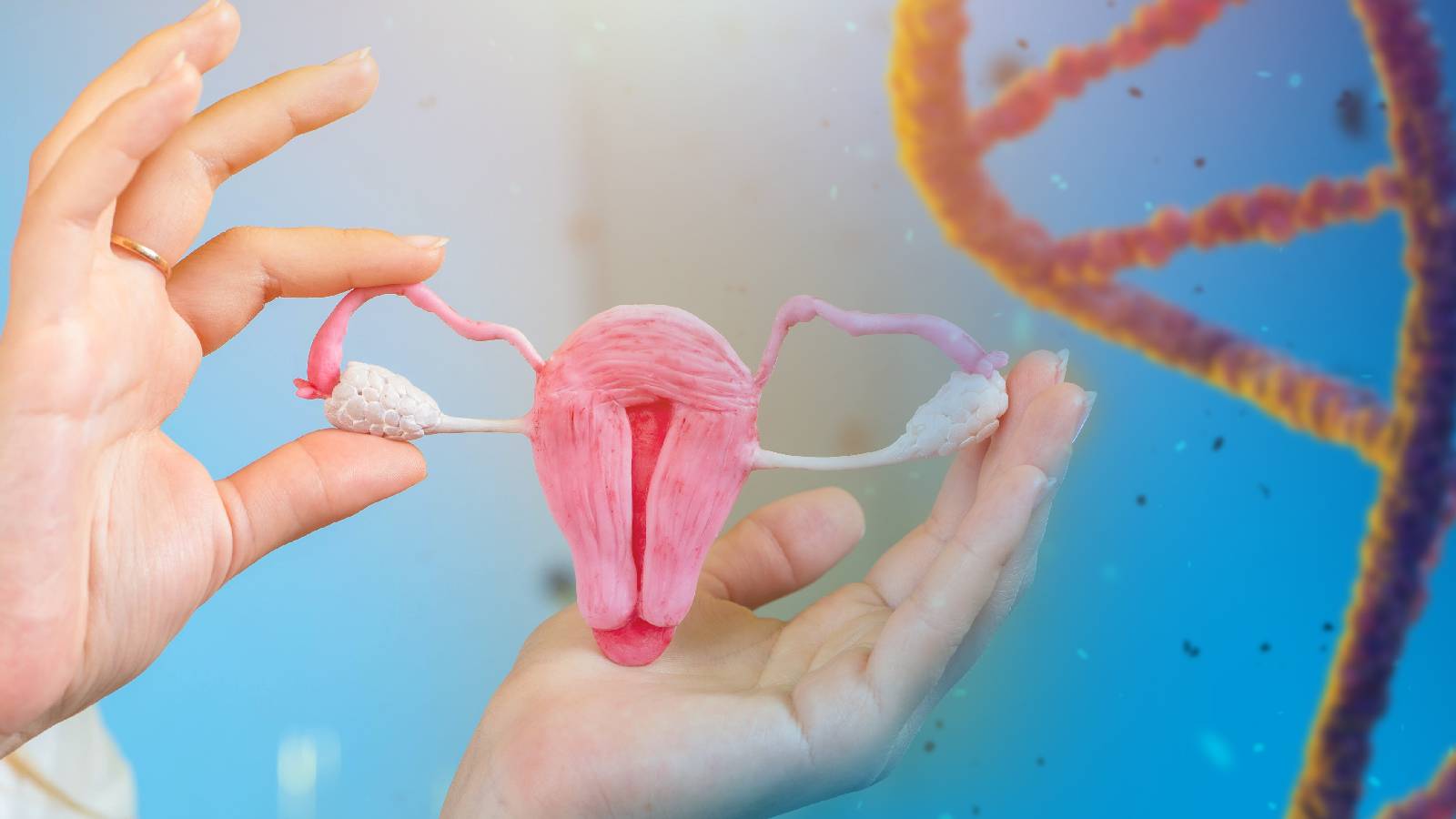
What are the fallopian tubes? These slender tubes connect the ovaries to the uterus. They play a crucial role in reproduction by transporting eggs from the ovaries to the uterus. Why are they important? Without them, natural fertilization wouldn't occur. How do they work? Tiny hair-like structures called cilia line the inside, helping move the egg along. Did you know? Each tube is about 10-12 cm long. Fun fact: They were named after Gabriele Falloppio, an Italian anatomist. Want to learn more? Keep reading to uncover 39 fascinating facts about these essential reproductive organs.
39 Facts about Fallopian Tubes
The fallopian tubes play a crucial role in the female reproductive system. These slender tubes connect the ovaries to the uterus, providing a pathway for eggs to travel and meet sperm for fertilization. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about these essential structures.
Anatomy and Structure
Understanding the basic anatomy of fallopian tubes helps appreciate their function.
-
Fallopian tubes are about 10-12 cm long. These tubes are roughly the length of a standard pencil, making them quite small yet incredibly important.
