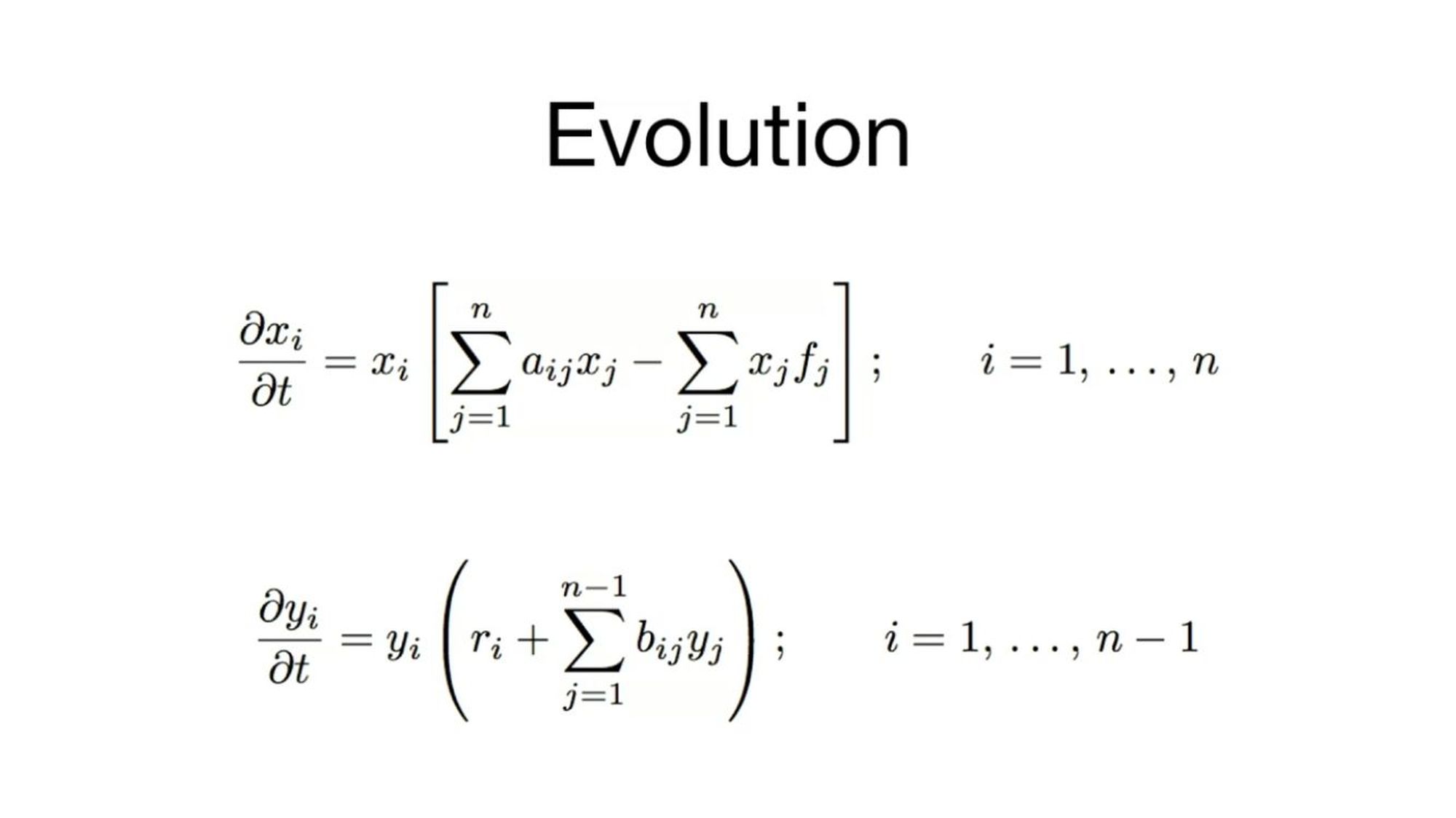
Evolution equations are mathematical expressions that describe how a system changes over time. These equations are crucial in fields like physics, biology, and economics. Ever wondered how scientists predict weather patterns or model population growth? They use evolution equations! These equations help us understand everything from the spread of diseases to the behavior of financial markets. By studying them, we can make better decisions and improve our world. Ready to dive into the fascinating world of evolution equations? Let's explore 37 intriguing facts that will expand your understanding and spark your curiosity!
What Are Evolution Equations?
Evolution equations describe how a system changes over time. They are used in physics, biology, economics, and many other fields. Here are some fascinating facts about evolution equations:
-
Evolution equations can be ordinary differential equations (ODEs) or partial differential equations (PDEs).
-
ODEs involve functions of a single variable and their derivatives, while PDEs involve functions of multiple variables and their partial derivatives.
