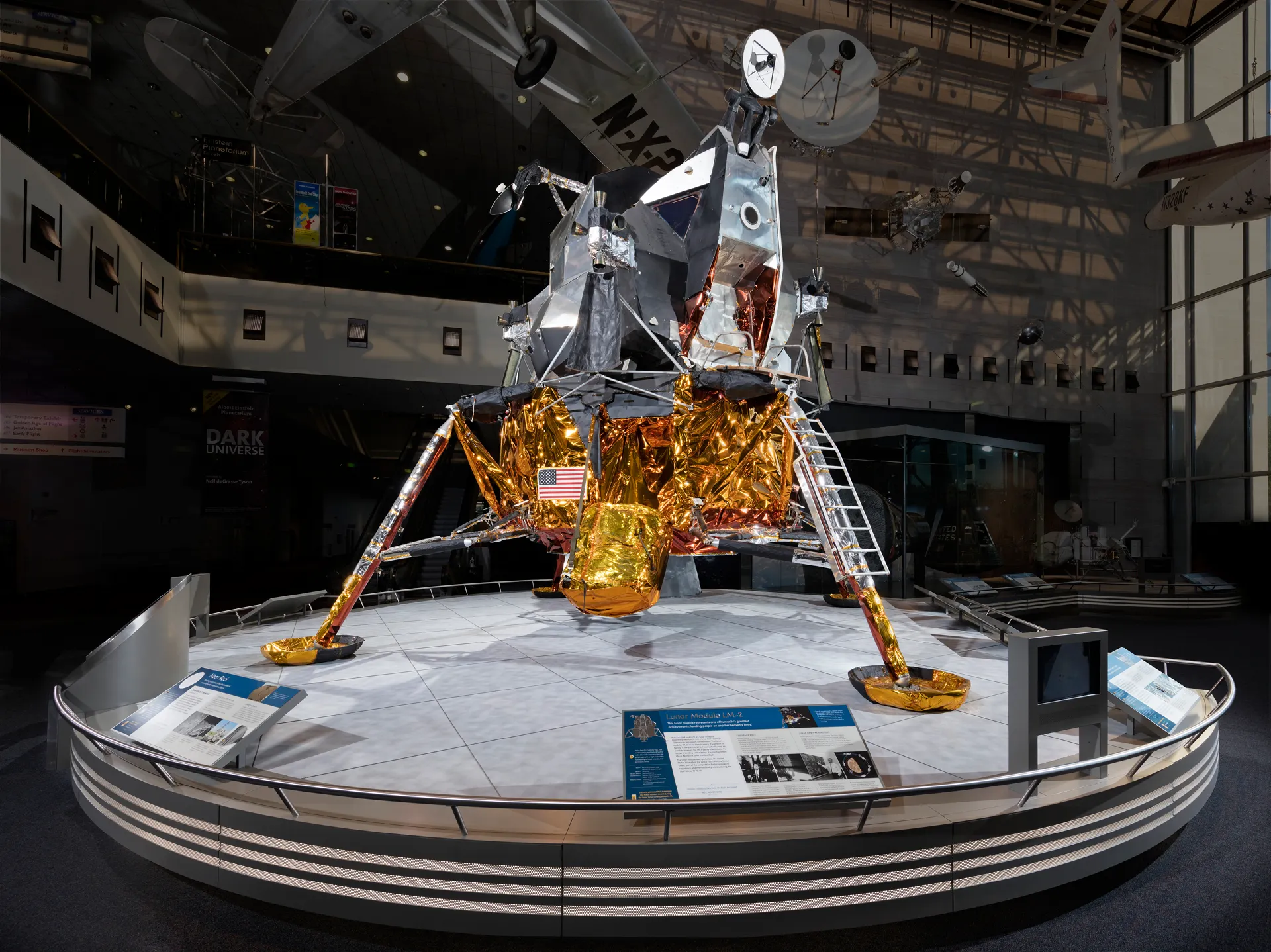
The Lunar Module, also known as the LM, played a critical role in humanity’s quest to conquer the moon. This ingenious spacecraft was specifically designed to transport astronauts from the Command Module down to the lunar surface and back. It was a marvel of engineering, pushing the boundaries of innovation and technology during the Apollo missions. With its distinct appearance and advanced capabilities, the Lunar Module continues to captivate our imagination even decades after its historic flights. In this article, we will delve into 16 astonishing facts about the Lunar Module that highlight its significance and shed light on the incredible achievements accomplished by the astronauts who used it as their gateway to the moon.
Key Takeaways:
- The Lunar Module was a crucial spacecraft that safely transported astronauts to and from the Moon’s surface during the Apollo missions, marking the first manned lunar landing in history.
- With its spider-like appearance, inflatable landing gear, and advanced navigation systems, the Lunar Module played a vital role in enabling astronauts to explore and conduct scientific research on the Moon.
Lunar Module’s Purpose
The primary purpose of the Lunar Module was to safely transport astronauts from the Command Module in lunar orbit to the Moon’s surface and back again.
