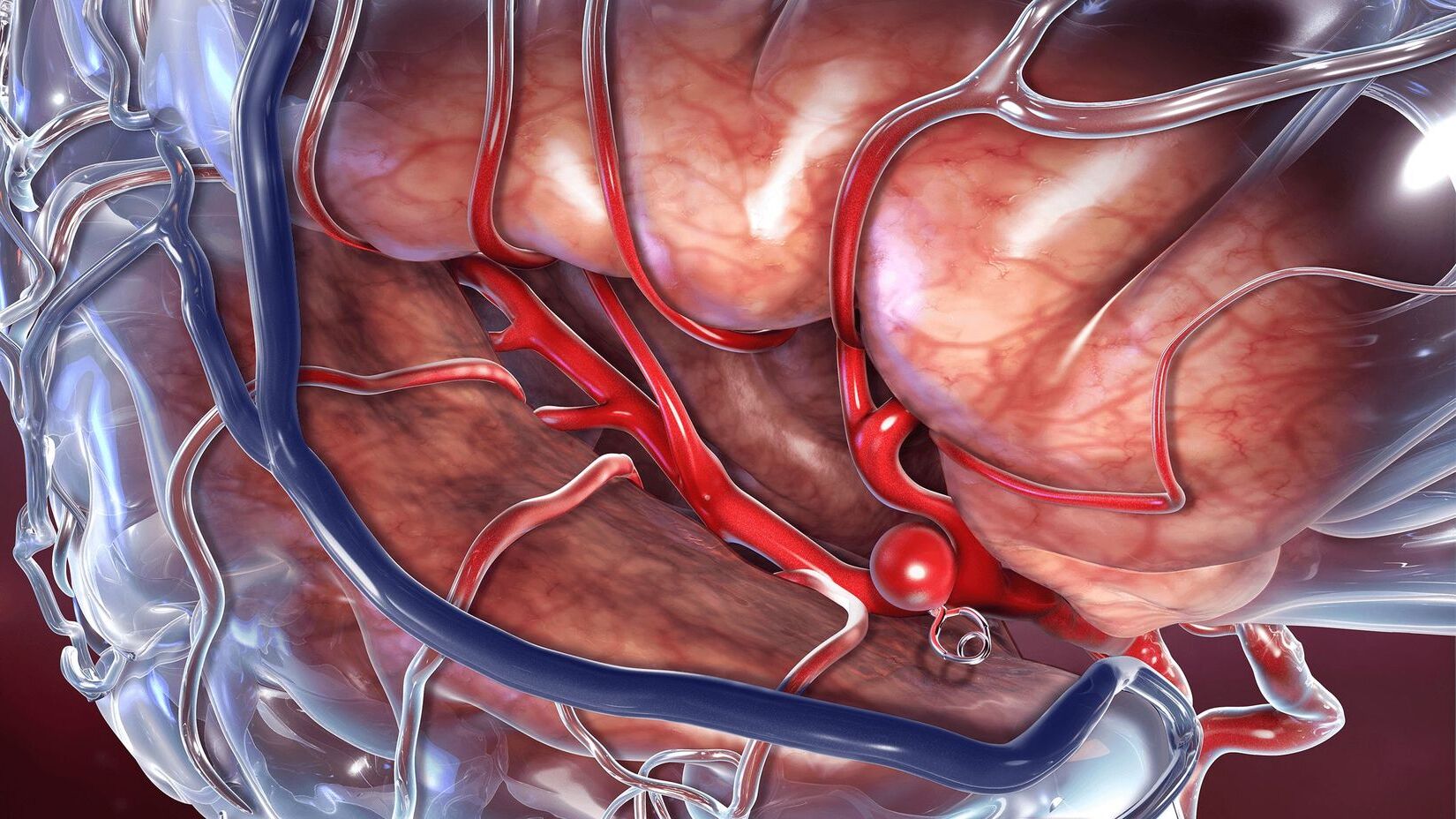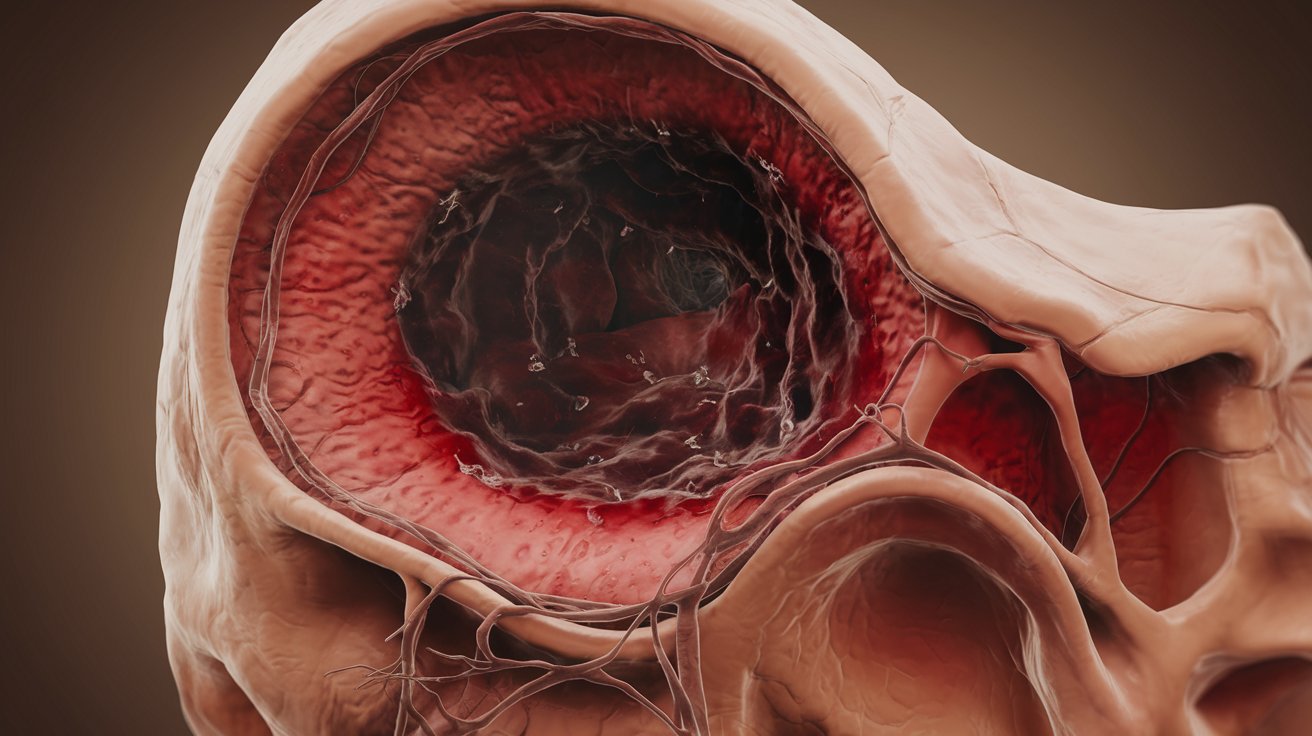
What exactly is cavernous sinus thrombosis? This rare but serious condition involves a blood clot forming in the cavernous sinuses, which are hollow spaces located under the brain and behind each eye socket. Often triggered by infections in the face or skull, it can also result from trauma or certain blood disorders. Symptoms include severe headaches, eye pain, swelling, and vision changes. Early recognition and treatment are crucial for a better outcome. Despite modern medical advances, this condition remains life-threatening, with significant risks of long-term complications. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatments can make a big difference in managing this critical health issue.
Key Takeaways:
- Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis is a rare but serious condition caused by blood clots in the brain. Recognizing symptoms early and seeking prompt treatment is crucial for a good outcome.
- Infections, trauma, and prothrombotic conditions can lead to Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis. Understanding the risk factors and symptoms is key to preventing and managing this condition effectively.
What is Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis?
