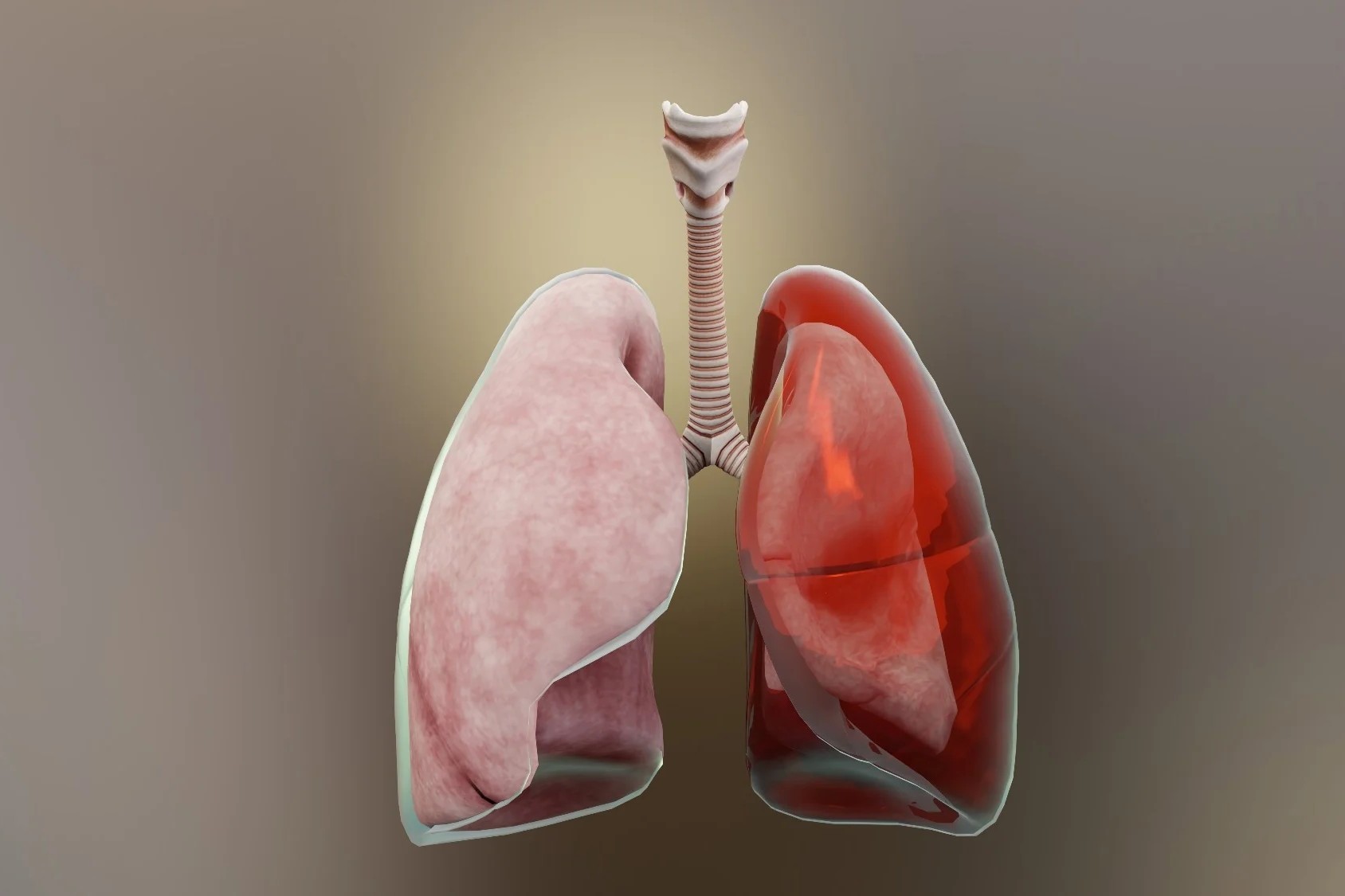
What is empyema? Empyema is a condition where pus gathers in the space between the lungs and the inner surface of the chest wall. This space is called the pleural cavity. What causes empyema? It often results from an infection like pneumonia. How serious is empyema? It can be quite serious and requires medical attention. What are the symptoms? Symptoms include chest pain, fever, cough, and difficulty breathing. How is it treated? Treatment usually involves antibiotics and sometimes surgery to drain the pus. Can empyema be prevented? Good hygiene and vaccinations can help prevent infections that might lead to empyema. Why is it important to know about empyema? Understanding this condition can help you recognize symptoms early and seek timely treatment.
What is Empyema?
Empyema is a medical condition where pus accumulates in the pleural cavity, the space between the lungs and the chest wall. This can cause severe health issues if not treated promptly. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about empyema.
