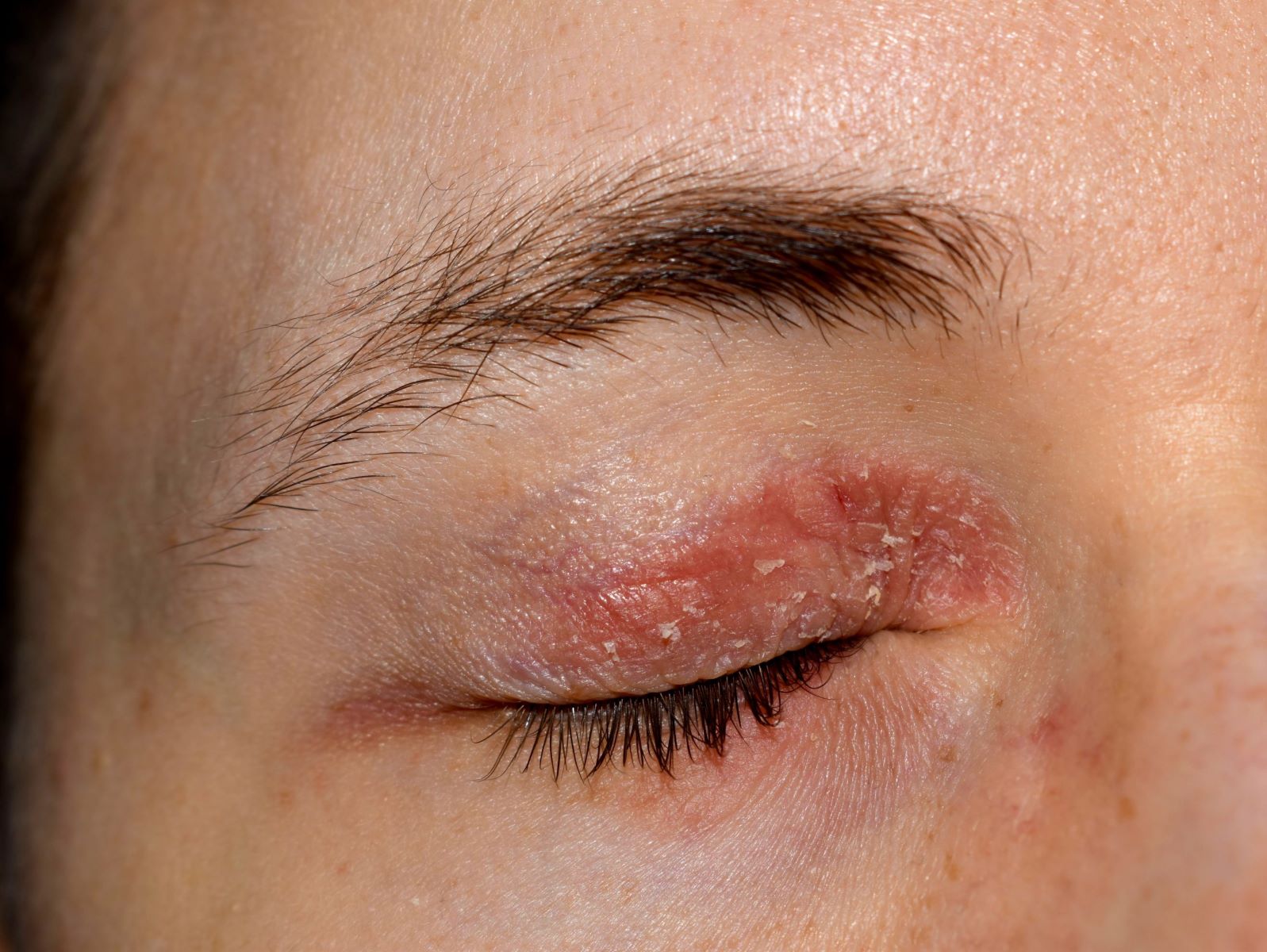
What is atopic conjunctivitis? Atopic conjunctivitis is an eye condition linked to atopic dermatitis, a chronic skin issue causing dry, itchy skin. This condition affects the eyes, leading to redness, itching, and watery discharge. Allergens like pollen, dust mites, and pet dander often trigger it. The immune system reacts by releasing histamines, causing inflammation. Symptoms can severely impact daily life, making tasks like reading or driving difficult. Diagnosis involves a thorough eye exam and sometimes allergy testing. Treatment includes antihistamine eye drops, mast cell stabilizers, and avoiding allergens. Severe cases may require referral to an ophthalmologist for specialized care.
Understanding Atopic Conjunctivitis
Atopic conjunctivitis is a condition that affects many people, especially those with atopic dermatitis. It can cause significant discomfort and impact daily life. Here are some important facts to help you understand this condition better.
-
Definition: Atopic conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the conjunctiva, the membrane covering the white part of the eye and the inner eyelid, often linked to atopic dermatitis.
-
Prevalence: A significant portion of patients with atopic dermatitis also experience conjunctivitis, although the exact prevalence can vary depending on the population studied.
-
Symptoms: Common symptoms include redness, itching, and watery discharge. The eyes may also appear swollen and inflamed.
Causes and Triggers
Understanding what causes and triggers atopic conjunctivitis can help in managing the condition more effectively.
-
Causes: The primary cause is the allergic response to allergens such as pollen, dust mites, or pet dander, which is common in individuals with atopic dermatitis.
-
Types of Allergens: Common allergens include pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and mold. These allergens trigger an immune response that leads to inflammation in the eyes.
-
Immune Response: The immune system produces IgE antibodies in response to allergens, which then trigger the release of histamines and other inflammatory substances. This reaction causes the symptoms of atopic conjunctivitis.