Cavernous sinus thrombosis (CST) is a rare but serious condition. It involves a blood clot in the cavernous sinuses, which are hollow spaces located under the brain and behind each eye socket. Understanding this condition can help in recognizing its symptoms and seeking timely treatment.
- Definition: Cavernous sinus thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot within the cavernous sinuses, which can be either septic or aseptic in origin.
Causes of Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis
Several factors can lead to the development of CST. Knowing these causes can help in preventing the condition.
-
Causes: The most common cause of cavernous sinus thrombosis is an infection in the face or skull, particularly in the middle third of the face, sinuses, ears, teeth, or mouth. Other causes include trauma, iatrogenic injuries, and prothrombotic conditions.
-
Infectious Causes: In up to 70% of cases, Staphylococcus aureus bacteria cause the infection leading to cavernous thrombosis. Other types of bacteria and some fungi may also cause infections that lead to this condition.
-
Non-Infectious Causes: Non-septic cavernous sinus thrombosis is extremely rare and can result from trauma, arteriovenous aneurysms, or tumor masses partially or totally occluding the sinus.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Symptoms of CST can be severe and sudden. Early recognition is crucial for effective treatment.
-
Symptoms: Symptoms of cavernous sinus thrombosis include a severe headache, particularly around the eye, swelling and bulging of the eye(s) and surrounding tissues, eye pain, double vision, high temperature, and periorbital edema.
-
Rapid Onset: The onset of septic cavernous sinus thrombosis is usually sudden and dramatic, with patients appearing acutely ill and experiencing high-grade fever.
-
Eye Findings: Eye findings include periorbital swelling, chemosis (swelling of the conjunctiva), and proptosis (bulging of the eye).
-
Vision Changes: Vision changes such as photophobia (sensitivity to light), diplopia (double vision), and loss of vision can occur due to the pressure build-up in the cavernous sinuses.
-
Diplopia: Diplopia follows involvement of the third cranial nerve, which can lead to double vision.
-
Optic Disc Swelling: The optic discs are swollen, and numerous hemorrhages around the disc occur when the orbital veins are occluded.
-
Corneal Clouding: The corneas are cloudy, and ulcers may develop due to the infection spreading to the eyes.
-
Pupillary Reactions: Pupillary reactions may be lost with diminished visual acuity, and the pupils may be dilated or small.
-
Fever and Headache: Fever and headache are common early clinical features of cavernous sinus thrombosis, similar to meningitis.
-
Vomiting and Nuchal Rigidity: Vomiting and nuchal rigidity (stiff neck) are also common symptoms that need to be differentiated from meningitis.
Diagnosing Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis
Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment. Various methods are used to confirm CST.
-
Diagnosis: Diagnosis is usually made through clinical evaluation together with imaging techniques such as computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
-
Imaging Techniques: CT scans and MRI scans are crucial for diagnosing cavernous sinus thrombosis by visualizing the blood clot and its impact on surrounding structures.
-
Blood Tests: Blood tests may be conducted to check for signs of infection or prothrombotic conditions.
Treatment Options
Timely and appropriate treatment can significantly improve outcomes for patients with CST.
-
Treatment: Treatment for cavernous sinus thrombosis typically involves antibiotics to address any underlying infection, anticoagulants to dissolve the clot, and corticosteroids to reduce inflammation.
-
Antibiotics: Antibiotics should be started immediately because they have the greatest effect on prognosis. The antibiotics will be given through an intravenous drip directly connected to one of the patient's veins.
-
Anticoagulants: Anticoagulants like heparin may be administered to help dissolve the clot and prevent further clots. Some patients may also need to take anticoagulant tablets for a few months or longer after leaving the hospital.
-
Corticosteroids: Corticosteroids can reduce inflammation and swelling in the body, which is crucial for managing the condition.
-
Surgical Drainage: In some cases, surgical drainage may be necessary to remove pus from the site of infection, such as from a boil or sinusitis.
-
Hospital Admission: Most patients will be admitted to an intensive care unit (ICU) for close monitoring and treatment.
