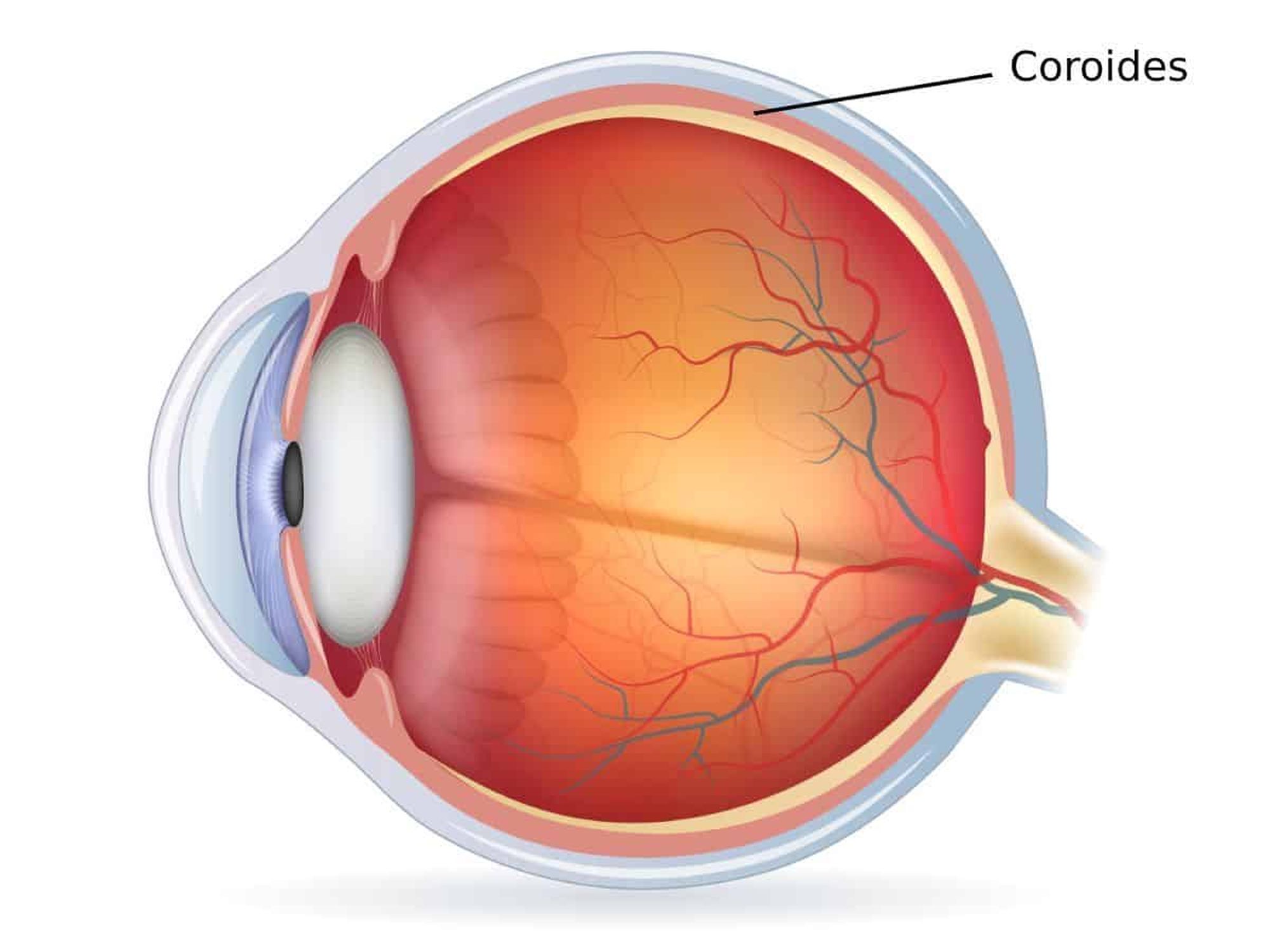
What is the choroid? The choroid is a vital part of the eye, nestled between the retina and the sclera. It’s a thin, vascular layer that supplies oxygen and nutrients to the outer retina. Without it, our vision would suffer greatly. This layer is rich in blood vessels and pigments, which help absorb excess light, preventing it from scattering inside the eye. The choroid also plays a role in temperature regulation and waste removal for the retina. Understanding the choroid can help us appreciate how our eyes function and maintain their health. Ready to learn more? Let's dive into 39 fascinating facts about the choroid!
What is the Choroid?
The choroid is a vital part of the eye, often overlooked but essential for vision. It lies between the retina and the sclera, providing nutrients and oxygen to the eye. Here are some fascinating facts about this crucial eye component.