-
The heat equation, a type of PDE, models how heat diffuses through a medium over time.
-
The Schrödinger equation, another PDE, describes how the quantum state of a physical system changes over time.
-
In biology, evolution equations can model population dynamics, such as how populations of species grow or decline.
Historical Background of Evolution Equations
Understanding the history behind these equations helps appreciate their development and significance.
-
Isaac Newton's laws of motion, formulated in the 17th century, are among the earliest examples of evolution equations.
-
The 18th-century mathematician Leonhard Euler made significant contributions to the development of ODEs.
-
Joseph Fourier introduced the heat equation in the early 19th century, revolutionizing the study of heat transfer.
-
The Schrödinger equation was formulated by Erwin Schrödinger in 1925, laying the foundation for quantum mechanics.
-
The Lotka-Volterra equations, developed in the 1920s, model predator-prey interactions in ecological systems.
Applications in Physics
Evolution equations play a crucial role in understanding physical phenomena.
-
The wave equation describes how waves, such as sound or light waves, propagate through a medium.
-
Maxwell's equations, a set of PDEs, describe how electric and magnetic fields evolve over time.
-
The Navier-Stokes equations model the flow of fluids, such as water or air.
-
The Einstein field equations, part of general relativity, describe how spacetime curvature evolves in the presence of matter and energy.
-
The diffusion equation models how particles spread out over time, such as ink diffusing in water.
Applications in Biology
Biological systems also rely on evolution equations for modeling and analysis.
-
The logistic growth equation models population growth with a carrying capacity, beyond which growth slows down.
-
The SIR model, a set of ODEs, describes the spread of infectious diseases by categorizing individuals as susceptible, infected, or recovered.
-
The chemostat model uses ODEs to describe the growth of microorganisms in a controlled environment with a constant nutrient supply.
-
Reaction-diffusion equations model how chemical substances interact and spread in biological systems.
-
The Hodgkin-Huxley model, a set of PDEs, describes how electrical signals propagate along neurons.
Applications in Economics
Economics also benefits from the use of evolution equations to model dynamic systems.
-
The Black-Scholes equation, a PDE, models the pricing of financial options over time.
-
The Solow-Swan model uses ODEs to describe long-term economic growth by considering capital accumulation, labor, and technological progress.
-
The Lotka-Volterra equations can also model competitive interactions between firms in an economic market.
-
The IS-LM model, a set of ODEs, describes the interaction between the real economy (investment-savings) and the monetary economy (liquidity preference-money supply).
-
The Ramsey-Cass-Koopmans model uses ODEs to analyze optimal savings and consumption over time.
Mathematical Techniques for Solving Evolution Equations
Various mathematical methods are used to solve evolution equations, each with its own strengths and limitations.
-
Analytical methods involve finding exact solutions using algebraic or calculus-based techniques.
-
Numerical methods, such as finite difference or finite element methods, approximate solutions using computational algorithms.
-
Perturbation methods involve finding an approximate solution by expanding around a known solution.
-
Transform methods, such as the Laplace or Fourier transform, convert differential equations into algebraic equations that are easier to solve.
-
Variational methods involve finding solutions by minimizing or maximizing a functional, often used in physics and engineering.
Challenges and Open Problems
Despite their widespread use, evolution equations present several challenges and open problems.
-
Nonlinear evolution equations are often difficult to solve due to their complexity and lack of superposition principle.
-
Stability analysis involves determining whether small perturbations in initial conditions lead to large changes in the solution over time.
-
Bifurcation theory studies how the qualitative behavior of solutions changes as parameters in the equation are varied.
-
Chaos theory explores how deterministic evolution equations can produce seemingly random behavior.
-
Inverse problems involve determining the parameters or inputs of an evolution equation from observed data, often an ill-posed problem.
Future Directions
The study of evolution equations continues to evolve, with new developments and applications emerging.
-
Machine learning and artificial intelligence are being used to develop new methods for solving evolution equations.
-
Multiscale modeling involves coupling evolution equations at different scales, such as molecular and macroscopic levels, to better understand complex systems.
Final Thoughts on Evolution Equations
Evolution equations play a crucial role in understanding how systems change over time. These mathematical tools help scientists and researchers predict behaviors in fields like physics, biology, and economics. From the heat equation to the wave equation, each type offers unique insights into dynamic processes. Knowing these equations can deepen your appreciation for the natural world and the laws governing it. Whether you're a student, a professional, or just curious, grasping the basics of evolution equations can be incredibly rewarding. They not only solve complex problems but also open doors to new discoveries. So, next time you encounter a changing system, remember the power of these equations. They’re more than just numbers and symbols; they’re keys to unlocking the mysteries of our universe. Keep exploring, keep questioning, and let the equations guide your way.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
