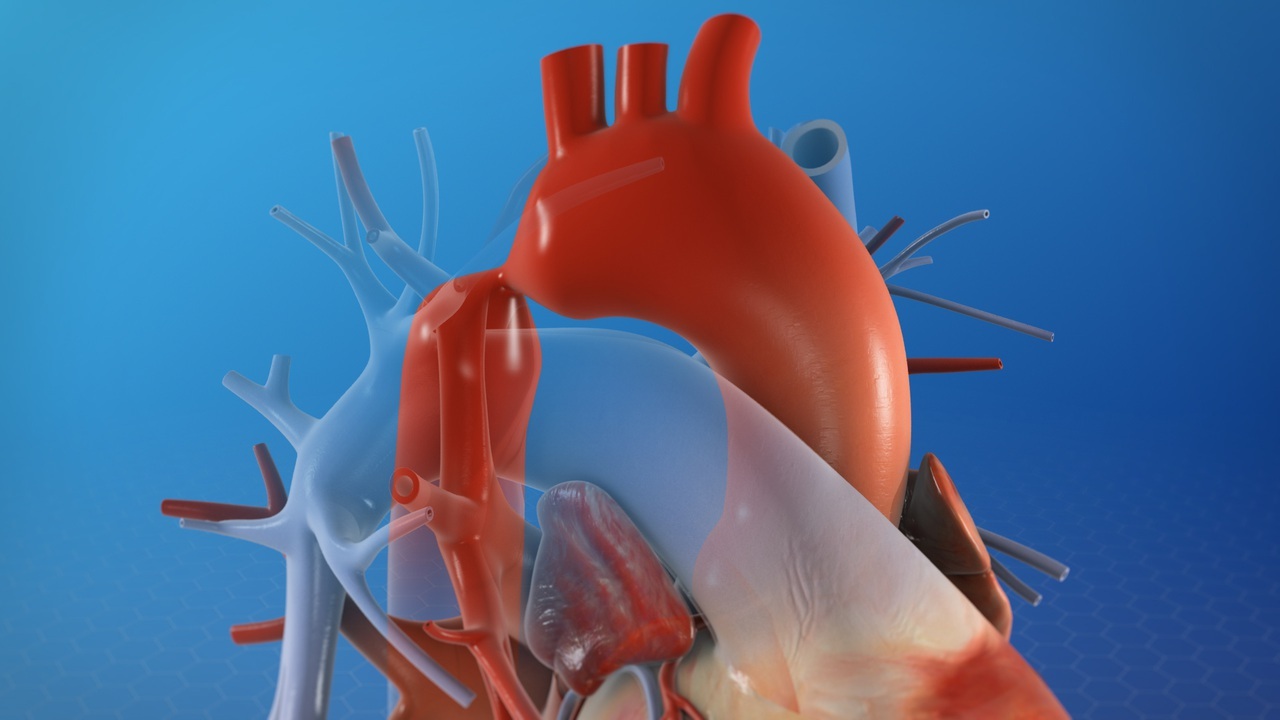
What is aortic coarctation? Aortic coarctation is a condition where the aorta, the large artery that carries blood from the heart to the rest of the body, becomes narrowed. This narrowing can restrict blood flow, causing the heart to work harder to pump blood through the constricted area. Symptoms can vary from mild to severe and may include high blood pressure, headaches, muscle weakness, or even heart failure. Diagnosis often involves imaging tests like echocardiograms, MRIs, or CT scans. Treatment options range from medication to manage symptoms to surgical procedures aimed at widening the narrowed section of the aorta. Understanding this condition is crucial for managing its impact on health.
What is Aortic Coarctation?
Aortic coarctation is a congenital heart defect where a part of the aorta is narrower than usual. This narrowing can restrict blood flow, causing various health issues. Here are some intriguing facts about this condition.
-
Congenital Condition: Aortic coarctation is present at birth, making it a congenital heart defect.
-
Narrowing of the Aorta: The condition involves a narrowing of the aorta, the major artery that carries blood from the heart to the rest of the body.
-
Location Matters: The narrowing usually occurs near the ductus arteriosus, a blood vessel in the fetal heart that normally closes after birth.
-
More Common in Males: Males are more frequently affected by aortic coarctation than females.
-
Associated with Other Defects: Often, it occurs alongside other congenital heart defects, such as a bicuspid aortic valve.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms and diagnosing aortic coarctation early can significantly improve outcomes. Here are some key points to consider.
