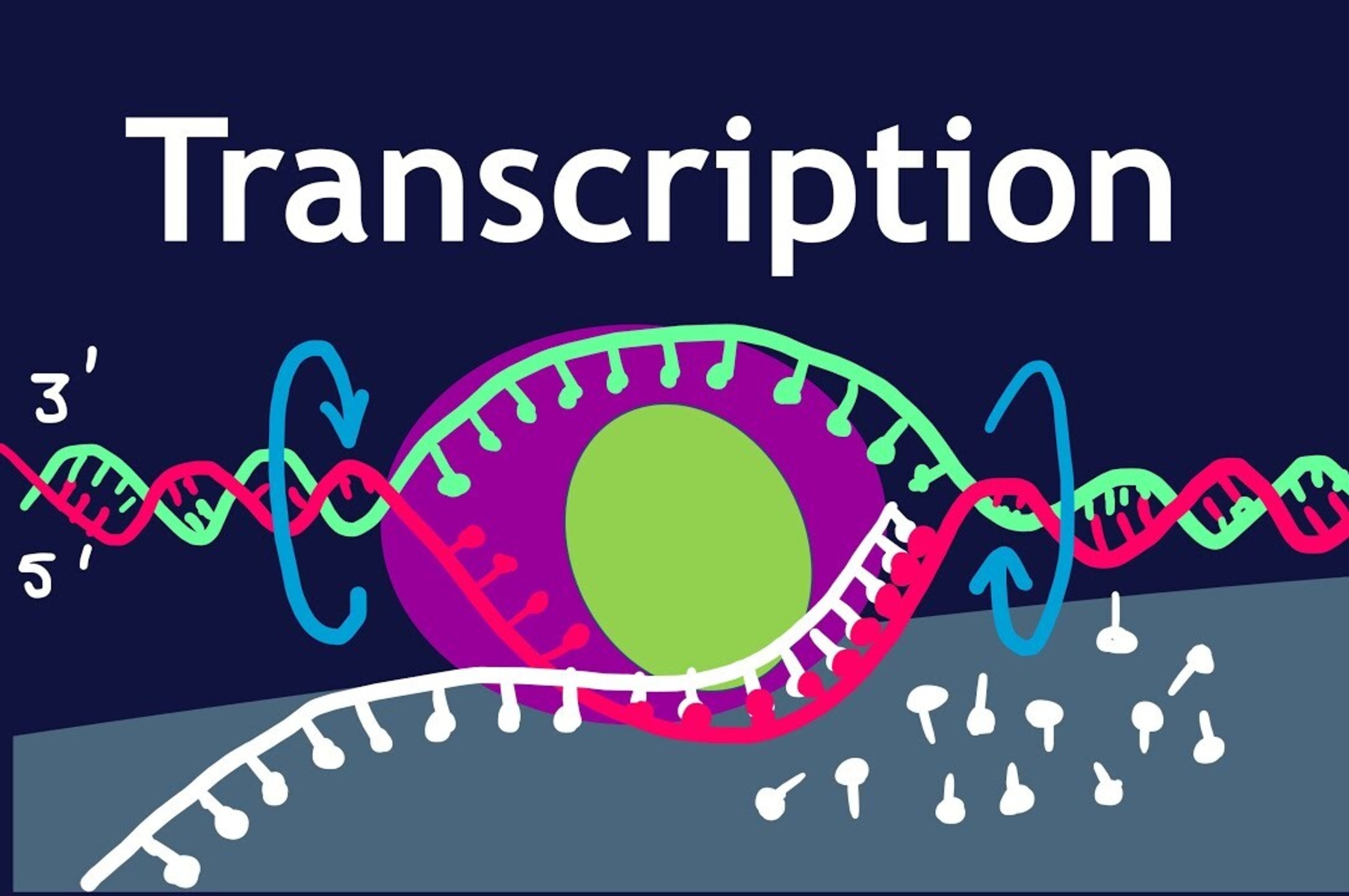
Gene Transcription Factors: The Master Regulators
Gene transcription factors are proteins that play a crucial role in the regulation of gene expression. They act as the master regulators by binding to specific regions on DNA and controlling the transcription process.
Diverse Functions of Transcription Factors
Transcription factors have diverse functions and can activate or repress gene expression. They are involved in crucial biological processes such as development, differentiation, and response to environmental signals.
The Three Main Types of Transcription Factors
There are three main types of transcription factors: activators, repressors, and enhancers. Activators promote transcription by binding to specific DNA sequences, while repressors inhibit transcription. Enhancers are DNA sequences that enhance the activity of transcription factors.
