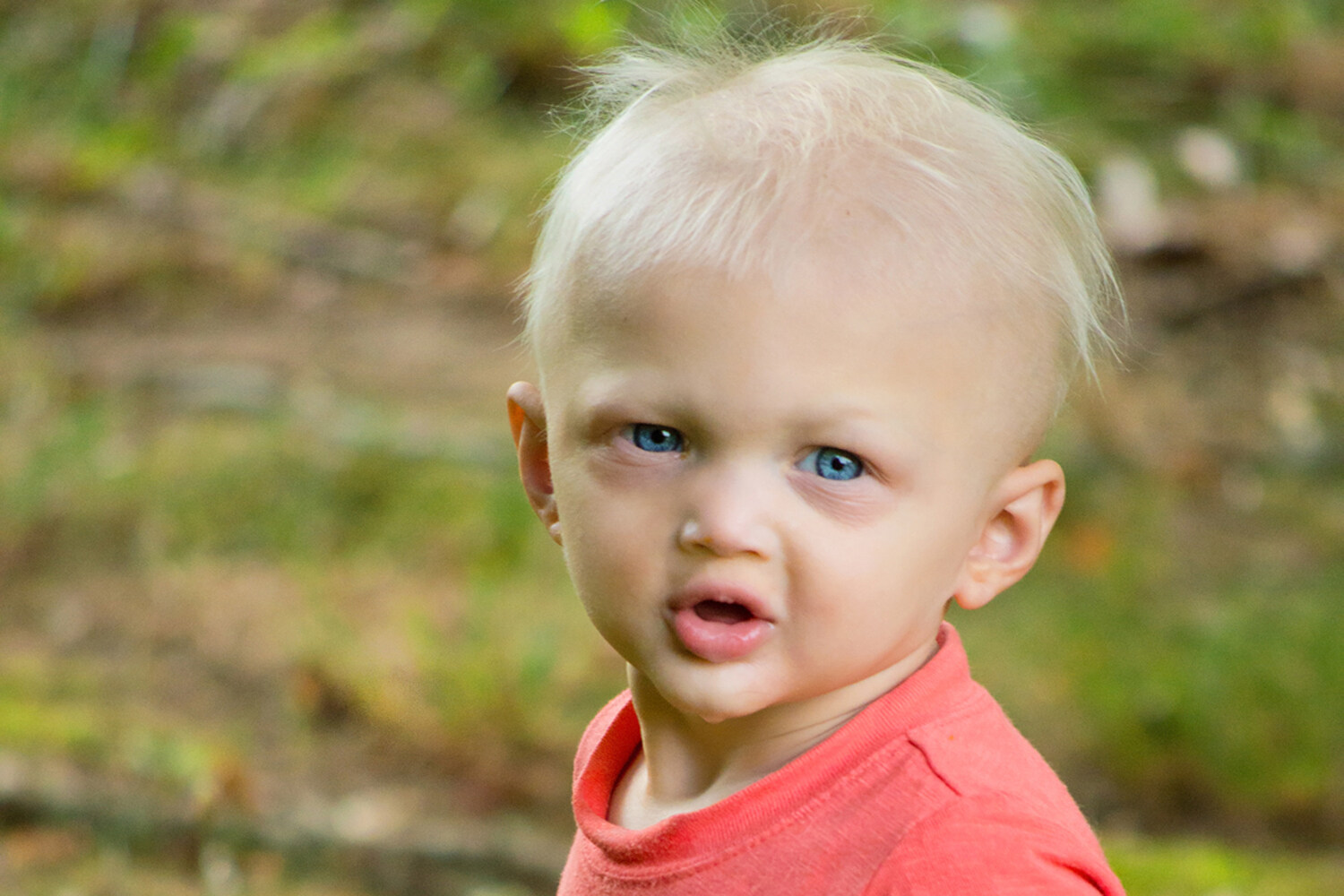
What is Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia? Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia (HED) is a rare genetic disorder affecting the development of skin, hair, nails, teeth, and sweat glands. Imagine having sparse hair, missing teeth, and trouble sweating. That's what life can be like for someone with HED. Affecting about 1 in 20,000 newborns, this condition is often inherited in an X-linked recessive pattern, meaning boys are more frequently affected. Symptoms can range from mild to severe, impacting daily life and health. Understanding HED is crucial for managing its symptoms and improving the quality of life for those affected.
Understanding Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia
Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia (HED) is a rare genetic disorder affecting the development of ectodermal tissues. These tissues include skin, hair, nails, teeth, and sweat glands. Let's dive into some key facts about this condition.
-
Definition: HED is a congenital disorder marked by abnormal development of ectodermal tissues, leading to symptoms like sparse hair, missing teeth, and reduced sweating.
-
Prevalence: This condition affects about 1 in 20,000 newborns globally, making it one of the more common forms of ectodermal dysplasia.
-
Genetic Basis: Mutations in the EDA gene cause most cases of HED. Other genes like EDAR, EDARADD, and WNT10A can also be involved.
Inheritance and Clinical Features
Understanding how HED is inherited and its clinical features can help in early diagnosis and management.
-
X-Linked Inheritance: HED is inherited in an X-linked recessive pattern, meaning males are more often affected, while females usually act as carriers.
