Dysdiadochokinesia might sound like a mouthful, but understanding it can be quite simple. This condition affects a person's ability to perform rapid, alternating movements. Imagine trying to quickly flip your hand back and forth or tap your foot repeatedly—dysdiadochokinesia makes these tasks difficult. It often points to issues in the cerebellum, the brain's coordination hub. Symptoms can include clumsiness, difficulty with tasks requiring fine motor skills, and even speech problems. Causes range from neurological disorders like multiple sclerosis to brain injuries. Diagnosing dysdiadochokinesia usually involves neurological exams and imaging tests. While there's no cure, treatments focus on managing symptoms through physical therapy and medication. Understanding this condition can help in recognizing early signs and seeking timely medical advice.
What is Dysdiadochokinesia?
Dysdiadochokinesia is a medical term that describes the inability to perform rapid, alternating movements. This condition often points to issues in the cerebellum, the part of the brain responsible for coordinating muscle movements. Let's dive into some intriguing facts about this condition.
-
Dysdiadochokinesia is a mouthful, but it breaks down into simpler parts: "dys" means bad or difficult, "diadocho" means successive, and "kinesia" means movement.
-
Cerebellum Connection: The cerebellum, located at the back of the brain, plays a crucial role in motor control. Damage to this area often results in dysdiadochokinesia.
-
Neurological Indicator: This condition can be an early sign of neurological disorders such as multiple sclerosis or Parkinson's disease.
-
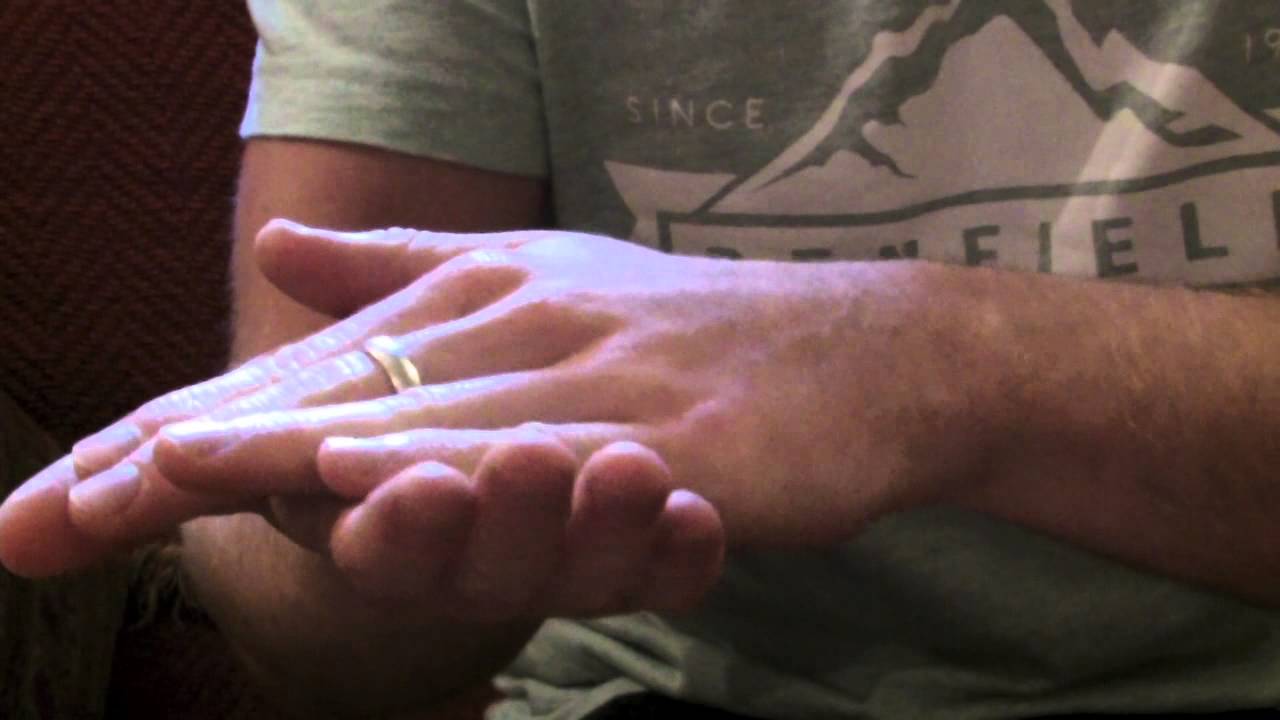
Testing for It: Doctors often ask patients to rapidly flip their hands back and forth on their laps to test for dysdiadochokinesia.
