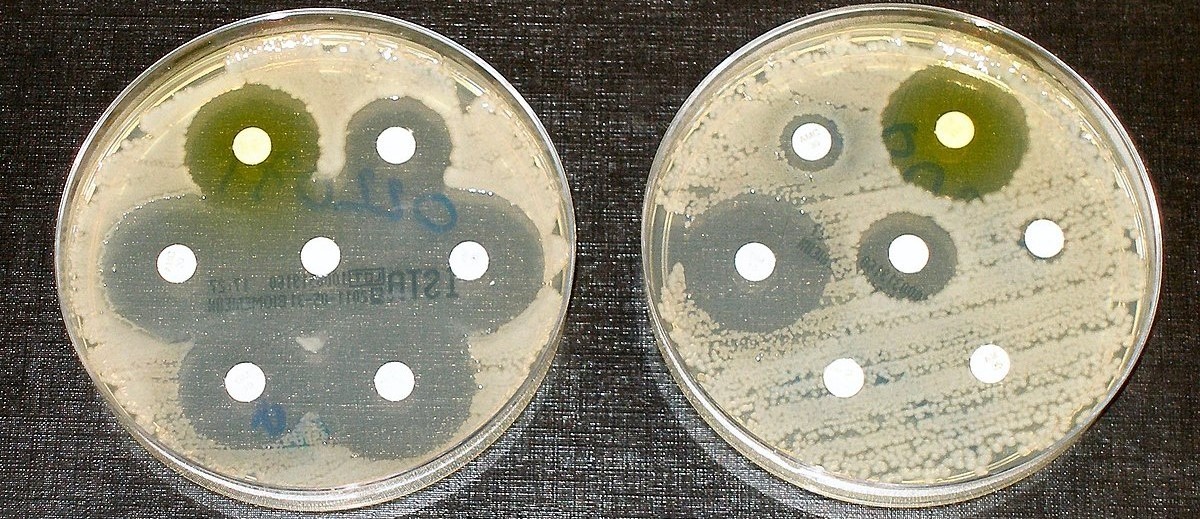
Antibiotics have undoubtedly revolutionized medicine by saving countless lives and effectively treating bacterial infections. However, a growing concern has arisen in recent years – antibiotic resistance. This phenomenon occurs when bacteria evolve and become immune to the effects of antibiotics, rendering these life-saving drugs ineffective. Antibiotic resistance poses a serious global threat, as it can lead to the spread of infections that are difficult or even impossible to treat.
In this article, we will delve into the enigmatic world of antibiotic resistance and explore 14 fascinating facts that shed light on this pressing issue. From the alarming rise in resistant infections to the contributing factors and potential consequences, we will unravel the complexities surrounding antibiotic resistance. So, let’s embark on this journey and gain a deeper understanding of the challenges we face in combating this increasingly urgent problem.
Key Takeaways:
- Antibiotic resistance is a serious global issue caused by overuse of antibiotics. It affects humans, animals, and healthcare systems, making it crucial to use antibiotics judiciously and develop new treatment strategies.
- Collaboration and public awareness are essential in combating antibiotic resistance. By working together and educating the public, we can reduce the misuse of antibiotics, develop rapid diagnostics, and implement effective treatment strategies.
Antibiotic resistance is a growing global concern
Antibiotic resistance refers to the ability of bacteria to withstand the drugs designed to kill them. It has become a significant worldwide issue, threatening the effectiveness of antibiotics in treating infections and diseases.
Antibiotic resistance can occur naturally or through human activities
Bacteria have the ability to naturally evolve and develop resistance to antibiotics over time. However, human activities such as the misuse and overuse of antibiotics in healthcare, agriculture, and animal husbandry have accelerated the emergence and spread of resistance.
Overuse of antibiotics contributes to resistance
Using antibiotics when they are not necessary or prescribed incorrectly can contribute to the development of antibiotic resistance. It is crucial to use antibiotics judiciously and only when they are truly needed to combat bacterial infections.
Antibiotic resistance affects both humans and animals
Antibiotic-resistant bacteria can be transmitted between humans and animals, posing a threat to public health. The use of antibiotics in veterinary medicine and livestock production can contribute to the development and spread of resistance.
Antibiotic resistance can lead to longer hospital stays and increased healthcare costs
When infections caused by antibiotic-resistant bacteria are difficult to treat, patients may require longer hospital stays, more intensive care, and costlier treatments. This places a significant burden on healthcare systems and individuals.
The development of new antibiotics is slow
Discovering and developing new antibiotics is a lengthy and complex process. It takes years of research and substantial investment to bring a new antibiotic to market. This slow pace contributes to the challenges of combating antibiotic resistance.
Antibiotic resistance is a threat to modern medicine
Without effective antibiotics, common medical procedures such as surgeries, cancer treatments, and organ transplants become riskier due to the increased chance of infection. Antibiotic resistance has the potential to unravel many advancements in modern medicine.
