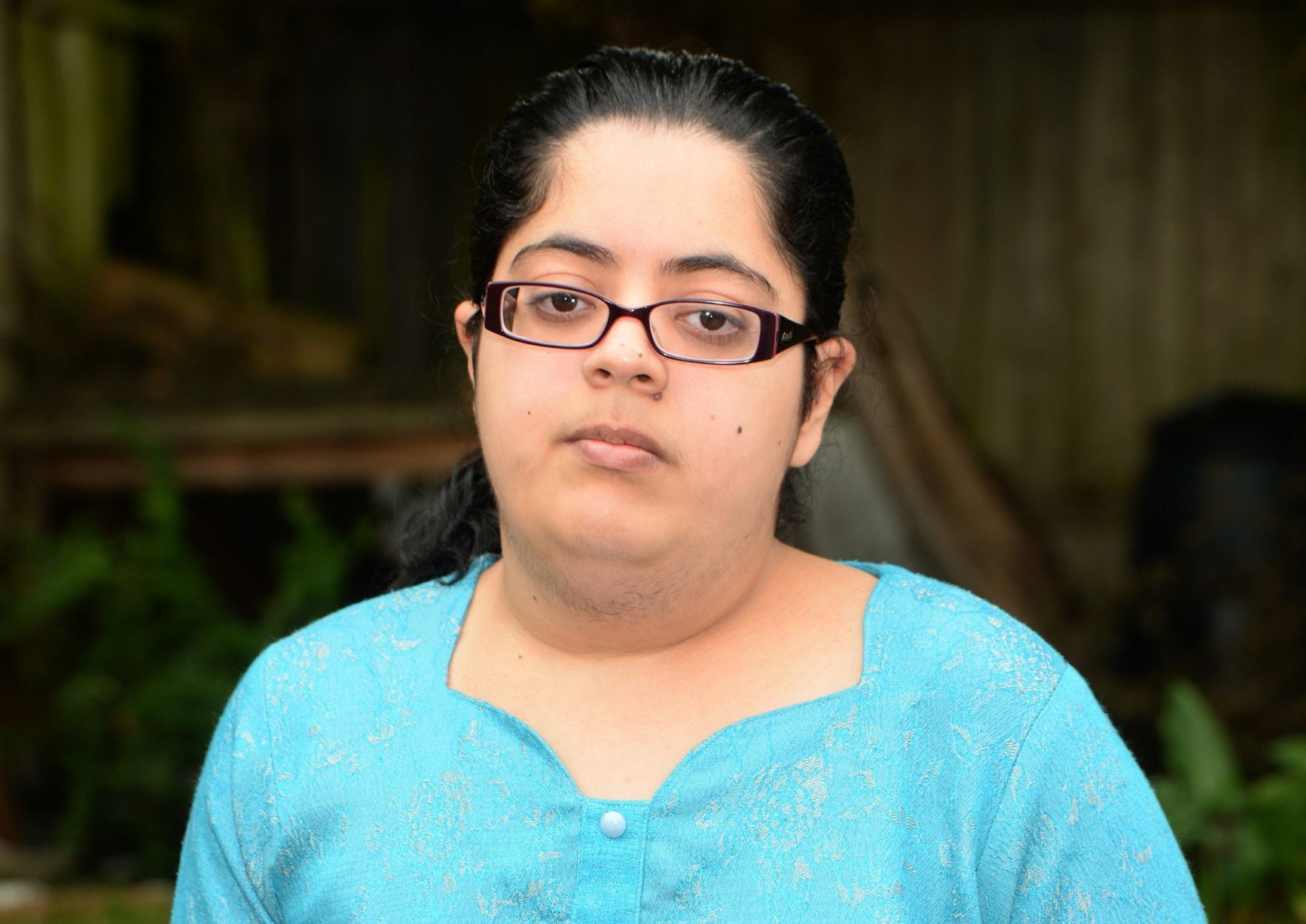
Laurence–Moon Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that affects multiple parts of the body. Characterized by obesity, intellectual disability, and vision problems, this condition can significantly impact daily life. Named after British doctors John Zachariah Laurence and Robert Charles Moon, who first described it in the 19th century, this syndrome is often confused with Bardet-Biedl Syndrome due to overlapping symptoms. Understanding Laurence–Moon Syndrome is crucial for those affected and their families. This article will provide 25 essential facts to help you grasp the complexities of this condition, from its causes to its symptoms and treatments. Let's dive into the world of Laurence–Moon Syndrome and uncover what makes it unique.
