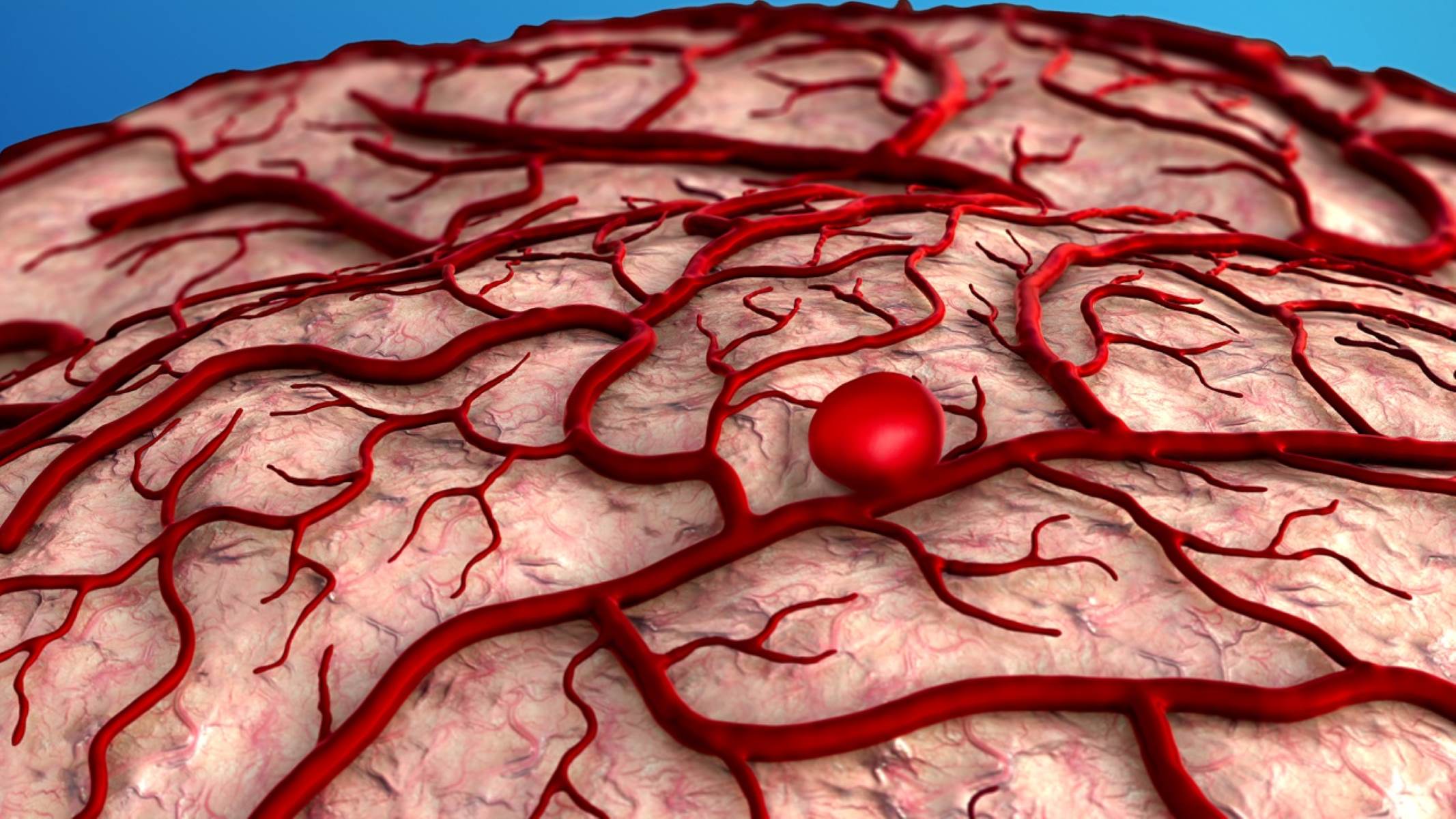
What exactly is an aneurysm? An aneurysm is a bulge in a blood vessel caused by a weakness in the blood vessel wall. This bulge can occur in various parts of the body, but it's most commonly found in the brain and aorta. Why should you care? Because if an aneurysm bursts, it can lead to life-threatening internal bleeding. Who is at risk? Factors like high blood pressure, smoking, and family history can increase your chances. How can you prevent it? Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, regular check-ups, and managing stress can help. Want to know more? Keep reading to uncover 50 facts about aneurysms that could save your life.
What is an Aneurysm?
An aneurysm is a bulge or ballooning in a blood vessel caused by a weakness in the vessel wall. They can occur in any blood vessel but are most common in the aorta, brain, legs, and spleen.
- An aneurysm can develop in any blood vessel in the body.
- The most common locations for aneurysms are the aorta and the brain.
- Aneurysms can be congenital, meaning present at birth.
- High blood pressure is a significant risk factor for developing an aneurysm.