-
Clinical Features: Affected individuals typically have sparse, light-colored, brittle hair that grows slowly. In some cases, hair may be absent.
-
Teeth Anomalies: Missing or malformed teeth are common. Present teeth may be peg-shaped and erupt later than usual.
-
Sweat Gland Defects: Reduced ability to sweat (hypohidrosis) due to fewer or dysfunctional sweat glands is a hallmark of HED, leading to heat intolerance.
-
Facial Features: Distinctive facial features include a prominent forehead, thick lips, and a flattened nasal bridge.
Skin, Respiratory, and Immune System Implications
HED affects more than just hair and teeth. It can also impact the skin, respiratory system, and immune function.
-
Skin Characteristics: The skin may appear thin, dry, and soft with abnormal pigmentation. Around the eyes, it may be darkly pigmented and finely wrinkled.
-
Respiratory Issues: Many individuals experience recurrent respiratory infections and may have underdeveloped or absent mucous glands in the respiratory tract.
-
Immune System Implications: Some patients may have decreased immune function, including hypogammaglobulinemia and autoimmune cytopenias, increasing infection risk.
-
Chronic Skin Conditions: Chronic skin problems like eczema, intertrigo, seborrheic dermatitis, and erythroderma are common.
Additional Physical Manifestations
HED can also affect nails, voice, and even gastrointestinal health.
-
Nail Involvement: While nails are typically unaffected, some cases may show brittle or thin nails.
-
Hoarseness of Voice: Abnormal development of laryngeal structures can cause hoarseness.
-
Gastroesophageal Reflux: Affected individuals may suffer from gastroesophageal reflux, leading to additional health complications.
-
Breast Aplasia/Hypoplasia: Rarely, affected males may experience unilateral or bilateral breast aplasia/hypoplasia.
Heat Tolerance and Hyperthermia
Managing body temperature is crucial for those with HED due to their reduced ability to sweat.
-
Heat Tolerance: Individuals often have a history of heat intolerance. The inability to sweat effectively leads to elevated core body temperatures, especially in hot environments.
-
Hyperthermia: Hyperthermia, or abnormally high body temperature, is a significant risk, potentially leading to life-threatening health problems if not managed properly.
Diagnosis and Variability in Expression
Diagnosing HED involves recognizing clinical features and understanding the variability in expression, especially among female carriers.
-
Diagnostic Features: Diagnosis is based on clinical features like sparse hair, missing teeth, and reduced sweating. Genetic testing can confirm mutations in the EDA gene or other associated genes.
-
Variability in Expression: Female carriers may show a range of clinical features, from a carrier state to full-blown disease, due to the random nature of X-inactivation.
Immunodeficiency and Cutaneous Manifestations
Some patients with HED may also present with immunodeficiency and various skin conditions.
-
Immunodeficiency: A subset of patients may have immunodeficiency in the form of hypogammaglobulinemia and autoimmune cytopenias, experiencing a milder decrease in sweating.
-
Cutaneous Manifestations: Conditions like erythroderma, seborrheic dermatitis, and intertrigo are common, significantly impacting quality of life.
Dental Features and Carrier Detection
Dental anomalies are a critical aspect of HED, and carrier detection is important for families with a history of the condition.
-
Dental Features: Affected individuals often have peg-shaped or missing teeth, leading to dental complications like malocclusion and difficulty with oral hygiene.
-
Carrier Detection: Genetic testing can identify female carriers who may pass the mutated gene to their offspring.
Management, Prognosis, and Genetic Counseling
While there is no cure for HED, management focuses on alleviating symptoms and preventing complications.
-
Management and Treatment: Management includes measures to control body temperature, dental care, and treatment of associated skin conditions.
-
Prognosis: Prognosis varies depending on symptom severity and associated complications. With proper management, many can lead relatively normal lives, though ongoing medical care may be required.
-
Genetic Counseling: Essential for families affected by HED, genetic counseling helps understand inheritance patterns, risk of recurrence, and options for prenatal diagnosis.
Prenatal Diagnosis, Research, and Awareness
Advances in genetic testing and research are improving the management of HED.
-
Prenatal Diagnosis: Possible through genetic testing of amniotic fluid or chorionic villus sampling, providing valuable information for at-risk families.
-
Research and Advances: Ongoing research aims to better understand the molecular mechanisms underlying HED and develop more effective treatments.
-
Awareness and Support: Raising awareness is crucial for improving diagnosis and management. Support groups and advocacy organizations provide emotional support and resources to affected individuals and their families.
Understanding Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia
Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia (HED) is a rare genetic disorder affecting hair, teeth, skin, and sweat glands. It’s caused by mutations in genes like EDA, EDAR, EDARADD, and WNT10A. This condition, often inherited in an X-linked recessive pattern, primarily impacts males. Symptoms include sparse hair, missing or malformed teeth, and reduced sweating, leading to heat intolerance. Distinctive facial features and chronic skin conditions are also common. Diagnosis relies on clinical features and genetic testing. While there’s no cure, management focuses on symptom relief and preventing complications. Genetic counseling and prenatal diagnosis are crucial for families with a history of HED. Ongoing research aims to improve understanding and treatment. Awareness and support from advocacy groups play a vital role in helping those affected. Understanding HED’s complexities can lead to better care and quality of life for individuals living with this condition.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.