What is an electrical network? An electrical network is a collection of interconnected electrical components designed to transfer electric energy. These components can include resistors, capacitors, inductors, switches, and power sources. Electrical networks are the backbone of modern technology, powering everything from household appliances to complex industrial machinery. Understanding these networks helps us grasp how electricity flows and how devices function. Whether you're a student, a hobbyist, or just curious, learning about electrical networks can be both fascinating and practical. Ready to dive into the world of circuits and currents? Let's get started!
What Are Electrical Networks?
Electrical networks are systems that connect various electrical components to perform a specific function. They can be simple, like a flashlight circuit, or complex, like the power grid that supplies electricity to entire cities.
- Electrical networks consist of interconnected electrical components like resistors, capacitors, inductors, and power sources.
- Power grids are large-scale electrical networks that distribute electricity from power plants to homes and businesses.
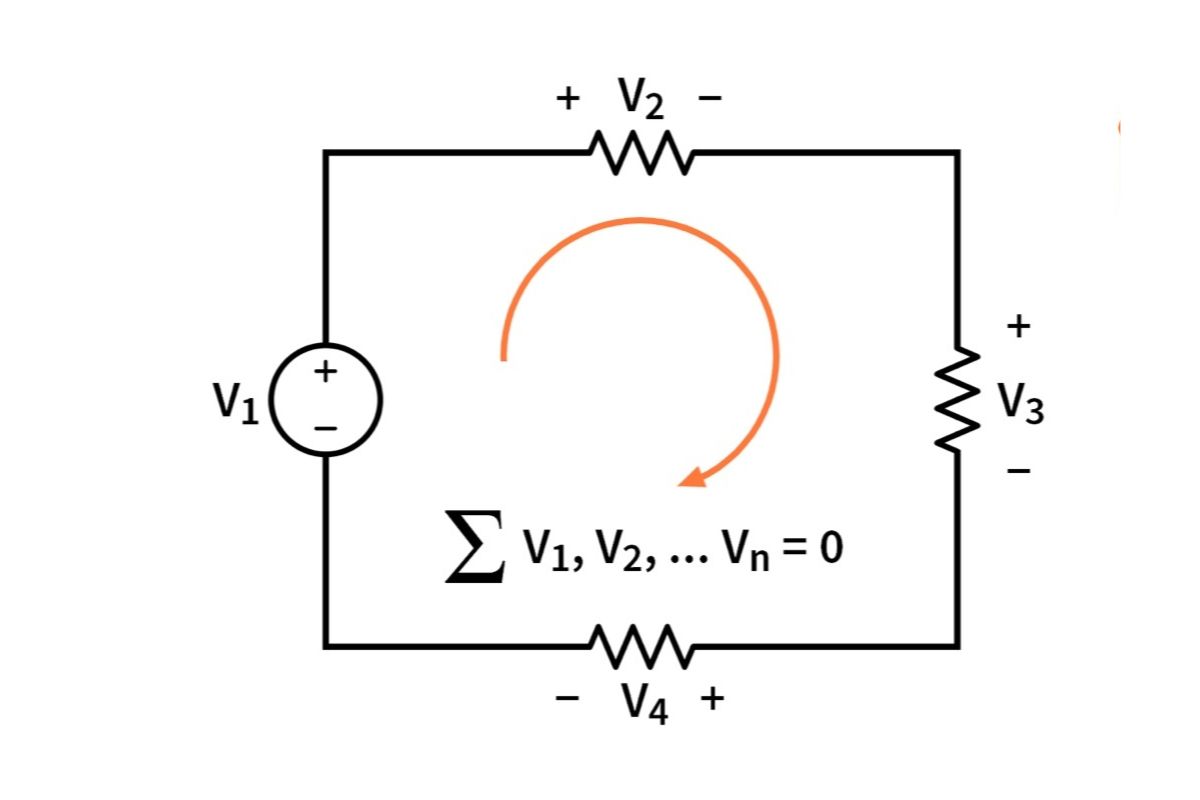
- Circuit diagrams are used to represent electrical networks visually, showing how components are connected.
- Nodes in an electrical network are points where two or more components are connected.
- Branches are the paths between nodes that contain electrical components.
Types of Electrical Networks
Different types of electrical networks serve various purposes. Understanding these types helps in designing and troubleshooting electrical systems.
- Series circuits have components connected end-to-end, so the same current flows through each component.
- Parallel circuits have components connected across the same two points, allowing current to split and flow through multiple paths.
