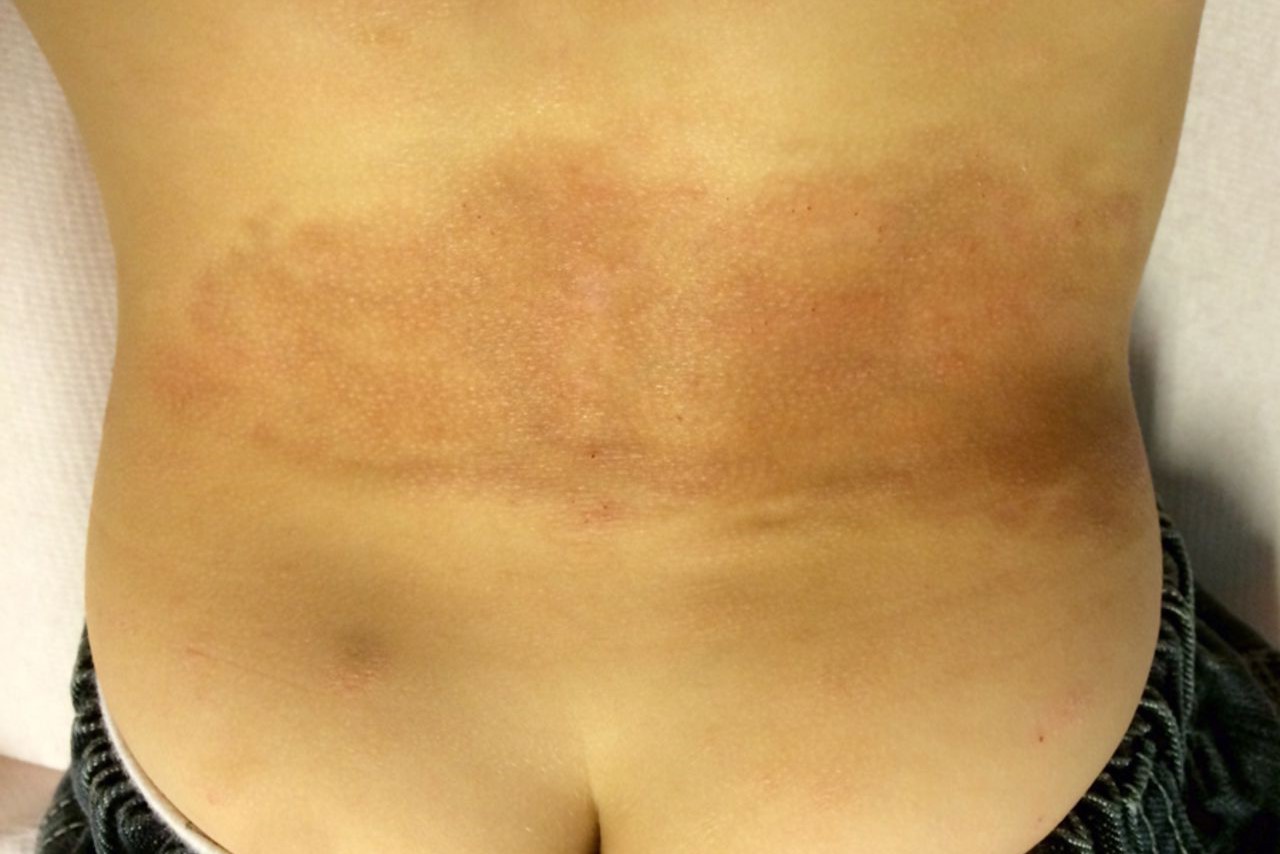
What is Atrophoderma? Atrophoderma is a rare skin condition where the skin progressively thins and shrinks, forming atrophic lesions. These lesions often appear on the face, neck, and upper torso. The exact cause remains unclear, but it is frequently linked to autoimmune disorders like lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, and dermatomyositis. Symptoms include flat or slightly depressed patches with a smooth, shiny surface. Diagnosis is primarily clinical, supported by medical history and physical examination. Treatment focuses on symptom management, using topical corticosteroids and moisturizers. Understanding atrophoderma's impact on quality of life and exploring potential treatments are crucial for those affected.
Understanding Atrophoderma
Atrophoderma is a rare skin condition that causes the skin to thin and shrink, forming atrophic lesions. These lesions can appear anywhere on the body but are most commonly found on the face, neck, and upper torso. Let's dive into some key facts about this condition.
-
Definition and Classification
Atrophoderma is classified into several subtypes, including atrophoderma vermiculata, atrophoderma linearis, and atrophoderma idiopathicum. Each subtype has unique clinical features. -
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of atrophoderma remains unclear. However, it is often linked to autoimmune disorders like lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, and dermatomyositis. Genetic predisposition, environmental factors, and certain medications also play a role. -
Symptoms
The primary symptom is the appearance of atrophic lesions. These can be flat or slightly depressed with a smooth, shiny surface. Lesions vary in size from small patches to large areas. -
Clinical Presentation
Symptoms usually develop gradually. Lesions may start as small patches that expand and merge over time. Sometimes, they are accompanied by hyperpigmentation or telangiectasias.
Diagnosing Atrophoderma
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for managing atrophoderma. Here are some important aspects of the diagnostic process.
-
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is mainly clinical, based on the characteristic appearance of the lesions. A thorough medical history and physical examination are essential. Biopsy may be performed to rule out other conditions. -
Differential Diagnosis
Atrophoderma can be confused with conditions like lichen sclerosus, morphea, and scleroderma. A differential diagnosis ensures accurate identification and treatment.