-
Empyema is often a complication of pneumonia, which is an infection of the lungs.
-
The term "empyema" comes from the Greek word "empyein," meaning "to suppurate" or "to produce pus."
-
Symptoms of empyema include chest pain, fever, cough, and difficulty breathing.
-
Empyema can be diagnosed through imaging tests like X-rays, CT scans, and ultrasounds.
-
There are two types of empyema: acute and chronic. Acute empyema develops quickly, while chronic empyema progresses over a longer period.
Causes of Empyema
Understanding the causes of empyema can help in its prevention and treatment. Here are some key causes:
-
Bacterial infections are the most common cause of empyema. Streptococcus pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus are frequent culprits.
-
Empyema can also result from a lung abscess, which is a collection of pus within the lung tissue.
-
Trauma to the chest, such as from a car accident or a fall, can lead to empyema.
-
Surgical procedures involving the chest or lungs can sometimes cause empyema as a complication.
-
Tuberculosis, a bacterial infection that primarily affects the lungs, can also lead to empyema.
Diagnosis of Empyema
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Here are some methods used to diagnose empyema:
-
A physical examination, including listening to the lungs with a stethoscope, can provide initial clues.
-
Blood tests can reveal signs of infection, such as elevated white blood cell counts.
-
Thoracentesis, a procedure where a needle is inserted into the pleural space to collect fluid, can confirm the presence of pus.
-
Pleural fluid analysis helps identify the type of bacteria causing the infection.
-
Bronchoscopy, a procedure that allows doctors to look inside the airways, can help diagnose empyema.
Treatment Options for Empyema
Treating empyema effectively requires a combination of medical and sometimes surgical interventions. Here are some common treatment options:
-
Antibiotics are the first line of treatment to combat the bacterial infection causing empyema.
-
Drainage of the pleural fluid is often necessary. This can be done using a chest tube or through thoracentesis.
-
In severe cases, surgery may be required to remove the infected tissue. This procedure is known as decortication.
-
Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) is a minimally invasive surgical option for treating empyema.
-
Pain management is crucial during treatment, as empyema can cause significant discomfort.
Complications of Empyema
Empyema can lead to several complications if not treated promptly. Here are some potential complications:
-
Pleural thickening, where the pleural membranes become scarred and thickened, can occur.
-
Lung abscesses, or pockets of pus within the lung tissue, can develop.
-
Sepsis, a life-threatening response to infection, can result from untreated empyema.
-
Respiratory failure, where the lungs cannot provide enough oxygen to the body, is a severe complication.
-
Chronic empyema can lead to long-term lung damage and reduced lung function.
Prevention of Empyema
Preventing empyema involves reducing the risk factors and taking proactive measures. Here are some prevention tips:
-
Vaccination against pneumonia and influenza can help prevent infections that may lead to empyema.
-
Prompt treatment of respiratory infections can reduce the risk of developing empyema.
-
Good hygiene practices, such as regular handwashing, can prevent the spread of infections.
-
Avoiding smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke can reduce the risk of lung infections.
-
Maintaining a healthy immune system through a balanced diet and regular exercise can help prevent infections.
Interesting Facts about Empyema
Here are some lesser-known but intriguing facts about empyema:
-
Empyema has been documented since ancient times, with references found in the writings of Hippocrates.
-
The first successful surgical treatment for empyema was performed in the 19th century.
-
Empyema can affect people of all ages, but it is more common in older adults and those with weakened immune systems.
-
In some cases, empyema can be caused by fungal infections, although this is rare.
-
Empyema is more common in developing countries due to limited access to healthcare and vaccinations.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to improve the diagnosis and treatment of empyema. Here are some current research trends:
-
Researchers are exploring new antibiotics and treatments to combat antibiotic-resistant bacteria causing empyema.
-
Advances in imaging technology are helping doctors diagnose empyema more accurately and quickly.
-
Studies are investigating the role of the immune system in the development and progression of empyema.
-
Clinical trials are testing new surgical techniques and minimally invasive procedures for treating empyema.
Final Thoughts on Empyema
Empyema, a serious condition, requires prompt attention. Knowing the symptoms like fever, chest pain, and difficulty breathing can save lives. Early diagnosis through imaging and lab tests ensures better outcomes. Treatment often involves antibiotics and drainage procedures. Ignoring it can lead to severe complications, including lung damage.
Understanding the risk factors such as pneumonia, lung infections, and weakened immune systems helps in prevention. Vaccinations and good hygiene practices play a crucial role in reducing the risk.
Stay informed, stay vigilant. If you or someone you know shows signs, seek medical help immediately. Knowledge is power, and in this case, it can be life-saving.
Empyema may sound daunting, but with the right information and timely action, it’s manageable. Keep these facts in mind, and you’ll be better prepared to handle this condition.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