-
High Blood Pressure: One of the most common symptoms is high blood pressure, especially in the arms.
-
Weak Pulse in Legs: A weak or absent pulse in the legs can indicate aortic coarctation.
-
Heart Murmur: Doctors often detect a heart murmur, an unusual sound heard during a heartbeat.
-
Shortness of Breath: Individuals may experience shortness of breath, particularly during exercise.
-
Headaches and Nosebleeds: Frequent headaches and nosebleeds can also be symptoms.
-
Diagnostic Imaging: Echocardiograms, MRIs, and CT scans are commonly used to diagnose the condition.
-
Electrocardiogram (ECG): An ECG can help detect heart abnormalities associated with aortic coarctation.
Treatment Options
Various treatments are available to manage aortic coarctation, ranging from medication to surgery. Here are some of the most common approaches.
-
Medication: Blood pressure medications can help manage symptoms.
-
Balloon Angioplasty: This procedure involves inflating a small balloon inside the narrowed part of the aorta to widen it.
-
Stent Placement: A stent, a small mesh tube, can be placed in the aorta to keep it open.
-
Surgical Repair: Surgery may involve removing the narrowed section of the aorta or bypassing it with a graft.
-
End-to-End Anastomosis: This surgical technique involves cutting out the narrowed section and connecting the two ends of the aorta.
-
Subclavian Flap Aortoplasty: This procedure uses a flap from the subclavian artery to widen the narrowed section.
Long-Term Outlook
Understanding the long-term outlook for those with aortic coarctation can help in managing the condition effectively.
-
Regular Follow-Ups: Lifelong follow-up care is essential to monitor heart health.
-
Risk of Re-Narrowing: There's a risk that the aorta may narrow again after treatment.
-
Exercise Restrictions: Some individuals may need to avoid strenuous activities.
-
Pregnancy Risks: Women with aortic coarctation should consult their doctor before becoming pregnant.
-
Endocarditis Risk: There's an increased risk of endocarditis, an infection of the heart lining.
-
Lifelong Medication: Some may need to take blood pressure medication for life.
Interesting Historical Facts
The history of aortic coarctation treatment is fascinating and has evolved significantly over the years.
-
First Described in 1760: The condition was first described by Giovanni Morgagni, an Italian anatomist, in 1760.
-
First Successful Surgery in 1944: The first successful surgical repair was performed by Dr. Clarence Crafoord in Sweden in 1944.
-
Balloon Angioplasty Introduced in 1982: Balloon angioplasty became a treatment option in 1982, revolutionizing care.
-
Stent Use in the 1990s: The use of stents to treat aortic coarctation began in the 1990s.
-
Advances in Imaging: Modern imaging techniques have greatly improved diagnosis and treatment planning.
Genetic and Environmental Factors
Both genetic and environmental factors can play a role in the development of aortic coarctation.
-
Genetic Mutations: Certain genetic mutations can increase the risk of developing the condition.
-
Family History: A family history of congenital heart defects can be a risk factor.
-
Environmental Exposures: Exposure to certain substances during pregnancy can increase the risk.
-
Associated Syndromes: Conditions like Turner syndrome are often associated with aortic coarctation.
-
Prenatal Diagnosis: Advances in prenatal imaging allow for early detection of the condition.
Impact on Daily Life
Living with aortic coarctation can impact daily life in various ways. Here are some aspects to consider.
-
Dietary Restrictions: A heart-healthy diet can help manage symptoms.
-
Regular Exercise: Moderate exercise is often recommended, but strenuous activities may need to be avoided.
-
Mental Health: Managing a chronic condition can affect mental health, making support important.
-
School and Work: Children and adults may need accommodations at school or work.
-
Social Activities: Participation in social activities may need to be adjusted based on physical limitations.
-
Support Groups: Joining support groups can provide emotional support and practical advice.
Final Thoughts on Aortic Coarctation
Understanding aortic coarctation is crucial for recognizing its impact on health. This condition, a narrowing of the aorta, can lead to serious complications if left untreated. Early detection and treatment, often through surgery or balloon angioplasty, significantly improve outcomes. Regular check-ups and monitoring are essential for those diagnosed, ensuring any changes are promptly addressed. Awareness of symptoms like high blood pressure, headaches, and leg cramps can lead to earlier diagnosis. Knowledge empowers patients and caregivers to seek timely medical advice. Remember, while aortic coarctation is a serious condition, advancements in medical science offer effective treatments and hope for a healthy future. Stay informed, stay proactive, and prioritize heart health.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.