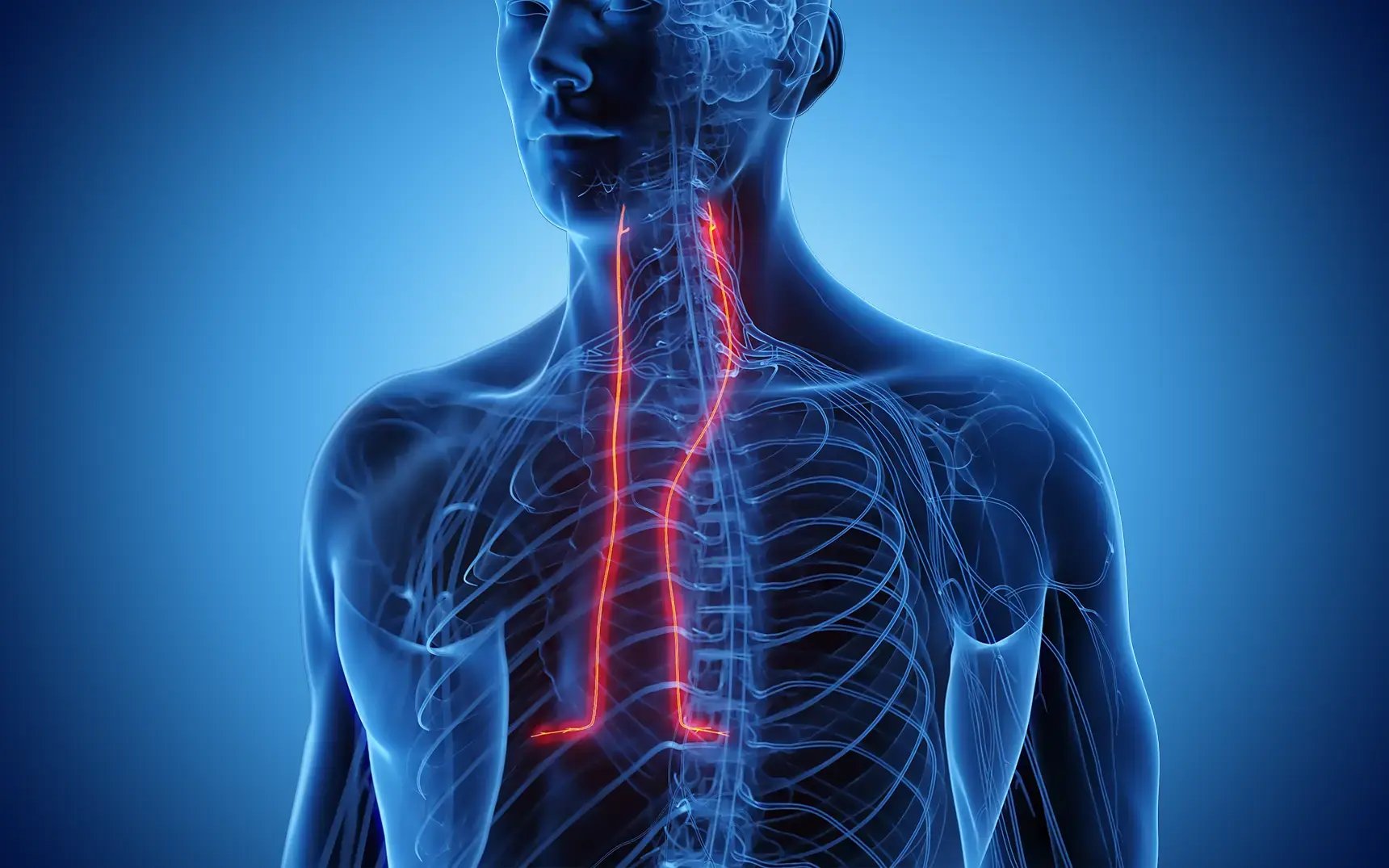
Ever wondered what the phrenic nerve does? This nerve plays a crucial role in breathing. It controls the diaphragm, the muscle that helps your lungs take in air. Without it, breathing would be impossible. The phrenic nerve starts in the neck and travels down to the diaphragm. It’s like a messenger, carrying signals from the brain to the diaphragm, telling it when to contract and relax. Injuries to this nerve can lead to serious breathing problems. Understanding the phrenic nerve can help you appreciate how your body works to keep you alive every second. Ready to learn more? Let's dive in!
