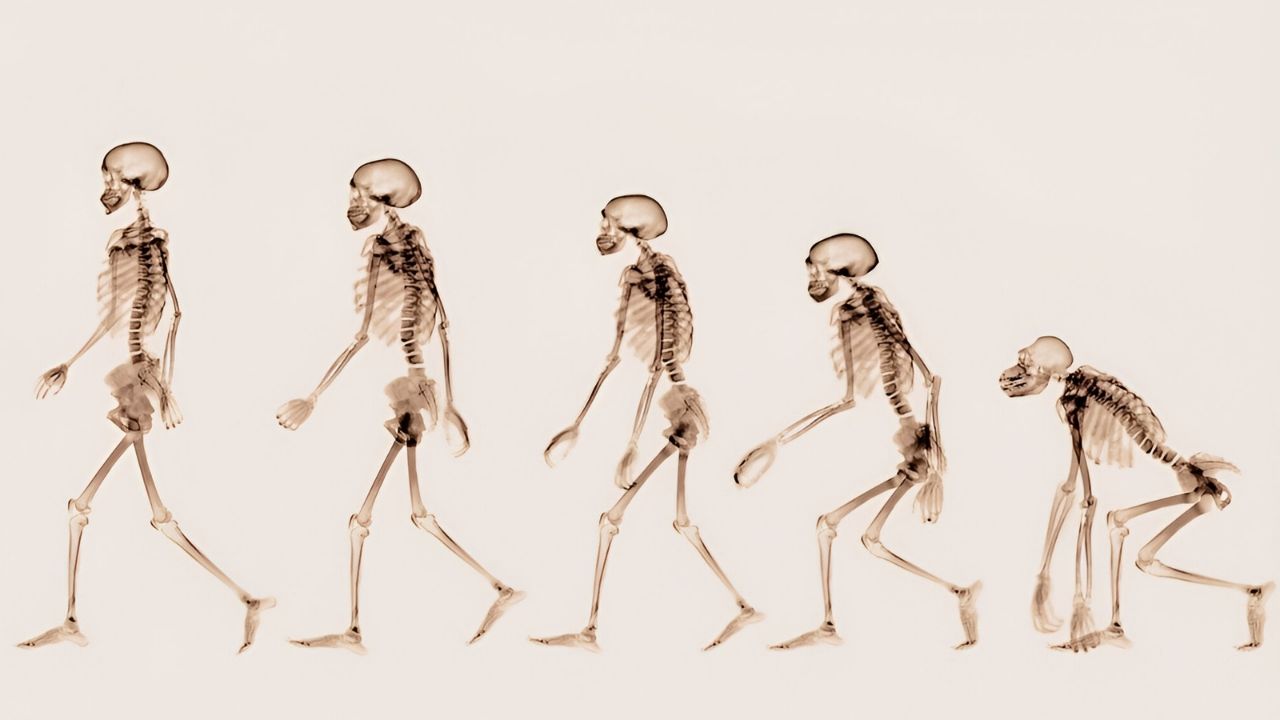
Bipedalism is what sets humans apart from most other animals. Walking on two legs might seem simple, but it's a complex trait with a fascinating history. Ever wondered why humans evolved to walk upright? Bipedalism offers many advantages, like freeing up hands for tool use and seeing over tall grass. However, it also comes with challenges, such as back pain and slower running speeds compared to four-legged animals. From ancient fossils to modern biomechanics, the study of bipedalism reveals much about our past and present. Ready to dive into 35 intriguing facts about walking on two legs? Let's get started!
Key Takeaways:
- Bipedalism, or walking on two legs, is a unique human trait that evolved over millions of years. It allows us to use our hands for tasks and has shaped our anatomy, culture, and society.
- While bipedalism offers many advantages, such as better vision and tool use, it also comes with challenges like back pain and childbirth difficulties. As humans continue to evolve, technology and medical interventions may help address these issues.
What is Bipedalism?
Bipedalism refers to walking on two legs. This form of movement is rare in the animal kingdom but has significant implications for those who practice it. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about bipedalism.
-
Humans are the only primates that are fully bipedal. While other primates like chimpanzees and gorillas can walk on two legs, they do so only occasionally. Humans, however, rely on bipedalism for everyday movement.
-
Bipedalism evolved over millions of years. The transition from quadrupedalism (walking on four legs) to bipedalism didn't happen overnight. It took millions of years of evolution for early hominins to develop this trait.
-
It frees up the hands. One of the biggest advantages of walking on two legs is that it allows the hands to be used for other tasks, such as carrying objects or using tools.
-
Bipedalism is energy efficient. Walking on two legs uses less energy than walking on all fours, which is beneficial for long-distance travel.
-
It changes the structure of the spine. Bipedalism requires a different spinal structure compared to quadrupedalism. The human spine has an S-shape that helps balance the body while walking upright.