Causes of Dysdiadochokinesia
Understanding what causes dysdiadochokinesia can help in diagnosing and treating it. Various factors can lead to this condition, ranging from brain injuries to genetic disorders.
-
Brain Injuries: Traumatic brain injuries can damage the cerebellum, leading to dysdiadochokinesia.
-
Stroke: A stroke affecting the cerebellum can disrupt the brain's ability to coordinate movements.
-
Multiple Sclerosis: This autoimmune disease damages the protective covering of nerves, affecting the cerebellum and causing dysdiadochokinesia.
-
Genetic Disorders: Conditions like Friedreich's ataxia, a genetic disorder, can also result in dysdiadochokinesia.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms and getting a proper diagnosis is crucial for managing dysdiadochokinesia. Here are some key points to consider.
-
Clumsiness: People with dysdiadochokinesia often appear clumsy or uncoordinated.
-
Difficulty with Tasks: Simple tasks like buttoning a shirt or typing can become challenging.
-
Speech Issues: Some individuals may experience slurred or slow speech.
-
Medical History: A thorough medical history and neurological exam are essential for diagnosis.
Treatment Options
While there is no cure for dysdiadochokinesia, various treatments can help manage the symptoms and improve quality of life.
-
Physical Therapy: Exercises designed to improve coordination and strength can be beneficial.
-
Occupational Therapy: This helps individuals adapt to daily activities and improve motor skills.
-
Medications: Drugs used to treat underlying conditions like multiple sclerosis or Parkinson's can also help manage dysdiadochokinesia.
-
Speech Therapy: For those with speech difficulties, therapy can improve communication skills.
Interesting Facts
Here are some lesser-known but fascinating facts about dysdiadochokinesia that you might find intriguing.
-
Historical Background: The term dysdiadochokinesia was first coined by German neurologist Heinrich Hoffmann in the 19th century.
-
Not Just Humans: Animals, particularly those used in neurological research, can also exhibit dysdiadochokinesia.
-
Age Factor: While it can affect people of all ages, older adults are more commonly diagnosed due to the higher prevalence of strokes and neurodegenerative diseases.
-
Gender Neutral: Dysdiadochokinesia affects both men and women equally.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand dysdiadochokinesia and develop more effective treatments. Here are some exciting developments.
-
Brain Imaging: Advanced imaging techniques like MRI and CT scans are helping researchers pinpoint the exact areas of the brain affected.
-
Genetic Studies: Research into genetic disorders linked to dysdiadochokinesia is providing new insights.
-
Robotics: Robotic devices are being developed to assist in physical therapy, offering more precise and consistent training.
-
Virtual Reality: VR technology is being explored as a tool for rehabilitation, providing immersive environments for therapy.
Everyday Life with Dysdiadochokinesia
Living with dysdiadochokinesia can be challenging, but many people find ways to adapt and thrive. Here are some tips and tricks.
-
Assistive Devices: Tools like button hooks and adaptive utensils can make daily tasks easier.
-
Support Groups: Connecting with others who have dysdiadochokinesia can provide emotional support and practical advice.
Final Thoughts on Dysdiadochokinesia
Dysdiadochokinesia (DDK) is a condition that affects the ability to perform rapid, alternating movements. It’s often linked to issues in the cerebellum, the part of the brain responsible for motor control. Recognizing DDK can help in diagnosing underlying neurological disorders like multiple sclerosis or cerebellar ataxia. Symptoms include clumsiness, difficulty with tasks requiring coordination, and sometimes speech problems. Treatment focuses on addressing the root cause and may involve physical therapy to improve motor skills. Early detection and intervention can make a significant difference in managing the condition. Understanding DDK is crucial for those affected and their caregivers, offering a pathway to better care and quality of life. Stay informed, seek medical advice if you notice symptoms, and remember that support is available.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