Potential Complications
Despite treatment, CST can lead to significant complications. Awareness of these can help in managing expectations and planning long-term care.
-
Complications: Despite modern treatment, cavernous sinus thrombosis is still a serious condition with significant complications. These can include long-term health problems such as persistent headaches, fits, and some degree of vision loss.
-
Mortality Rate: Cavernous sinus thrombosis is fatal in about 1 in 3 cases if left untreated.
-
Long-Term Sequelae: Even with prompt treatment, many patients experience long-term sequelae such as vision problems, diplopia, and stroke.
-
Vision Problems: Just under 20% of people who survive cavernous sinus thrombosis have vision problems, which can range from mild to severe.
-
Diplopia: Diplopia is a common complication, resulting from the involvement of the third cranial nerve.
-
Stroke Risk: There is a risk of developing dangerous clots in other parts of the body, such as the legs (deep vein thrombosis), lungs (pulmonary embolism), or brain (stroke).
Importance of Early Recognition
Early recognition of CST symptoms can significantly improve outcomes. Knowing what to look for can save lives.
-
Early Recognition: Early recognition of cavernous sinus thrombosis is critical for a good outcome. The condition often presents with fever, headache, eye findings such as periorbital swelling, and ophthalmoplegia.
-
Prognosis: Prompt treatment with antibiotics and anticoagulants has significantly improved the prognosis, with more than 70% of people surviving the condition.
Rare Cases and Other Considerations
CST can sometimes occur under unusual circumstances. Awareness of these can help in understanding the full scope of the condition.
-
Rare Cases: Rarely, cavernous sinus thrombosis can occur after having some types of coronavirus (COVID-19) vaccine. Symptoms can appear between 4 days and 4 weeks after vaccination.
-
Symptom Progression: Symptoms related to the eyes (bulging, swelling) may happen shortly after the headache or gradually develop over several days.
-
Clinical Evaluation: Clinical evaluation is crucial for diagnosing cavernous sinus thrombosis, as it shares symptoms with more common conditions like an eye infection or a migraine.
The Role of Healthcare Providers
Managing CST requires a coordinated effort from various healthcare professionals. Their role is vital in ensuring effective treatment.
-
Interprofessional Team: An interprofessional team is essential in caring for patients with cavernous sinus thrombosis, as it requires a coordinated approach to manage the condition effectively.
-
Education and Awareness: Educating patients and healthcare providers about the risks and symptoms of cavernous sinus thrombosis is crucial for early recognition and treatment.
Risk Factors and Prevention
Understanding risk factors can help in preventing CST. Taking preventive measures can reduce the likelihood of developing this condition.
-
Risk Factors: Risk factors for developing cavernous sinus thrombosis include facial infections, sinusitis, orbital cellulitis, pharyngitis, or otitis, as well as traumatic injuries or surgeries.
-
Thrombophilic Disorders: Thrombophilic disorders increase the risk of developing cavernous sinus thrombosis, especially in the setting of facial infections or trauma.
-
Modern Treatment: Modern treatment with antibiotics and anticoagulation has significantly improved the outcome for patients with cavernous sinus thrombosis, but the risk of long-term sequelae remains significant.
-
Prevention: Preventing infections in the face or skull is crucial in reducing the risk of developing cavernous sinus thrombosis. This can be achieved through good hygiene practices and prompt treatment of infections.
Final Thoughts on Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis
Cavernous sinus thrombosis (CST) is a rare but serious condition that demands immediate attention. It often stems from infections in the face or skull, leading to symptoms like severe headaches, eye pain, and vision changes. Early recognition and treatment with antibiotics, anticoagulants, and sometimes corticosteroids are crucial for improving outcomes. Despite advances in medical care, CST can still result in long-term complications such as vision problems and stroke. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options can help in managing this life-threatening condition effectively. Educating healthcare providers and patients about CST is essential for early diagnosis and better prognosis. Preventing facial infections through good hygiene and prompt treatment can reduce the risk of developing CST. Stay informed and vigilant to protect yourself and loved ones from this dangerous condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.