-
Each tube has four main parts. These parts include the infundibulum, ampulla, isthmus, and interstitial part, each playing a specific role in egg transport.
-
The infundibulum has finger-like projections called fimbriae. Fimbriae help capture the egg released from the ovary and guide it into the tube.
-
The ampulla is the widest section. This part is where fertilization usually occurs, as it provides a spacious environment for sperm and egg to meet.
-
The isthmus is a narrow, muscular section. It helps propel the fertilized egg towards the uterus through rhythmic contractions.
-
The interstitial part passes through the uterine wall. This section connects the fallopian tube to the uterus, completing the pathway for the egg.
Function and Physiology
The fallopian tubes are not just passive conduits; they actively participate in reproduction.
-
Cilia line the inner surface of the tubes. These tiny hair-like structures move in a wave-like motion to help transport the egg.
-
Peristaltic contractions aid in egg movement. These muscle contractions ensure the egg moves smoothly towards the uterus.
-
The tubes provide a nourishing environment. Secretions from the tube's lining support the egg and sperm, facilitating fertilization.
-
Sperm can survive in the tubes for up to five days. This extended survival time increases the chances of fertilization.
-
The tubes play a role in early embryo development. The fertilized egg, or zygote, begins to divide and grow as it travels through the tube.
Health and Medical Conditions
Various conditions can affect the fallopian tubes, impacting fertility and overall health.
-
Blocked tubes can cause infertility. Blockages prevent the egg and sperm from meeting, making natural conception difficult.
-
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) can damage the tubes. This infection often leads to scarring and blockages.
-
Endometriosis can affect the tubes. This condition causes tissue similar to the uterine lining to grow outside the uterus, potentially blocking the tubes.
-
Ectopic pregnancies often occur in the tubes. When a fertilized egg implants in the tube instead of the uterus, it can cause serious complications.
-
Tubal ligation is a permanent form of birth control. This surgical procedure involves cutting or sealing the tubes to prevent pregnancy.
-
Salpingectomy is the removal of one or both tubes. This surgery may be necessary due to ectopic pregnancy, cancer, or other conditions.
-
Hydrosalpinx is a condition where the tube fills with fluid. This can cause blockages and affect fertility.
-
Tubal factor infertility accounts for 25-30% of infertility cases. Issues with the tubes are a significant cause of infertility in women.
Interesting Facts
Beyond their basic functions, fallopian tubes have some intriguing aspects.
-
Named after Gabriele Falloppio. This Italian anatomist first described the tubes in the 16th century.
-
They are also called oviducts. This term highlights their role in egg transport.
-
The tubes can regenerate to some extent. After minor damage, they can heal and regain function.
-
Tubal pregnancies can be life-threatening. Immediate medical attention is crucial to prevent complications.
-
Some animals have multiple oviducts. For example, birds have two oviducts, each serving one ovary.
-
Tubal flushing can improve fertility. This procedure involves flushing the tubes with a special solution to clear blockages.
-
The tubes are highly vascular. A rich blood supply supports their function and health.
-
Hormones regulate tube function. Estrogen and progesterone influence the tube's environment and motility.
-
Tubal cannulation can open blocked tubes. This minimally invasive procedure uses a catheter to clear blockages.
-
The tubes are sensitive to infections. Prompt treatment of infections can prevent long-term damage.
-
Tubal reanastomosis can reverse tubal ligation. This surgery reconnects the tubes to restore fertility.
-
The tubes play a role in immune defense. They help protect the reproductive tract from infections.
-
Tubal polyps can occur. These growths may cause blockages and affect fertility.
-
The tubes can twist, causing pain. This rare condition, called tubal torsion, requires immediate medical attention.
-
Tubal cysts can form. These fluid-filled sacs may need treatment if they cause symptoms.
-
The tubes are involved in the menstrual cycle. They help transport the egg released during ovulation.
-
Tubal scarring can result from surgery. Previous surgeries in the pelvic area can lead to scarring and blockages.
-
The tubes can be visualized with imaging techniques. Ultrasound, hysterosalpingography, and laparoscopy help diagnose tubal issues.
-
Tubal health is crucial for fertility. Healthy tubes are essential for natural conception.
-
Research continues to explore tubal function. Scientists study the tubes to improve fertility treatments and understand reproductive health better.
Final Thoughts on Fallopian Tubes
Fallopian tubes play a crucial role in human reproduction. These slender tubes connect the ovaries to the uterus, providing a pathway for eggs to travel and meet sperm for fertilization. Without them, natural conception wouldn't be possible.
Understanding their function helps in recognizing issues like ectopic pregnancies or blockages, which can impact fertility. Regular check-ups and awareness of symptoms can lead to early detection and treatment of potential problems.
Fallopian tubes might be small, but their importance in the reproductive system is immense. They are a testament to the intricate design of the human body.
So, next time you think about reproduction, remember the vital role these tubes play. Knowledge about them not only enriches our understanding but also empowers us to take better care of our reproductive health.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
