Continuous Theory is a branch of mathematical logic that extends classical model theory to structures with a continuous domain. But what exactly does that mean? Imagine trying to describe the behavior of real numbers or functions in a way that’s more flexible than traditional logic. This theory helps mathematicians and scientists understand complex systems like quantum mechanics, probability, and even certain areas of computer science. Why should you care? Because it provides tools for solving problems that discrete mathematics can't handle. From understanding the behavior of fluids to optimizing algorithms, continuous theory offers a unique lens through which to view the world. Ready to dive into some intriguing facts? Let's get started!
What is Continuous Theory?
Continuous theory is a branch of mathematics that deals with continuous variables and functions. It plays a crucial role in various fields such as physics, engineering, and economics. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about this intriguing subject.
-
Continuous Variables: Unlike discrete variables, continuous variables can take any value within a given range. This makes them essential for modeling real-world phenomena.
-
Calculus Foundation: Continuous theory forms the basis of calculus, which is used to study change and motion. Calculus is divided into differential and integral calculus.
-
Real Numbers: Continuous theory relies heavily on real numbers, which include all rational and irrational numbers. Real numbers are essential for measuring continuous quantities.
-
Limits: The concept of limits is fundamental in continuous theory. Limits help in understanding the behavior of functions as they approach a specific point.
-
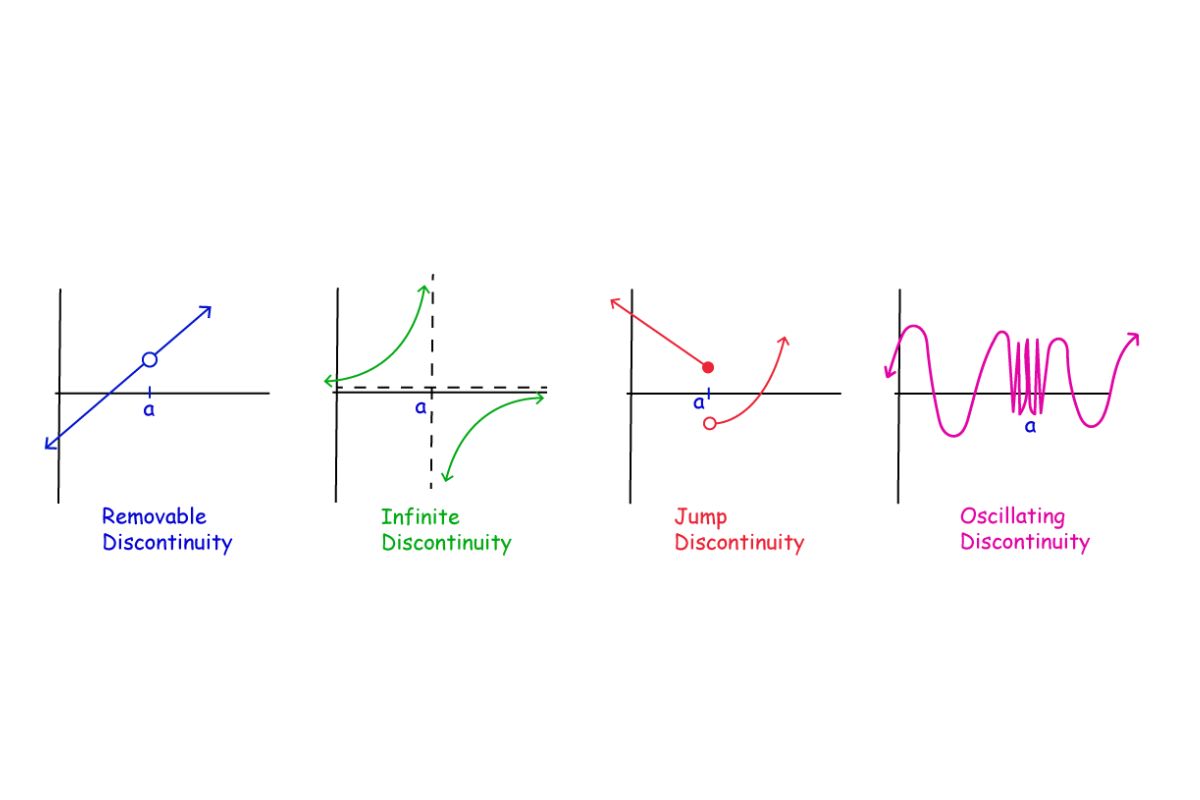
Continuity: A function is continuous if it does not have any breaks, jumps, or holes. This property is crucial for ensuring smooth transitions in mathematical models.