What is Laurence–Moon Syndrome?
Laurence–Moon Syndrome (LMS) is a rare genetic disorder that affects multiple parts of the body. It is often confused with Bardet-Biedl Syndrome due to overlapping symptoms. Here are some intriguing facts about this condition.
-
Rare Genetic Disorder: LMS is extremely rare, with only a few hundred cases reported worldwide.
-
First Described in 1866: The syndrome was first described by doctors John Laurence and Robert Moon in 1866.
-
Autosomal Recessive Inheritance: LMS is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, meaning both parents must carry the gene for a child to be affected.
-
Affects Multiple Systems: This syndrome impacts various body systems, including the nervous system, eyes, kidneys, and endocrine system.
Symptoms of Laurence–Moon Syndrome
The symptoms of LMS can vary widely from person to person. Here are some of the most common ones.
-
Progressive Vision Loss: Many individuals with LMS experience progressive vision loss due to retinal degeneration.
-
Intellectual Disability: Cognitive impairment is a common feature, though its severity can vary.
-
Obesity: A significant number of people with LMS struggle with obesity, often starting in childhood.
-
Polydactyly: Some individuals may have extra fingers or toes, a condition known as polydactyly.
-
Hypogonadism: This condition often leads to underdeveloped sexual organs and delayed puberty.
Diagnosing Laurence–Moon Syndrome
Diagnosing LMS can be challenging due to its rarity and the overlap of symptoms with other conditions.
-
Genetic Testing: Genetic testing is the most definitive way to diagnose LMS.
-
Clinical Evaluation: A thorough clinical evaluation, including a detailed family history, is crucial for diagnosis.
-
Ophthalmologic Examination: Eye exams can help identify retinal degeneration, a key symptom of LMS.
-
MRI and CT Scans: Imaging tests like MRI and CT scans can help assess brain and kidney abnormalities.
Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for LMS, various treatments can help manage its symptoms.
-
Vision Aids: Devices like magnifiers and screen readers can assist those with vision loss.
-
Special Education: Tailored educational programs can help individuals with intellectual disabilities.
-
Weight Management: Diet and exercise programs are essential for managing obesity.
-
Hormone Therapy: Hormone replacement therapy can help address hypogonadism.
Living with Laurence–Moon Syndrome
Living with LMS presents unique challenges, but support and resources can make a significant difference.
-
Support Groups: Connecting with others who have LMS can provide emotional support and practical advice.
-
Occupational Therapy: This can help individuals develop skills needed for daily living.
-
Assistive Technology: Tools like speech-to-text software can aid communication and learning.
-
Regular Monitoring: Ongoing medical check-ups are crucial for managing symptoms and preventing complications.
Research and Future Directions
Research into LMS is ongoing, with scientists working to better understand and treat this condition.
-
Genetic Research: Studies are exploring the specific genes involved in LMS to develop targeted therapies.
-
Clinical Trials: Some clinical trials are investigating new treatments for symptoms like retinal degeneration and obesity.
-
Patient Registries: Registries help researchers collect data on LMS, improving understanding and treatment options.
-
Awareness Campaigns: Raising awareness about LMS can lead to earlier diagnosis and better support for affected individuals.
Understanding Laurence–Moon Syndrome
Laurence–Moon Syndrome (LMS) is a rare genetic disorder that affects multiple body systems. It's characterized by retinitis pigmentosa, obesity, hypogonadism, polydactyly, and intellectual disability. This condition is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, meaning both parents must carry the gene for a child to be affected. Early diagnosis and intervention can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Living with LMS can be challenging, but support from healthcare professionals, family, and community can make a significant difference. Genetic counseling is recommended for families with a history of LMS to understand the risks and implications. Research continues to explore better treatments and potential cures, offering hope for those affected.
By spreading awareness and understanding of Laurence–Moon Syndrome, we can foster a more inclusive and supportive environment for individuals and families dealing with this condition.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.