Combination therapies can help combat resistance
Using multiple antibiotics in combination can be an effective strategy to combat resistant bacteria. This approach targets different mechanisms of resistance and makes it harder for bacteria to develop resistance to multiple drugs simultaneously.
Antibiotic resistance can be spread through the environment
Antibiotic-resistant bacteria can enter the environment through contaminated soil, water, and food. This can contribute to the spread of resistance genes among different bacterial populations, making it more challenging to control.
Public awareness and education are essential in combating antibiotic resistance
Increasing public awareness about the proper use of antibiotics, the consequences of resistance, and the importance of infection prevention measures can play a significant role in mitigating the spread of antibiotic resistance.
Vaccination can help reduce the need for antibiotics
By preventing infections through vaccination, the need for antibiotics can be reduced. Vaccines help to protect against various diseases and reduce the reliance on antimicrobial drugs.
Developing rapid diagnostics is crucial
Rapid diagnostic tests that can quickly identify antibiotic-resistant infections are essential for guiding appropriate treatment. This enables healthcare providers to prescribe the most effective antibiotics and avoid unnecessary use.
Antibiotic stewardship programs are critical
Implementing antibiotic stewardship programs in healthcare settings can help optimize the use of antibiotics, ensuring they are prescribed only when necessary and at appropriate dosages. This helps to minimize the development and spread of resistance.
Collaboration is key in addressing antibiotic resistance
Addressing antibiotic resistance requires a collaborative effort among healthcare professionals, researchers, policymakers, and the general public. By working together, we can implement effective strategies to combat this global health challenge.
Conclusion
Antibiotic resistance is a pressing global issue that poses significant challenges in the field of medicine. As bacteria evolve and develop resistance to antibiotics, it becomes increasingly difficult to treat infections effectively. The rise of antibiotic-resistant strains has led to longer and more complicated treatment courses, increased healthcare costs, and higher mortality rates.
Understanding the enigmatic nature of antibiotic resistance is crucial in finding innovative solutions to combat this problem. The 14 facts mentioned in this article shed light on various aspects of antibiotic resistance, from the mechanisms of resistance to the role of human behavior in exacerbating the issue.
By recognizing these facts and spreading awareness, we can strive to implement better antibiotic stewardship, promote the development of novel antibiotics, and explore alternative approaches for treating bacterial infections. It is vital that we work together as a global community to address this challenge and ensure the effectiveness of antibiotics for future generations.
FAQs
Q: What is antibiotic resistance?
A: Antibiotic resistance refers to the ability of bacteria to survive and grow despite being exposed to antibiotics that would normally kill them.
Q: How does antibiotic resistance develop?
A: Antibiotic resistance can develop through various mechanisms, such as genetic mutations in bacteria or the acquisition of resistance genes from other bacteria.
Q: How does antibiotic misuse contribute to resistance?
A: Misusing antibiotics, such as not completing a full course of treatment or using them for viral infections, can contribute to the development of antibiotic resistance.
Q: Are bacteria the only ones that can become resistant to antibiotics?
A: No, other microbes like fungi and viruses can also develop resistance to antibiotics.
Q: Is antibiotic resistance a global problem?
A: Yes, antibiotic resistance is a global problem that affects people of all ages and in all countries.
Q: Can antibiotic resistance be reversed?
A: While some cases of antibiotic resistance can be reversed, it is becoming increasingly challenging as new resistant strains emerge.
Q: How can antibiotic resistance be prevented?
A: Antibiotic resistance can be prevented through responsible antibiotic use, proper infection control practices, and the development of new antibiotics.
Q: Are there any natural alternatives to antibiotics?
A: Yes, there are natural alternatives like probiotics, essential oils, and certain plant extracts that show promise in fighting bacterial infections.
Q: Can antibiotic resistance spread from person to person?
A: Yes, antibiotic-resistant bacteria can spread from person to person through direct contact, contaminated surfaces, or through the air.
Q: Are all bacteria resistant to antibiotics?
A: No, not all bacteria are resistant to antibiotics. However, the prevalence of antibiotic-resistant strains is increasing.
Q: Can antibiotic resistance be detected in a laboratory?
A: Yes, laboratories can perform tests to determine if bacteria are resistant to specific antibiotics.
Q: Can antibiotic resistance affect animal health too?
A: Yes, antibiotic resistance is a concern in veterinary medicine as well, as it can impact the health of animals and the safety of the food supply.
Q: Are there any new antibiotics being developed?
A: There is ongoing research and development of new antibiotics, but the process is complex and time-consuming.
Q: Is there anything individuals can do to help combat antibiotic resistance?
A: Yes, individuals can contribute by following prescribed antibiotic regimens, not sharing antibiotics, and practicing good hygiene to prevent infections.
Antibiotic resistance is a complex issue, but understanding its intricacies can help us combat this growing threat. If you're curious about the genetic underpinnings of microbes, the alarming rise of new infectious diseases, or how genes can be transferred between organisms, we've got you covered. Explore our articles on microbial genetics, emerging infectious diseases, and horizontal gene transfer to gain a deeper understanding of these fascinating topics and their implications for our health and well-being.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