- The choroid is rich in blood vessels, making it one of the most vascularized tissues in the body.
- It contains a dark pigment that helps absorb excess light, preventing it from scattering inside the eye.
- The choroid's primary function is to supply oxygen and nutrients to the outer layers of the retina.
- It extends from the optic nerve at the back of the eye to the ora serrata, the junction between the retina and the ciliary body.
- The choroid is part of the uveal tract, which also includes the iris and the ciliary body.
Structure of the Choroid
Understanding the structure of the choroid can help appreciate its role in eye health. It consists of several layers, each with a specific function.
- The choroid has four main layers: Bruch's membrane, the choriocapillaris, Sattler's layer, and Haller's layer.
- Bruch's membrane is the innermost layer, acting as a barrier between the retina and the choroid.
- The choriocapillaris is a network of capillaries that supplies blood to the outer retina.
- Sattler's layer contains medium-sized blood vessels.
- Haller's layer consists of larger blood vessels and is the outermost layer of the choroid.
Functions of the Choroid
The choroid performs several critical functions that are essential for maintaining healthy vision.
- It regulates the temperature of the retina by dissipating heat generated by light absorption.
- The choroid helps maintain intraocular pressure by controlling the flow of aqueous humor.
- It plays a role in the immune response of the eye, protecting against infections.
- The choroid's blood vessels help remove waste products from the retina.
- It supports the growth and repair of retinal cells by providing essential nutrients.
Choroid and Eye Diseases
The choroid can be affected by various eye diseases, impacting vision and overall eye health.
- Choroiditis is an inflammation of the choroid that can cause vision loss if untreated.
- Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) involves changes in the choroid, leading to central vision loss.
- Choroidal neovascularization (CNV) occurs when abnormal blood vessels grow in the choroid, often associated with AMD.
- Choroidal melanoma is a rare but serious cancer that originates in the choroid.
- Central serous chorioretinopathy (CSC) involves fluid accumulation under the retina, often linked to choroidal dysfunction.
Interesting Facts about the Choroid
Here are some lesser-known but intriguing facts about the choroid that highlight its complexity and importance.
- The choroid is thicker in nocturnal animals, helping them see better in low light.
- It contains melanocytes, cells that produce the pigment melanin.
- The choroid's blood flow is one of the highest in the body, crucial for retinal health.
- In some birds, the choroid has a structure called the pecten, which is thought to nourish the retina.
- The choroid can change thickness in response to light exposure, a process known as choroidal thickness modulation.
Choroid in Different Species
The choroid varies among different species, reflecting their unique visual needs and environments.
- In fish, the choroid contains a structure called the choroidal gland, which helps regulate buoyancy.
- Birds of prey have a highly vascularized choroid, aiding their sharp vision.
- The choroid in reptiles often has a reflective layer called the tapetum lucidum, enhancing night vision.
- In mammals, the choroid's structure and function are similar to humans, supporting detailed vision.
- Some amphibians have a choroid that adapts to both aquatic and terrestrial environments.
Advances in Choroid Research
Recent research has provided new insights into the choroid's role in eye health and disease.
- Optical coherence tomography (OCT) allows detailed imaging of the choroid, aiding in disease diagnosis.
- Studies have shown that choroidal thickness can be an indicator of various eye conditions.
- Research on choroidal blood flow has improved understanding of diseases like AMD and diabetic retinopathy.
- Advances in gene therapy hold promise for treating choroidal diseases.
- Investigations into the choroid's immune functions are uncovering new ways to combat eye infections.
Choroid and Lifestyle
Certain lifestyle factors can influence the health of the choroid and overall eye health.
- A diet rich in antioxidants supports choroidal health by reducing oxidative stress.
- Regular eye exams can help detect choroidal changes early, preventing vision loss.
- Smoking has been linked to choroidal thinning and increased risk of AMD.
- Maintaining healthy blood pressure supports choroidal blood flow and retinal health.
Final Thoughts on Choroid Plexus
The choroid plexus plays a crucial role in brain health. It produces cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), which cushions the brain and spinal cord, removes waste, and provides nutrients. This small but mighty structure also acts as a barrier, protecting the brain from harmful substances. Understanding its functions helps us appreciate how our brains stay healthy and function properly.
Research on the choroid plexus continues to reveal new insights, potentially leading to treatments for neurological disorders. From its role in CSF production to its protective functions, the choroid plexus is vital for maintaining a stable environment for the brain.
By learning about the choroid plexus, we gain a deeper understanding of our brain's complex workings. This knowledge not only fascinates but also underscores the importance of ongoing research in neuroscience.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