- Smoking increases the risk of aneurysms due to its impact on blood vessel health.
Types of Aneurysms
There are several types of aneurysms, each with unique characteristics and risks. Understanding these types can help in identifying and managing them effectively.
- Aortic aneurysms occur in the aorta, the main artery carrying blood from the heart.
- Cerebral aneurysms happen in the brain and can lead to strokes if they rupture.
- Peripheral aneurysms occur in arteries other than the aorta and brain, like those in the legs.
- Ventricular aneurysms form in the heart's ventricles, often after a heart attack.
- Splenic artery aneurysms are found in the artery that supplies blood to the spleen.
Symptoms of Aneurysms
Symptoms can vary depending on the aneurysm's location and size. Some aneurysms may not show symptoms until they rupture.
- Small aneurysms often have no symptoms.
- Aortic aneurysms may cause back pain or a pulsating feeling in the abdomen.
- Cerebral aneurysms can cause headaches, vision problems, or neck pain.
- Peripheral aneurysms might cause pain or swelling in the affected limb.
- Sudden, severe pain can indicate a ruptured aneurysm, which is a medical emergency.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the causes and risk factors can help in preventing aneurysms or catching them early.
- Genetic factors can play a role in the development of aneurysms.
- High cholesterol levels can contribute to the weakening of blood vessel walls.
- Chronic high blood pressure puts extra stress on blood vessels.
- Infections can sometimes lead to aneurysms, particularly in the aorta.
- Trauma or injury to blood vessels can cause aneurysms.
Diagnosis of Aneurysms
Early detection is crucial for managing aneurysms and preventing complications. Various diagnostic tools are used to identify aneurysms.
- Ultrasound is commonly used to detect aortic aneurysms.
- CT scans provide detailed images of blood vessels and can identify aneurysms.
- MRI scans offer a non-invasive way to detect cerebral aneurysms.
- Angiography involves injecting a dye into blood vessels to make them visible on X-rays.
- Regular screenings are recommended for individuals with a family history of aneurysms.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the aneurysm's size, location, and risk of rupture. Options range from monitoring to surgical intervention.
- Watchful waiting is often recommended for small, asymptomatic aneurysms.
- Medications can help manage risk factors like high blood pressure and cholesterol.
- Endovascular repair involves inserting a stent to reinforce the blood vessel wall.
- Open surgery may be necessary for large or ruptured aneurysms.
- Lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking and maintaining a healthy diet, can reduce risk.
Complications of Aneurysms
Aneurysms can lead to severe complications if not managed properly. Understanding these risks can highlight the importance of early detection and treatment.
- A ruptured aneurysm can cause life-threatening internal bleeding.
- Blood clots can form in aneurysms, leading to blockages in other vessels.
- Aneurysms can compress nearby nerves or organs, causing pain or dysfunction.
- Infection of an aneurysm, though rare, can lead to severe complications.
- Aneurysms in the brain can cause strokes if they rupture.
Prevention of Aneurysms
While not all aneurysms can be prevented, certain lifestyle changes and medical interventions can reduce the risk.
- Controlling blood pressure through diet, exercise, and medication can prevent aneurysms.
- Avoiding smoking reduces the risk of developing aneurysms.
- Regular exercise strengthens the cardiovascular system and reduces aneurysm risk.
- Eating a diet low in saturated fats and cholesterol supports blood vessel health.
- Regular medical check-ups can help detect aneurysms early.
Interesting Facts About Aneurysms
Aneurysms have some fascinating aspects that go beyond their medical implications. Here are some intriguing tidbits.
- The word "aneurysm" comes from the Greek word "aneurysma," meaning "dilation."
- Famous historical figures, including Albert Einstein, have died from aneurysms.
- Some aneurysms can grow very slowly, taking years to become problematic.
- Women are more likely to develop cerebral aneurysms than men.
- Aneurysms are more common in people over the age of 60.
Research and Advances
Ongoing research continues to improve our understanding and treatment of aneurysms. Here are some recent advancements.
- Genetic research is uncovering new risk factors for aneurysms.
- Advances in imaging technology are making it easier to detect aneurysms early.
- New surgical techniques are reducing recovery times and improving outcomes.
- Studies are exploring the use of stem cells to repair damaged blood vessels.
- Researchers are developing medications that could prevent aneurysm growth.
Final Thoughts on Aneurysms
Aneurysms are serious medical conditions that can affect anyone. Understanding the symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options is crucial for early detection and prevention. Regular check-ups, a healthy lifestyle, and being aware of family history can significantly reduce the risk. If you experience sudden, severe headaches, vision problems, or other unusual symptoms, seek medical attention immediately.
Remember, knowledge is power. The more you know about aneurysms, the better prepared you'll be to take action if needed. Stay informed, stay healthy, and don't hesitate to consult healthcare professionals for advice or concerns. By staying vigilant and proactive, you can protect yourself and your loved ones from the potentially life-threatening consequences of aneurysms.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.