What is Hypernatremia? Hypernatremia is a condition where the sodium levels in your blood are abnormally high. This imbalance can lead to serious health issues if not addressed promptly. Why does it happen? It usually occurs when there’s a loss of water in the body or an excessive intake of sodium. Who is at risk? Older adults, infants, and those with certain medical conditions are more susceptible. What are the symptoms? Common signs include extreme thirst, confusion, muscle twitching, and even seizures. How is it treated? Treatment often involves rehydration and addressing the underlying cause. Understanding hypernatremia is crucial for maintaining good health.
What is Hypernatremia?
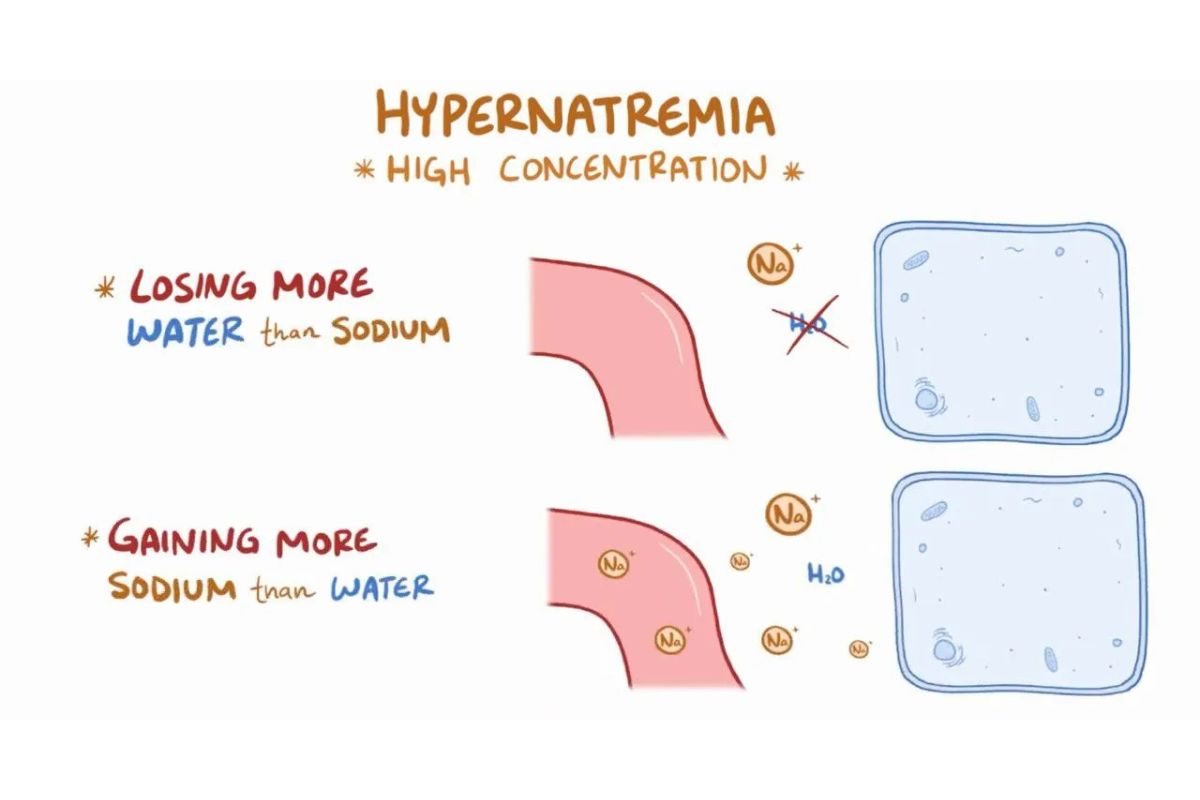
Hypernatremia is a condition where there's too much sodium in the blood. This can lead to serious health problems if not treated. Let's dive into some interesting facts about this condition.
-
Sodium Levels: Hypernatremia occurs when sodium levels in the blood exceed 145 milliequivalents per liter (mEq/L).
-
Water Loss: It often results from water loss rather than sodium gain. This can happen due to dehydration or excessive sweating.
-
Kidney Function: The kidneys play a crucial role in regulating sodium levels. When they fail to function properly, hypernatremia can occur.