- Combination circuits include both series and parallel connections within the same network.
- AC (Alternating Current) networks use current that changes direction periodically, commonly used in household power supplies.
- DC (Direct Current) networks use current that flows in one direction, often found in batteries and electronic devices.
Components of Electrical Networks
Each component in an electrical network plays a specific role. Knowing these components is crucial for understanding how electrical networks function.
- Resistors limit the flow of electric current, protecting other components from damage.
- Capacitors store and release electrical energy, used in filtering and energy storage applications.
- Inductors store energy in a magnetic field when electrical current flows through them, used in transformers and filters.
- Diodes allow current to flow in one direction only, used for rectification and signal modulation.
- Transistors act as switches or amplifiers, essential in modern electronic devices.
Electrical Network Analysis
Analyzing electrical networks helps engineers design efficient systems and troubleshoot issues. Various methods and tools are used for this purpose.
- Ohm's Law relates voltage, current, and resistance in a circuit, fundamental for network analysis.
- Kirchhoff's Laws include Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) and Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL), essential for analyzing complex networks.
- Thevenin's Theorem simplifies a network to a single voltage source and series resistance, making analysis easier.
- Norton's Theorem simplifies a network to a single current source and parallel resistance.
- Superposition Theorem states that the voltage or current in a linear network with multiple sources is the sum of the voltages or currents from each source acting alone.
Applications of Electrical Networks
Electrical networks are used in various applications, from simple household devices to complex industrial systems. Understanding these applications highlights the importance of electrical networks in daily life.
- Power distribution networks deliver electricity from power plants to consumers, ensuring reliable power supply.
- Communication systems use electrical networks to transmit data over long distances, essential for telephones and the internet.
- Automotive electrical systems control various functions in vehicles, including lighting, ignition, and infotainment.
- Home appliances like refrigerators, washing machines, and microwaves rely on electrical networks for operation.
- Industrial automation uses electrical networks to control machinery and processes, improving efficiency and productivity.
Safety in Electrical Networks
Safety is paramount when working with electrical networks. Proper precautions and safety measures can prevent accidents and injuries.
- Circuit breakers protect electrical networks by interrupting the flow of current in case of overload or short circuit.
- Fuses provide overcurrent protection by melting and breaking the circuit when current exceeds a safe level.
- Grounding ensures that excess electrical energy is safely dissipated into the earth, preventing electric shocks.
- Insulation prevents accidental contact with live wires, reducing the risk of electric shock.
- Personal protective equipment (PPE) like gloves and goggles protect individuals working with electrical networks.
Innovations in Electrical Networks
Advancements in technology have led to innovations in electrical networks, improving efficiency and reliability.
- Smart grids use digital technology to monitor and manage electricity distribution, enhancing reliability and efficiency.
- Renewable energy integration allows electrical networks to incorporate energy from sources like solar and wind, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- Energy storage systems like batteries and supercapacitors store excess energy for later use, improving grid stability.
- Microgrids are small-scale electrical networks that can operate independently or in conjunction with the main grid, providing resilience during outages.
- Wireless power transfer technology allows electrical energy to be transmitted without wires, enabling new applications like wireless charging.
Challenges in Electrical Networks
Despite their importance, electrical networks face several challenges that need to be addressed to ensure reliable operation.
- Aging infrastructure in many power grids requires upgrades and maintenance to prevent failures and outages.
- Cybersecurity threats pose risks to modern electrical networks, necessitating robust security measures.
- Load balancing ensures that electricity supply matches demand, preventing blackouts and brownouts.
- Power quality issues like voltage sags and surges can damage sensitive equipment, requiring mitigation measures.
- Environmental impact of electrical networks, including greenhouse gas emissions from power generation, needs to be minimized through sustainable practices.
The Power of Electrical Networks
Electrical networks shape our world. From powering homes to running industries, they’re the backbone of modern life. Understanding their complexity helps us appreciate the convenience they bring. These networks aren’t just wires and poles; they’re intricate systems ensuring our gadgets work, our lights stay on, and our cities function smoothly.
Knowing these 40 facts gives you a glimpse into the marvels of electrical engineering. It’s fascinating how something so essential often goes unnoticed. Next time you flip a switch or charge your phone, remember the vast network making it possible.
Electrical networks are evolving, becoming smarter and more efficient. As technology advances, so will these systems, continuing to power our lives in ways we can’t yet imagine. Stay curious, stay informed, and never underestimate the power behind the plug.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