Symptoms and Impact
The symptoms of atopic conjunctivitis can be quite bothersome and affect daily activities.
-
Eye Discharge: The discharge from the eyes can be watery or thick and may contain mucus or pus. This discharge is often a result of the body's attempt to flush out the allergen.
-
Eye Sensitivity: Individuals with atopic conjunctivitis may experience sensitivity to light, which can exacerbate the discomfort and make it difficult to perform daily activities.
-
Itching and Irritation: The itching and irritation caused by atopic conjunctivitis can be intense and may lead to excessive rubbing of the eyes, which can further irritate the condition.
-
Impact on Daily Life: The symptoms of atopic conjunctivitis can significantly impact daily life, making it difficult to perform tasks that require clear vision, such as reading or driving.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Proper diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing atopic conjunctivitis effectively.
-
Diagnosis: Diagnosis is often based on clinical presentation and medical history. A thorough eye examination by an ophthalmologist may be necessary to rule out other conditions.
-
Diagnostic Workup: In some cases, a diagnostic workup may include skin prick testing or specific IgE testing to identify common aeroallergens.
-
Treatment Options: Treatment typically involves antihistamine eye drops or mast cell stabilizer eye drops to reduce inflammation and itching. In severe cases, oral antihistamines may be prescribed.
-
Antihistamine Eye Drops: These drops work by blocking histamine receptors, thereby reducing the allergic response and associated symptoms.
-
Mast Cell Stabilizer Eye Drops: These drops prevent the release of histamines from mast cells, thereby reducing inflammation and itching.
-
Oral Antihistamines: In severe cases, oral antihistamines may be prescribed to provide systemic relief from allergic symptoms.
-
Topical Corticosteroids: In some cases, topical corticosteroids may be used to reduce inflammation, but their use should be limited due to potential side effects.
Preventive Measures
Taking preventive measures can help reduce the frequency and severity of atopic conjunctivitis flare-ups.
-
Avoiding Allergens: One of the most effective treatments is avoiding the allergens that trigger the condition. This can include using HEPA filters, avoiding exposure to pets, and wearing protective eyewear.
-
Eye Care Products: Using eye care products such as artificial tears can help lubricate the eyes and reduce discomfort. However, these products should not contain preservatives that can irritate the eyes further.
-
Ophthalmologist Referral: In severe cases, referral to an ophthalmologist is recommended for further diagnostic workup and treatment. Atopic keratoconjunctivitis, a severe form of the condition, can lead to keratitis and blindness if not properly managed.
Complications and Co-existing Conditions
Atopic conjunctivitis can lead to complications if not managed properly and may coexist with other conditions.
-
Atopic Keratoconjunctivitis: This is a severe form of atopic conjunctivitis that involves inflammation of the cornea and conjunctiva. It requires prompt medical attention to prevent long-term complications.
-
Complications: Untreated or poorly managed atopic conjunctivitis can lead to complications such as corneal ulcers, vision loss, and chronic eye irritation.
-
Co-pathogenic Factors: Other factors such as blepharitis (inflammation of the eyelids) or infestation with demodex mites can also contribute to the development of atopic conjunctivitis in individuals with atopic dermatitis.
Diagnosis and Treatment Consensus
There is a general consensus among healthcare professionals on how to approach the diagnosis and treatment of atopic conjunctivitis.
-
Aetiological Classification: The classification of conjunctivitis can sometimes be straightforward, such as allergic rhinoconjunctivitis during pollen season or purulent infectious conjunctivitis in conjunction with impetiginized atopic dermatitis. However, in some cases, more extensive diagnostic workup is required.
-
Consensus Recommendations: There is consensus among dermatologists to initiate relevant treatment with eye drops or oral antihistamines before referring patients to an ophthalmologist for further management.
-
Skin Prick Testing: Skin prick testing or specific IgE testing for common aeroallergens is recommended for patients with atopic dermatitis and conjunctivitis to identify specific allergens and tailor treatment accordingly.
Interdisciplinary Care and Economic Impact
Managing atopic conjunctivitis often requires a team approach and can have significant economic implications.
-
Interdisciplinary Care: Effective management of atopic conjunctivitis requires coordination with an interdisciplinary team including dermatologists, ophthalmologists, and primary care physicians to address underlying systemic conditions and ensure comprehensive care.
-
Economic Burden: Atopic conjunctivitis imposes significant economic and social burdens on individuals and healthcare systems. The cost of treating bacterial conjunctivitis alone in the United States is estimated to be between $377 million and $857 million annually.
Seasonal Trends and Prevention
Understanding seasonal trends and preventive strategies can help manage atopic conjunctivitis more effectively.
-
Seasonal Trends: The occurrence of atopic conjunctivitis can vary seasonally. Allergic conjunctivitis is more prevalent during the spring and summer months when pollen counts are higher.
-
Prevention Strategies: Preventive strategies include avoiding exposure to known allergens, using protective eyewear, and maintaining good eye hygiene practices. Regular eye examinations by an ophthalmologist can also help in early detection and management of the condition.
Key Takeaways on Atopic Conjunctivitis
Atopic conjunctivitis, linked to atopic dermatitis, brings discomfort and potential complications. Symptoms like redness, itching, and watery discharge can disrupt daily life. Allergens such as pollen, dust mites, and pet dander often trigger this condition. Diagnosis involves clinical evaluation and sometimes skin prick tests. Treatments include antihistamine eye drops, mast cell stabilizers, and in severe cases, oral antihistamines or topical corticosteroids. Avoiding allergens and using protective eyewear can help manage symptoms. Severe cases may require an ophthalmologist's intervention to prevent complications like corneal ulcers. Effective management needs a team approach, including dermatologists and primary care physicians. Regular eye exams and good eye hygiene are crucial. Understanding these aspects can improve quality of life for those affected.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