Two-Part Design
The Lunar Module consisted of two parts: the descent stage, which brought the module to the lunar surface, and the ascent stage, which returned the astronauts to the Command Module.
First Manned Lunar Landing
The Lunar Module made history on July 20, 1969, when it carried Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin to the surface of the Moon during the Apollo 11 mission, marking the first manned lunar landing.
Spider-Like Appearance
The Lunar Module had a distinctive spider-like appearance, with four legs that provided stability during landing and takeoff.
Weight and Size
The Lunar Module stood at about 7 meters tall and weighed approximately 15,195 kilograms.
Propulsion System
The descent stage of the Lunar Module was powered by a rocket engine, while the ascent stage used a separate engine for lunar takeoff.
Lower Gravity on the Moon
The Lunar Module was designed to operate in the lower gravity environment of the Moon, allowing for easier takeoff and landing compared to Earth.
Inflatable Landing Gear
The landing gear of the Lunar Module was inflatable, providing shock absorption during landing to ensure a smooth touchdown on the lunar surface.
Modular Design
The Lunar Module had a modular design, allowing for various configurations depending on the mission objectives. This flexibility was essential for the success of the Apollo program.
Limited Space
Inside the Lunar Module, there was limited space for the astronauts. The descent stage served as a living and working area, while the ascent stage contained the controls and seats for the crew.
Lunar Rover Transportation
For the later Apollo missions, the Lunar Module was equipped with a folding ramp and docking port to enable the astronauts to unload and use the lunar rover for extended surface exploration.
Lunar Module Jettison
After returning to the Command Module, the Lunar Module was jettisoned and intentionally crashed into the Moon’s surface to provide seismic data for scientific research.
Precise Navigation
The Lunar Module had advanced navigation systems, including radar and guidance computers, to ensure accurate landing on the predetermined landing site.
Life Support Systems
The Lunar Module provided life support systems, including oxygen, temperature control, and waste management, to sustain the astronauts during their lunar surface activities.
Multiple Missions
A total of six manned lunar landings were accomplished with the Lunar Module between 1969 and 1972, each contributing valuable scientific data and expanding our knowledge of the Moon.
National Historic Landmark
The Lunar Module holds a special place in history and was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1984, recognizing its significant contribution to space exploration.
The Lunar Module remains an extraordinary engineering achievement and a symbol of human ingenuity and exploration. Its remarkable design and performance enabled the successful landing and exploration of the Moon by the Apollo astronauts, leaving an indelible mark on our understanding of our closest celestial neighbor.
Conclusion
From its incredible design and engineering to its historic Apollo missions, the Lunar Module continues to fascinate and inspire both space enthusiasts and the general public. Its important role in landing humans on the Moon cannot be overstated, and the impact of its legacy is still felt today. With its ability to withstand the harsh conditions of space and provide a safe haven for astronauts, the Lunar Module represents a monumental achievement in human space exploration.
As the gateway to the Moon, the Lunar Module opened a new era of discovery and sparked our collective imagination about what lies beyond our home planet. Its significance in space history will forever be remembered as a testament to the ingenuity and determination of the brilliant minds that made it possible. The Lunar Module truly is a marvel of human innovation and a symbol of our unwavering desire to explore the unknown.
FAQs
1. How did the Lunar Module work?
The Lunar Module consisted of two parts: the descent stage and the ascent stage. The descent stage provided propulsion and served as a landing gear, while the ascent stage housed the crew and was responsible for returning them back to the Command Module in lunar orbit.
2. How many Lunar Modules were built?
A total of 15 Lunar Modules were built and launched as part of the Apollo missions. These modules were instrumental in delivering astronauts safely to the Moon’s surface and played a crucial role in the success of the Apollo program.
3. How long did the Lunar Module missions last?
The duration of Lunar Module missions varied depending on the specific mission objectives. The Apollo 11 mission, which famously landed the first astronauts on the Moon, had a total elapsed time of approximately eight days. The actual time spent on the lunar surface by the crew was about 21.5 hours.
4. Can the Lunar Module still be seen today?
Several Lunar Modules are still visible today, as they were left behind on the Moon’s surface after the astronauts returned to Earth. These abandoned modules serve as a reminder of our incredible achievements in space exploration and act as silent witnesses to humanity’s first steps on another celestial body.
5. Were there any accidents or close calls involving the Lunar Module?
While there were some challenges and technical issues during the Apollo missions, no major accidents occurred specifically related to the Lunar Module. The modules were meticulously designed and extensively tested to ensure the safety of the crew during lunar landings and takeoffs.
6. What advancements in technology were made because of the Lunar Module?
The development of the Lunar Module pushed the boundaries of engineering and technology, leading to advancements in areas such as lightweight materials, propulsion systems, and life support systems. Many of the technologies and lessons learned from the Lunar Module program have been applied to subsequent space missions and continue to shape our understanding of space exploration.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