Applications in Physics
Continuous theory is widely used in physics to describe natural phenomena. Here are some interesting facts about its applications in this field.
-
Motion Equations: Newton's laws of motion are based on continuous theory. They describe how objects move and interact with forces.
-
Wave Functions: In quantum mechanics, wave functions are continuous functions that describe the probability of finding a particle in a particular state.
-
Electromagnetic Fields: Maxwell's equations, which describe electromagnetic fields, are based on continuous theory. These equations are fundamental to understanding light and radio waves.
-
Thermodynamics: Continuous theory helps in modeling the behavior of gases and liquids in thermodynamics. It is used to derive equations like the ideal gas law.
-
Relativity: Einstein's theory of relativity uses continuous mathematics to describe the curvature of spacetime and the behavior of objects in strong gravitational fields.
Engineering and Technology
Engineering relies heavily on continuous theory for designing and analyzing systems. Here are some key facts about its role in this field.
-
Control Systems: Continuous theory is used to design control systems that regulate the behavior of machines and processes.
-
Signal Processing: Engineers use continuous mathematics to analyze and process signals in communication systems.
-
Structural Analysis: Continuous theory helps in analyzing the stress and strain in structures like bridges and buildings.
-
Fluid Dynamics: Engineers use continuous mathematics to model the flow of fluids in pipes and open channels.
-
Heat Transfer: Continuous theory is essential for understanding how heat is transferred in different materials.
Economics and Finance
Continuous theory also finds applications in economics and finance. Here are some intriguing facts about its use in these fields.
-
Supply and Demand: Economists use continuous functions to model supply and demand curves.
-
Optimization: Continuous mathematics helps in finding the optimal solutions for various economic problems.
-
Risk Management: Financial analysts use continuous theory to model and manage risks in investments.
-
Market Analysis: Continuous functions are used to analyze trends and patterns in financial markets.
-
Pricing Models: Continuous mathematics is used to develop pricing models for options and other financial derivatives.
Biological Sciences
Continuous theory is not limited to physical sciences and engineering; it also plays a role in biological sciences. Here are some interesting facts about its applications in this field.
-
Population Dynamics: Biologists use continuous models to study the growth and decline of populations.
-
Epidemiology: Continuous theory helps in modeling the spread of diseases and the effectiveness of interventions.
-
Neural Networks: Continuous mathematics is used to model the behavior of neural networks in the brain.
-
Genetics: Continuous functions help in understanding the inheritance patterns of genes.
-
Ecology: Continuous theory is used to model the interactions between different species in an ecosystem.
Computer Science
Continuous theory also has applications in computer science. Here are some key facts about its role in this field.
-
Algorithms: Continuous mathematics is used to develop algorithms for solving complex problems.
-
Machine Learning: Continuous functions are essential for training machine learning models.
-
Graphics: Computer graphics rely on continuous mathematics to render smooth images and animations.
-
Cryptography: Continuous theory helps in developing secure encryption algorithms.
-
Data Analysis: Continuous mathematics is used to analyze large datasets and extract meaningful insights.
Final Thoughts on Continuous Theory
Continuous theory is a fascinating subject that bridges many areas of science and mathematics. From calculus to physics, it plays a crucial role in understanding how things change over time. This theory helps explain natural phenomena, like how planets orbit the sun or how heat spreads through a material. It’s not just for scientists, though. Engineers use it to design everything from bridges to computer algorithms. Even economists rely on continuous theory to predict market trends. So, whether you’re solving a math problem or figuring out how to make your car more fuel-efficient, continuous theory is at work. Understanding its basics can give you a new perspective on the world around you. Keep exploring, keep questioning, and you’ll find that continuous theory is a key to unlocking many of life’s mysteries.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
