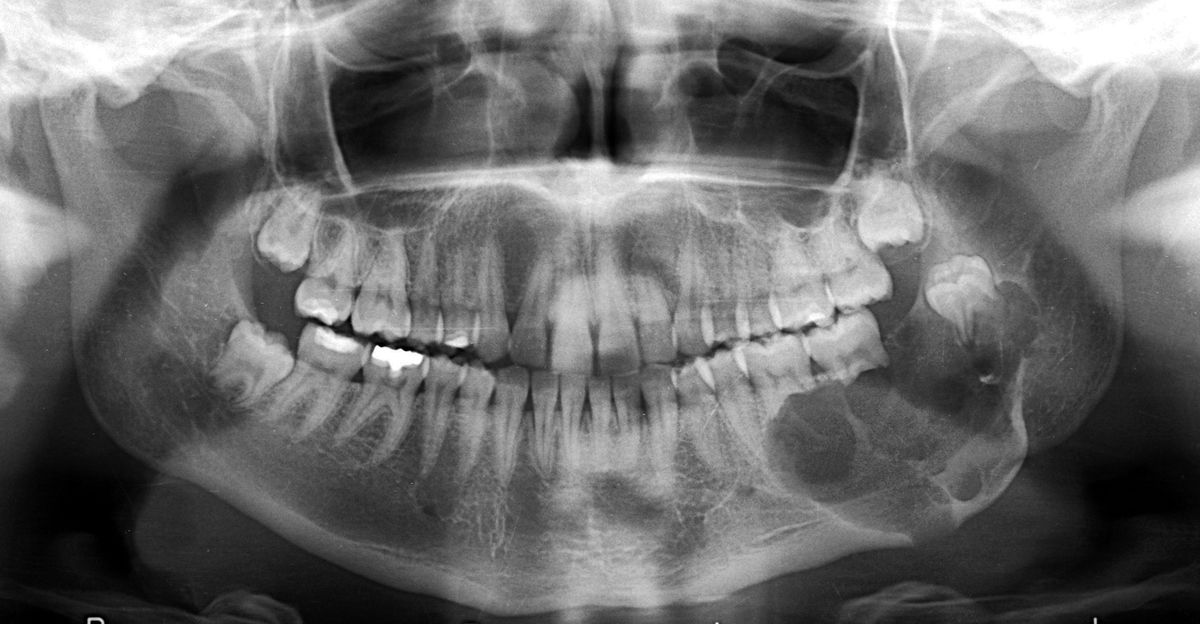
Odontogenic tumors might sound like a mouthful, but they’re actually quite fascinating. These growths originate from the tissues that form teeth. While some are harmless, others can be more serious. Did you know that these tumors can develop in both children and adults? They come in various types, each with unique characteristics. For instance, ameloblastomas are known for their aggressive nature, while odontomas are usually benign and often discovered accidentally during routine dental X-rays. Understanding these tumors is crucial for early detection and treatment. Ready to learn more? Here are 33 intriguing facts about odontogenic tumors that will expand your knowledge and maybe even surprise you!
What is an Odontogenic Keratocyst?
An odontogenic keratocyst (OKC) is a type of jaw cyst that originates from the dental lamina, which is part of the tissue that forms teeth. These cysts can be aggressive and have a high recurrence rate. They are often discovered during routine dental X-rays.
- OKCs are most commonly found in the lower jaw (mandible). They often appear in the area near the third molars or wisdom teeth.
- They can grow quite large before causing noticeable symptoms. This makes early detection through X-rays crucial.
- OKCs can be associated with Nevoid Basal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome (NBCCS). This genetic condition increases the risk of developing multiple OKCs.
- They are lined by a thin layer of keratinized epithelium. This unique lining differentiates them from other types of cysts.
- OKCs can cause displacement of teeth. As they grow, they can push teeth out of their normal alignment.
- They are more common in males than females. The reason for this gender difference is not well understood.
- OKCs can occur at any age but are most common in people between 10 and 40 years old. This wide age range makes regular dental check-ups important for everyone.
- They can be asymptomatic for a long time. Many people do not realize they have an OKC until it is found on an X-ray.
- Surgical removal is the primary treatment. Complete removal is necessary to reduce the risk of recurrence.
- Recurrence rates can be as high as 60%. This high rate of recurrence makes follow-up care essential.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Odontogenic Keratocysts
While OKCs can be asymptomatic, there are certain signs and diagnostic methods that can help identify them.
- Swelling in the jaw is a common symptom. This swelling can be painless or accompanied by discomfort.
- Pain or discomfort in the jaw can occur. This is usually a sign that the cyst has grown significantly.
- Drainage of fluid from the cyst can happen. This fluid is often clear or yellowish.
- X-rays are the most common diagnostic tool. They can reveal the presence of a cyst even if there are no symptoms.
- CT scans and MRIs can provide more detailed images. These imaging techniques can help determine the size and exact location of the cyst.
- Biopsy is sometimes necessary. A small sample of the cyst lining can be examined under a microscope to confirm the diagnosis.
- Dental professionals often discover OKCs during routine check-ups. Regular dental visits are crucial for early detection.
- OKCs can sometimes be mistaken for other types of cysts or tumors. Accurate diagnosis is important for proper treatment.
- Genetic testing may be recommended for those with multiple OKCs. This can help identify underlying conditions like NBCCS.
Treatment and Management of Odontogenic Keratocysts
Effective management of OKCs involves a combination of surgical and non-surgical approaches.
- Marsupialization is a less invasive treatment option. This procedure involves creating a small opening in the cyst to allow it to drain and shrink.
- Enucleation is the complete surgical removal of the cyst. This is the most common treatment method.
- Curettage involves scraping the cyst lining after enucleation. This helps remove any remaining cyst cells.
- Chemical cauterization can reduce recurrence rates. Applying a chemical agent to the cyst site can help destroy residual cells.
- Cryotherapy involves freezing the cyst site. This method can also help reduce the risk of recurrence.
- Regular follow-up appointments are essential. Monitoring for recurrence is crucial for long-term management.
- Radiographic monitoring is often used during follow-up. X-rays can help detect any new cyst formation.
- Patients may need multiple surgeries. Due to the high recurrence rate, additional surgeries may be necessary.
- Adjunctive therapies like decompression can be used. This involves placing a small tube in the cyst to allow it to drain over time.
- Maintaining good oral hygiene is important. This can help prevent complications and support overall dental health.
Complications and Prognosis of Odontogenic Keratocysts
Understanding potential complications and the long-term outlook for those with OKCs is important for effective management.
- Infection is a possible complication. If the cyst becomes infected, it can cause pain and swelling.
- Pathologic fractures of the jaw can occur. Large cysts can weaken the jawbone, making it more susceptible to fractures.
- Malignant transformation is rare but possible. In very rare cases, OKCs can develop into cancer.
- The overall prognosis for OKCs is generally good with proper treatment. Regular monitoring and appropriate management can help ensure a positive outcome.
Final Thoughts on Odontogenic Tumors
Odontogenic tumors, though rare, are fascinating and complex. These growths originate from the tissues that form teeth, and they can vary greatly in their behavior and treatment. Some are benign and slow-growing, while others can be aggressive and require more extensive treatment. Understanding the different types, such as ameloblastomas and odontomas, helps in early detection and effective management. Regular dental check-ups play a crucial role in identifying these tumors early, ensuring better outcomes. Awareness and education about these conditions can lead to timely intervention and improved patient care. Remember, if you notice any unusual changes in your oral health, consult a dental professional promptly. Knowledge about odontogenic tumors empowers you to take proactive steps in maintaining your oral health. Stay informed, stay healthy.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