Treatment and Management
Managing atrophoderma involves a combination of symptomatic treatment and addressing underlying conditions. Here are some treatment options.
-
Treatment Options
There is no specific treatment for atrophoderma. Management is largely symptomatic. Topical corticosteroids and moisturizers may help alleviate symptoms. Systemic corticosteroids might be prescribed for associated autoimmune disorders. -
Prognosis
Prognosis varies depending on the underlying cause and extent of lesions. Some cases may resolve spontaneously, while others persist indefinitely. -
Quality of Life Impact
Atrophoderma can significantly impact quality of life due to aesthetic concerns. Psychological support and counseling may be necessary.
Genetic and Environmental Factors
Both genetic and environmental factors can influence the development and progression of atrophoderma. Let's explore these aspects.
-
Genetic Considerations
While not typically inherited, atrophoderma can occur in families with a history of autoimmune disorders. Genetic testing may be considered in such cases. -
Environmental Factors
Exposure to environmental factors like UV radiation can exacerbate atrophoderma. Protecting the skin from the sun and using protective clothing can help manage symptoms.
Medications and Autoimmune Associations
Certain medications and autoimmune disorders are closely linked to atrophoderma. Understanding these associations is key to effective management.
-
Medications
Medications like antimalarials and immunosuppressants may trigger or worsen atrophoderma. Stopping these medications under medical supervision may help. -
Autoimmune Associations
Atrophoderma is often associated with autoimmune disorders such as lupus erythematosus and scleroderma. Managing these underlying conditions is crucial.
Skin Care and Psychological Support
Proper skin care and psychological support are essential components of managing atrophoderma. Here are some tips and considerations.
-
Skin Care
Maintaining good skin care practices is vital. Using gentle cleansers and moisturizers can help keep the skin hydrated and reduce lesion appearance. -
Psychological Support
Atrophoderma can have significant psychological implications. Seeking psychological support can help individuals cope with body image and self-esteem issues.
Surgical and Lifestyle Considerations
In some cases, surgical intervention and lifestyle modifications may be necessary. Let's look at these options.
-
Surgical Options
Surgical intervention may be considered to improve lesion appearance. This should be done under the guidance of a dermatologist. -
Lifestyle Modifications
Avoiding smoking and reducing stress can help manage symptoms. Making these lifestyle changes can have a positive impact.
Nutritional and Complementary Therapies
Nutrition and complementary therapies can play a role in managing atrophoderma. Here are some considerations.
-
Nutritional Considerations
Maintaining a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients is important for skin health. Vitamin D deficiencies may exacerbate atrophoderma. -
Complementary Therapies
Therapies like acupuncture and herbal remedies may help alleviate symptoms. These should be used under healthcare provider guidance.
Research and Support
Ongoing research and support groups are crucial for advancing our understanding and management of atrophoderma. Here are some key points.
-
Research and Development
Research into atrophoderma is ongoing. Studies focus on underlying causes and potential treatments. Participating in clinical trials may provide access to new treatments. -
Support Groups
Joining support groups can provide emotional support and connect individuals with others experiencing similar conditions. -
Awareness and Education
Raising awareness about atrophoderma is important. Educating healthcare providers can help ensure accurate diagnosis and management.
Genetic Testing and Environmental Protection
Genetic testing and protecting the skin from environmental factors are important considerations. Let's explore these aspects.
-
Genetic Testing
Genetic testing may be considered in families with a history of autoimmune disorders. This can help identify individuals at risk. -
Environmental Protection
Protecting the skin from UV radiation can help manage symptoms. Using protective clothing and sunscreen reduces the risk of exacerbation.
Medication and Autoimmune Management
Managing medications and underlying autoimmune disorders is crucial for treating atrophoderma. Here are some key points.
-
Medication Management
Managing medications that may trigger or worsen atrophoderma is crucial. Stopping these medications under medical supervision can help. -
Autoimmune Management
Managing underlying autoimmune disorders is essential. This may involve using immunosuppressants or other medications.
Skin Hygiene and Psychological Impact
Maintaining good skin hygiene and addressing the psychological impact of atrophoderma are important. Here are some tips.
-
Skin Hygiene
Maintaining good skin hygiene is important. Using gentle cleansers and moisturizers can help keep the skin hydrated and reduce lesion appearance. -
Psychological Impact
Atrophoderma can have significant psychological implications. Seeking psychological support can help individuals cope with body image and self-esteem issues.
Surgical Considerations and Future Research
Surgical intervention and future research are important aspects of managing atrophoderma. Let's explore these areas.
-
Surgical Considerations
Surgical intervention may be considered to improve lesion appearance. This should be done under the guidance of a dermatologist. -
Future Research Directions
Future research should focus on identifying underlying causes and developing effective treatments. Advanced diagnostic techniques and innovative therapeutic approaches are essential.
Final Thoughts on Atrophoderma
Atrophoderma is a rare skin condition that causes the skin to thin and shrink, leading to atrophic lesions. It often links to autoimmune disorders like lupus and scleroderma. Symptoms include flat or slightly depressed lesions that can expand over time. Diagnosis is mainly clinical, sometimes requiring a biopsy to rule out similar conditions. Treatment focuses on symptom management, using topical corticosteroids and moisturizers. Psychological support is crucial due to the impact on self-esteem and body image. Protecting the skin from environmental factors and maintaining good skin care practices can help manage symptoms. Ongoing research aims to uncover more about the causes and potential treatments. Understanding and managing atrophoderma involves a comprehensive approach, addressing both physical and emotional aspects.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