What is Phrenic?
Phrenic refers to anything related to the diaphragm, a crucial muscle in the respiratory system. This muscle plays a vital role in breathing, separating the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about the phrenic nerve and its functions.
The Phrenic Nerve
The phrenic nerve is essential for breathing. It controls the diaphragm, enabling inhalation and exhalation.
- The phrenic nerve originates in the neck, specifically from the C3 to C5 spinal nerves.
- It is the only nerve that provides motor control to the diaphragm.
- Damage to the phrenic nerve can lead to diaphragmatic paralysis, affecting breathing.
- The phrenic nerve also provides sensory information from parts of the pleura and pericardium.
- It is a mixed nerve, containing both motor and sensory fibers.
Diaphragm Functions
The diaphragm is more than just a muscle for breathing. It has several other important roles.
- The diaphragm helps in expelling vomit, feces, and urine by increasing intra-abdominal pressure.
- It acts as a barrier between the thoracic and abdominal cavities.
- During inspiration, the diaphragm contracts and flattens, increasing the volume of the thoracic cavity.
- During expiration, the diaphragm relaxes and returns to its dome shape, decreasing thoracic volume.
- The diaphragm also assists in the lymphatic drainage of the lower body.
Phrenic Nerve Pathways
Understanding the pathways of the phrenic nerve can help in diagnosing and treating various medical conditions.
- The phrenic nerve travels downward through the thorax to reach the diaphragm.
- It passes anterior to the root of the lung.
- The right phrenic nerve passes through the vena cava hiatus in the diaphragm.
- The left phrenic nerve pierces the diaphragm separately from the vena cava.
- Both nerves innervate the diaphragm from its lower surface.
Clinical Significance
The phrenic nerve and diaphragm have significant clinical implications.
- Phrenic nerve injury can occur during surgical procedures, especially those involving the neck or chest.
- Diaphragmatic hernias can result from congenital defects or trauma, affecting breathing.
- Hiccups are caused by involuntary contractions of the diaphragm.
- Phrenic nerve stimulation is a treatment for patients with diaphragmatic paralysis.
- The sniff test is used to assess diaphragmatic function by observing diaphragm movement during a quick nasal inhalation.
Interesting Facts
Here are some lesser-known facts about the phrenic nerve and diaphragm.
- The word "phrenic" comes from the Greek word "phren," meaning diaphragm or mind.
- Ancient Greeks believed the diaphragm was the seat of emotions and thought.
- The diaphragm is the primary muscle used in singing and playing wind instruments.
- Some animals, like birds, do not have a diaphragm and use other muscles for respiration.
- The diaphragm has openings for the esophagus, aorta, and inferior vena cava.
Phrenic Nerve Disorders
Various disorders can affect the phrenic nerve and diaphragm, impacting respiratory health.
- Phrenic nerve palsy can result from viral infections, trauma, or autoimmune diseases.
- Diaphragmatic flutter is a rare condition causing rapid, involuntary contractions of the diaphragm.
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) can lead to phrenic nerve degeneration and respiratory failure.
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) can cause diaphragmatic dysfunction.
- Phrenic nerve tumors, although rare, can compress the nerve and impair its function.
Diagnostic and Treatment Approaches
Medical professionals use various techniques to diagnose and treat phrenic nerve and diaphragm issues.
- Electromyography (EMG) can assess the electrical activity of the diaphragm.
- Ultrasound imaging helps visualize diaphragm movement and detect abnormalities.
- Surgical procedures, like diaphragmatic plication, can improve breathing in patients with diaphragmatic paralysis.
Final Thoughts on Phrenic Nerve
The phrenic nerve plays a crucial role in our daily lives. It controls the diaphragm, which is essential for breathing. Without it, we wouldn't be able to inhale or exhale properly. This nerve also has sensory functions, sending signals from the diaphragm to the brain. Damage to the phrenic nerve can lead to serious health issues like diaphragmatic paralysis. Knowing about this nerve helps us appreciate the complexity of our bodies. It's amazing how such a small part can have such a big impact. So, next time you take a deep breath, remember the phrenic nerve working behind the scenes. Understanding these facts can help you make better health choices and recognize symptoms if something goes wrong. Stay curious and keep learning about the wonders of the human body.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