Transcription Factors Function in Complex Networks
Transcription factors do not work alone. They function in complex networks and interact with other proteins and regulatory elements to fine-tune gene expression. This allows for precise control and coordination of cellular processes.
Transcription Factors and Disease
Aberrant regulation of transcription factors can lead to various diseases. Mutations or dysregulation of transcription factors have been associated with cancer, developmental disorders, autoimmune diseases, and neurodegenerative diseases.
Coordinated Regulation by Transcription Factors
Transcription factors often work together in coordinated networks to regulate gene expression. This enables cells to respond to complex signals and ensures proper development and functioning of tissues and organs.
Environmental Influences on Transcription Factors
Transcription factors can be influenced by environmental factors such as stress, hormones, and external signals. They can activate or suppress gene expression in response to these cues, allowing organisms to adapt to changing conditions.
Transcription Factors and Evolution
Transcription factors have played a significant role in the evolution of species. Changes in transcription factor binding sites can lead to alterations in gene regulation, contributing to the diversity of organisms and their adaptation to different environments.
Transcription Factors as Therapeutic Targets
Given their crucial role in gene regulation, transcription factors have emerged as potential therapeutic targets for various diseases. By modulating their activity, it may be possible to treat or prevent diseases by restoring normal gene expression patterns.
These are just 9 extraordinary facts about gene transcription factors, but they represent the fascinating world of gene regulation that scientists continue to explore. Understanding the intricate mechanisms by which transcription factors control gene expression opens up new avenues for disease research and therapeutic interventions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, gene transcription factors play a critical role in regulating gene expression and ultimately shaping the development and functioning of living organisms. These remarkable proteins are able to bind to specific DNA sequences, thus influencing the process of transcription and controlling which genes are activated or repressed.
Through their ability to interact with other cellular components, gene transcription factors are involved in a wide range of biological processes, including embryonic development, immune response, and disease progression. Their multifaceted nature and intricate regulatory mechanisms make them an exciting area of study in the field of biology.
By delving deeper into the extraordinary facts about gene transcription factors, we gain a greater understanding of the complexity and elegance of molecular biology. Further research in this area will undoubtedly uncover even more fascinating insights, leading to breakthroughs in medicine, biotechnology, and our overall understanding of life itself.
FAQs
Q: What are gene transcription factors?
A: Gene transcription factors are proteins that bind to specific DNA sequences and regulate the process of transcription, controlling which genes are turned on or off.
Q: How do gene transcription factors work?
A: Gene transcription factors work by binding to specific DNA sequences known as enhancers or promoters, either activating or repressing the transcription of nearby genes.
Q: What is the significance of gene transcription factors?
A: Gene transcription factors play a crucial role in various biological processes, such as embryonic development, immune response, and disease progression. They help determine cell fate and regulate gene expression in response to internal and external signals.
Q: Can gene transcription factors be mutated?
A: Yes, mutations in gene transcription factors can lead to dysregulation of gene expression, resulting in a wide range of diseases and disorders, including cancer and developmental abnormalities.
Q: How many gene transcription factors are there?
A: It is estimated that the human genome encodes for about 1,600 to 2,000 different gene transcription factors.
Q: Are gene transcription factors specific to certain genes?
A: Yes, gene transcription factors exhibit specificity for certain DNA sequences, allowing them to selectively regulate the transcription of specific genes.
Q: Can gene transcription factors interact with other proteins?
A: Yes, gene transcription factors can interact with other proteins to form complexes that regulate gene expression. These interactions can modify the activity, stability, or localization of the transcription factors.
Q: Can gene transcription factors be targeted for therapeutic purposes?
A: Yes, targeting gene transcription factors holds potential for therapeutic interventions, as modulating their activity can lead to the upregulation or downregulation of specific genes involved in disease pathways.
Q: What is the latest research on gene transcription factors?
A: The latest research on gene transcription factors focuses on understanding their precise mechanisms of action, exploring their role in disease development, and developing novel strategies for targeted gene regulation and gene therapy.
Transcription factors, nature's master regulators, work tirelessly behind the scenes to orchestrate gene expression. Their fascinating roles don't end there; RNA polymerase, a key player in transcription, has its own set of captivating secrets waiting to be discovered. Gene regulation is an enigmatic process that keeps scientists on their toes, constantly unraveling new layers of complexity. Lastly, epigenetics adds another dimension to this intricate dance, revealing how our environment and experiences can shape our genetic destiny without altering the DNA sequence itself. Dive deeper into these topics and prepare to be amazed by the wonders of molecular biology.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