Evolutionary Advantages of Bipedalism
Bipedalism offers several evolutionary advantages that have helped humans survive and thrive. Here are some key benefits.
-
Better field of vision. Walking upright allows for a higher vantage point, making it easier to spot predators and other dangers from a distance.
-
Improved thermoregulation. Bipedalism exposes less of the body to direct sunlight, helping to regulate body temperature more effectively.
-
Enhanced ability to carry food and offspring. Being able to walk on two legs means that early humans could carry food and their young more efficiently, aiding in survival.
-
Facilitates long-distance travel. Bipedalism is well-suited for covering long distances, which was crucial for early humans who needed to migrate for food and resources.
-
Allows for complex tool use. The ability to use hands for tasks other than walking enabled early humans to develop and use complex tools, giving them an edge over other species.
Anatomical Changes Due to Bipedalism
The shift to bipedalism brought about significant anatomical changes. These adaptations are evident in various parts of the human body.
-
Pelvic structure. The human pelvis is shorter and broader than that of quadrupedal animals, providing better support for internal organs while standing upright.
-
Leg length. Humans have longer legs relative to their body size compared to quadrupedal animals, aiding in efficient bipedal movement.
-
Foot arches. The human foot has arches that act as shock absorbers, making walking and running more efficient.
-
Knee joints. Human knees are designed to lock in place, providing stability while standing and walking.
-
Big toe alignment. Unlike other primates, the human big toe is aligned with the other toes, aiding in balance and forward movement.
Bipedalism in Other Species
While humans are the most well-known bipeds, other species also exhibit bipedal traits, albeit less frequently.
-
Birds. Many birds are bipedal, using their legs for walking and running while their wings are used for flight.
-
Kangaroos. These marsupials use bipedal hopping as their primary mode of locomotion, which is both energy-efficient and fast.
-
Dinosaurs. Many dinosaurs, including the famous Tyrannosaurus rex, were bipedal, using their two legs for walking and running.
-
Lizards. Some lizard species, like the basilisk lizard, can run on two legs, especially when escaping predators.
-
Apes. While not fully bipedal, apes like chimpanzees and bonobos can walk on two legs for short distances.
Challenges of Bipedalism
Despite its advantages, bipedalism also comes with its own set of challenges and drawbacks.
-
Back pain. The human spine is prone to issues like herniated discs and lower back pain due to the stresses of upright walking.
-
Knee problems. The knee joints are susceptible to injuries and conditions like arthritis because they bear much of the body's weight.
-
Childbirth difficulties. The shape of the human pelvis, adapted for bipedalism, makes childbirth more challenging compared to other primates.
-
Balance issues. Walking on two legs requires a fine-tuned sense of balance, making humans more prone to falls.
-
Slower speed. Compared to quadrupedal animals, humans are generally slower runners, which can be a disadvantage in certain situations.
Cultural and Social Impacts of Bipedalism
Bipedalism has also influenced human culture and social structures in various ways.
-
Development of tools. The ability to use hands for tasks other than walking led to the creation of tools, which played a crucial role in human development.
-
Social interactions. Standing upright allows for better eye contact and non-verbal communication, enhancing social interactions.
-
Art and writing. Free hands enabled early humans to create art and develop writing systems, which are fundamental to human culture.
-
Agriculture. Bipedalism facilitated the development of agriculture by allowing humans to use tools for farming.
-
Urbanization. The ability to walk long distances and carry goods contributed to the development of cities and complex societies.
Future of Bipedalism
As humans continue to evolve, bipedalism may also undergo changes. Here are some possibilities.
-
Technological aids. Advances in technology, such as exoskeletons, could enhance human mobility and reduce the physical strain of bipedalism.
-
Medical interventions. Improved medical treatments for conditions like arthritis and back pain could make bipedalism more sustainable.
-
Genetic evolution. Over time, humans may evolve to have even more efficient bipedal traits, reducing the drawbacks associated with upright walking.
-
Space travel. As humans explore other planets, bipedalism may adapt to different gravitational conditions, leading to new forms of movement.
-
Artificial intelligence. AI and robotics could lead to the development of bipedal robots that mimic human movement, opening up new possibilities for exploration and labor.
The Fascinating World of Bipedalism
Bipedalism, walking on two legs, has shaped human evolution in remarkable ways. This unique form of movement sets humans apart from most other animals. It allows for greater visibility over tall grass, freeing hands for tool use and carrying objects. Bipedalism also contributes to energy efficiency over long distances, crucial for early human survival.
Understanding bipedalism offers insights into our ancestors' lives and how they adapted to their environments. It highlights the intricate relationship between physical traits and survival strategies. From the structure of our spine to the alignment of our feet, every aspect of our anatomy plays a role in making bipedalism possible.
In essence, bipedalism is more than just a way of moving; it's a defining characteristic of what makes us human. Embracing this knowledge enriches our appreciation of human history and the incredible journey of evolution.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
