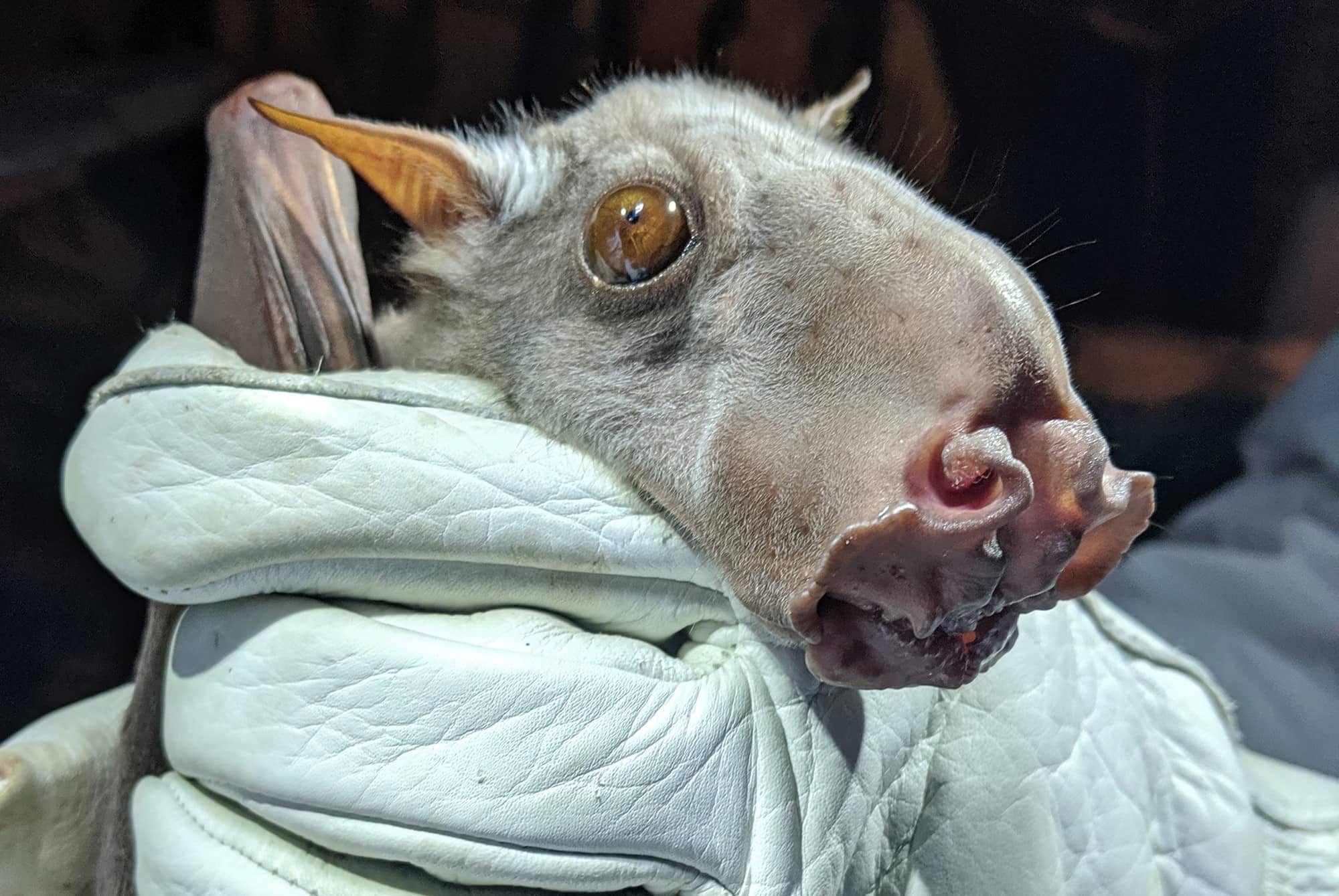
Did you know that the hammer-headed bat, also known as Hypsignathus monstrosus, is one of the most unique bats in the world? These fascinating creatures are native to the forests of Central and West Africa. Male hammer-headed bats are easily recognized by their large, hammer-shaped heads, which they use to produce loud honking calls to attract females. Unlike most bats, they have a wingspan that can reach up to three feet, making them the largest bat species in Africa. Their diet mainly consists of fruit, especially figs, but they occasionally snack on insects. Despite their unusual appearance, hammer-headed bats play a crucial role in their ecosystem by helping with seed dispersal. Ready to learn more about these incredible creatures? Let's dive into 35 amazing facts about hammer-headed bats!
Key Takeaways:
- The hammer-headed bat, native to Africa, has a unique appearance and behaviors, such as the male's hammer-shaped head used for vocalizations and their role in seed dispersal.