-
Elderly at Risk: Older adults are more susceptible due to decreased thirst sensation and kidney function.
-
Symptoms: Common symptoms include thirst, confusion, muscle twitching, and seizures.
-
Severe Cases: In severe cases, hypernatremia can lead to brain swelling, coma, or even death.
Causes of Hypernatremia
Understanding the causes can help in preventing and managing hypernatremia effectively.
-
Dehydration: One of the most common causes is dehydration, which can result from not drinking enough water.
-
Diabetes Insipidus: This condition causes excessive urination, leading to water loss and increased sodium concentration.
-
Diuretic Use: Certain medications like diuretics can cause the body to lose water, increasing sodium levels.
-
Burns: Severe burns can lead to fluid loss, contributing to hypernatremia.
-
Diarrhea: Prolonged diarrhea can result in significant water loss, causing sodium levels to rise.
-
Fever: High fever can lead to increased sweating and water loss, contributing to hypernatremia.
Diagnosing Hypernatremia
Early diagnosis is key to managing hypernatremia effectively. Here are some facts about how it's diagnosed.
-
Blood Tests: A simple blood test can measure sodium levels and diagnose hypernatremia.
-
Urine Tests: Urine tests can help determine the cause by measuring sodium concentration in the urine.
-
Medical History: Doctors often review a patient's medical history to identify potential causes like medication use or underlying conditions.
-
Physical Examination: A physical exam can reveal signs of dehydration or other symptoms associated with hypernatremia.
Treatment Options
Treating hypernatremia involves addressing the underlying cause and restoring normal sodium levels.
-
Fluid Replacement: The primary treatment is fluid replacement, either orally or intravenously.
-
Medication Adjustment: Adjusting or discontinuing medications that contribute to water loss can help manage the condition.
-
Dietary Changes: Reducing sodium intake through dietary changes can also be beneficial.
-
Monitoring: Regular monitoring of sodium levels is essential to ensure they return to normal.
-
Hospitalization: Severe cases may require hospitalization for intensive treatment and monitoring.
Preventing Hypernatremia
Prevention is always better than cure. Here are some ways to prevent hypernatremia.
-
Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water, especially during hot weather or exercise, can prevent dehydration.
-
Monitor Medications: Be aware of medications that can cause water loss and discuss alternatives with your doctor.
-
Balanced Diet: Eating a balanced diet with appropriate sodium levels can help maintain normal sodium levels.
-
Regular Check-ups: Regular medical check-ups can help detect early signs of hypernatremia and other health issues.
Interesting Facts
Here are some lesser-known facts about hypernatremia that might surprise you.
-
Rare in Healthy Individuals: Hypernatremia is relatively rare in healthy individuals with normal access to water.
-
Thirst Mechanism: The body's natural thirst mechanism usually prevents hypernatremia by signaling when to drink water.
-
Athletes at Risk: Endurance athletes are at higher risk due to prolonged sweating and inadequate fluid replacement.
-
Infants: Infants, especially those who are breastfed, can be at risk if they don't receive enough fluids.
-
Mental Health: Certain mental health conditions can increase the risk due to neglect of self-care and hydration.
-
Hospitalized Patients: Patients in hospitals, especially those on IV fluids or certain medications, are at higher risk.
-
Climate Impact: People living in hot climates are more susceptible due to increased water loss through sweating.
-
Rapid Correction Risks: Rapid correction of hypernatremia can be dangerous, potentially causing brain swelling.
-
Chronic vs. Acute: Chronic hypernatremia develops slowly over time, while acute hypernatremia occurs suddenly and is more dangerous.
Final Thoughts on Hypernatremia
Hypernatremia, a condition marked by high sodium levels in the blood, can have serious health implications if not addressed promptly. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments is crucial for managing this condition effectively. Key factors include dehydration, excessive salt intake, and certain medical conditions. Symptoms like confusion, muscle twitching, and seizures should never be ignored. Treatment often involves rehydration and addressing the underlying cause. Prevention is equally important—staying hydrated, monitoring sodium intake, and regular medical check-ups can help keep hypernatremia at bay. Knowledge is power, and being informed about hypernatremia can make a significant difference in maintaining good health. Always consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice and treatment options. Stay vigilant, stay healthy.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