- Hammer-headed bats face threats like habitat loss and hunting, but conservation efforts are underway to protect these fascinating creatures and their important role in ecosystems.
Hammer-Headed Bat: An Overview
The hammer-headed bat, also known as the hammer-headed fruit bat, is a fascinating creature native to Africa. Known for its unique appearance and intriguing behaviors, this bat species has captivated the interest of scientists and nature enthusiasts alike. Here are some incredible facts about the hammer-headed bat.
Unique Physical Characteristics
The hammer-headed bat stands out due to its distinctive features. Let's explore what makes this bat so unique.
- The hammer-headed bat gets its name from the male's large, hammer-shaped head, which is used to amplify vocalizations.
- Males are significantly larger than females, with wingspans reaching up to 38 inches.
- Their fur is typically dark brown or gray, providing camouflage in their forest habitats.
- Males have large, inflatable throat pouches that help produce loud, resonant calls.
- Females, in contrast, have more typical bat-like heads and lack the throat pouches.
Habitat and Distribution
Understanding where these bats live can provide insight into their behaviors and adaptations.
- Hammer-headed bats are primarily found in the tropical rainforests of Central and West Africa.
- They prefer habitats near rivers and swamps, where fruit is abundant.
- These bats roost in trees, often hanging upside down from branches.
- They are known to form large colonies, sometimes consisting of hundreds of individuals.
- Seasonal migrations occur in response to food availability, with bats traveling long distances.
Diet and Feeding Habits
The hammer-headed bat's diet is as interesting as its appearance. Here's what they eat and how they find their food.
- These bats are frugivores, primarily feeding on fruits like figs, bananas, and mangoes.
- They use their keen sense of smell to locate ripe fruit from great distances.
- Hammer-headed bats play a crucial role in seed dispersal, helping to maintain healthy forest ecosystems.
- Occasionally, they may consume nectar and pollen, contributing to pollination.
- Their strong jaws and sharp teeth allow them to easily tear through tough fruit skins.
Reproduction and Lifespan
Reproduction in hammer-headed bats involves unique behaviors and strategies. Let's delve into their mating rituals and life cycle.
- Males attract females through loud, honking calls during the breeding season.
- These calls can be heard up to a mile away, showcasing the male's strength and fitness.
- Females give birth to a single pup after a gestation period of about six months.
- Pups are born with their eyes open and are fully furred, ready to cling to their mothers.
- The average lifespan of a hammer-headed bat in the wild is around 20 years.
Social Behavior and Communication
Hammer-headed bats exhibit fascinating social behaviors and communication methods. Here's how they interact with each other.
- Males establish territories and defend them aggressively during the breeding season.
- Vocalizations play a key role in communication, with different calls used for mating, warning, and social interactions.
- These bats are known to groom each other, strengthening social bonds within colonies.
- They use echolocation to navigate and find food in the dark, emitting high-pitched sounds that bounce off objects.
- Social hierarchies exist within colonies, with dominant males often having better access to resources.
Conservation Status and Threats
Despite their resilience, hammer-headed bats face several threats. Understanding these challenges is crucial for their conservation.
- Habitat loss due to deforestation is a significant threat to hammer-headed bats.
- Hunting for bushmeat poses another risk, as these bats are sometimes targeted by local communities.
- Climate change impacts their food sources and roosting sites, further endangering their populations.
- Conservation efforts include habitat protection and raising awareness about the importance of bats in ecosystems.
- Hammer-headed bats are currently listed as "Least Concern" by the IUCN, but ongoing threats could change their status.
Interesting Tidbits
Here are some additional fascinating facts about hammer-headed bats that highlight their uniqueness.
- Hammer-headed bats are the largest bats in Africa, with males weighing up to 16 ounces.
- They are also known as "big-lipped bats" due to their prominent lips used in vocalizations.
- These bats have a slow reproductive rate, with females typically giving birth only once a year.
- Hammer-headed bats are nocturnal, emerging at dusk to forage for food.
- They have few natural predators, with birds of prey and large snakes being their primary threats.
Final Thoughts on Hammer-Headed Bats
Hammer-headed bats are fascinating creatures with unique features and behaviors. Their distinctive head shape, large size, and nocturnal habits make them stand out in the animal kingdom. These bats play a crucial role in their ecosystems, helping with pollination and seed dispersal. Despite their somewhat eerie appearance, they are vital for maintaining the balance of their habitats.
Understanding these bats better can help in conservation efforts and biodiversity preservation. They face threats from habitat loss and hunting, making it important to raise awareness about their significance. By learning more about hammer-headed bats, we can appreciate the diversity of life on our planet and the intricate roles each species plays.
Next time you think of bats, remember the hammer-headed bat and its unique contributions to nature. They truly are remarkable creatures worth protecting.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.