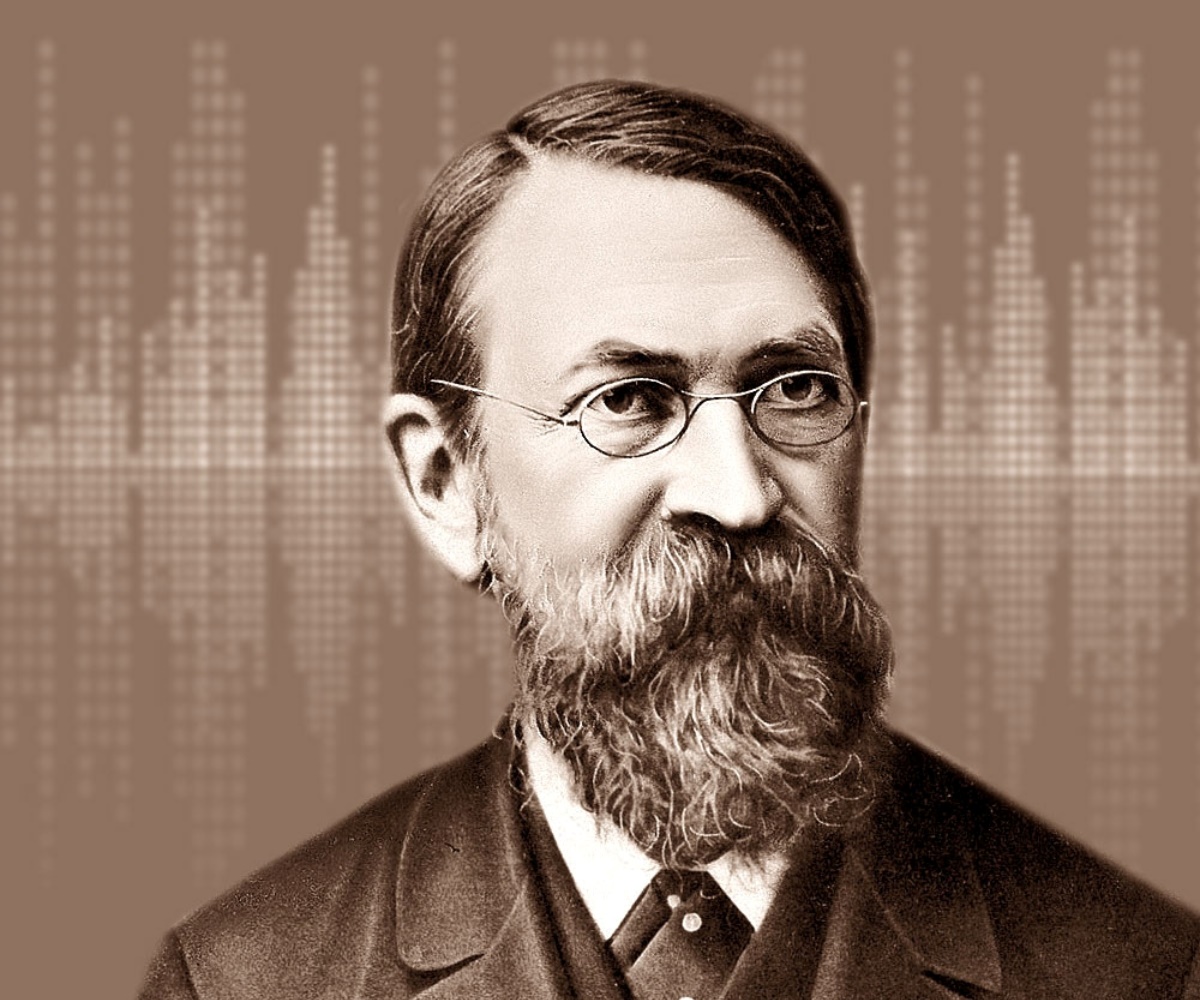
Ernst Mach, an Austrian physicist, philosopher, and psychologist, made numerous significant contributions to various fields of knowledge during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. With his insatiable curiosity and brilliant mind, Mach explored and advanced our understanding of topics ranging from mechanics and optics to the philosophy of science. Through his groundbreaking work and revolutionary ideas, Mach left an indelible mark on the scientific community and continues to influence researchers and scholars today. In this article, we will delve into 15 captivating facts about Ernst Mach, shedding light on his life, achievements, and enduring legacy. So, buckle up and get ready to embark on an intriguing journey through the extraordinary life of Ernst Mach.
Key Takeaways:
- Ernst Mach was a brilliant scientist and philosopher who made significant contributions to physics, psychology, and philosophy. His work on the Doppler effect, shock waves, and the Mach number continues to impact aviation and our understanding of the universe.
- Mach’s ideas on the relationship between physical stimuli and human perception have shaped our understanding of sensory perception. His curiosity, open-mindedness, and influence on fields like cosmology and logical positivism continue to inspire scientists and thinkers today.
Early Life and Education
Ernst Mach was born on February 18, 1838, in Chirlitz, in what is now the Czech Republic. He studied physics and mathematics at the University of Vienna.
Contributions to Science
Mach made significant contributions to various scientific disciplines, including physics, psychology, and philosophy. He is best known for his work on the Doppler effect and the study of shock waves.
The Mach Number
Mach introduced the concept of the “Mach number,” which is a dimensionless quantity used to describe the speed of an object relative to the speed of sound in a medium. It is widely used in aviation and supersonic flow analysis.
Mach’s Principle of Inertia
Mach proposed the “Mach’s Principle of Inertia,” which states that the inertia of an object is determined by the distribution of all the matter in the universe. This concept had a significant impact on the development of Einstein’s theory of general relativity.
The Mach Band
The Mach Band is a visual illusion named after Ernst Mach. It refers to the enhancement of contrast between light and dark areas of an image near the boundary of those regions.
Mach’s Experimental Investigations
Mach conducted numerous experiments to investigate various phenomena, including the effect of the rotation of the Earth on inertia and the behavior of shock waves. His meticulous approach to experimentation greatly influenced later scientists.
Mach’s Influence on Psychophysics
Mach’s research in psychophysics, the study of the relationship between physical stimuli and human perception, had a profound impact on the field. His ideas shaped the development of theories related to sensory perception.
Mach’s Critique of Newtonian Space and Time
Mach criticized the absolute notions of space and time in Newtonian physics, advocating for a relational view where the properties of space and time depend on the distribution of matter. His views challenged the prevailing scientific worldview of his time.
Mach’s Influence on Logical Positivism
Mach’s philosophical ideas influenced the development of logical positivism, a philosophical movement that emphasized the importance of empirical verification in understanding the world. His emphasis on observation and experience resonated with the positivist thinkers of the early 20th century.
Mach’s Academic Career
Mach held various academic positions throughout his career, including a professorship at the University of Vienna. He mentored several prominent scientists, including Ludwig Boltzmann and Sigmund Freud.
Mach’s Literary Contributions
Mach was not only a prolific scientist but also a skilled writer. He authored several books, including “The Science of Mechanics” and “The Analysis of Sensations,” which explored his ideas on physics, psychology, and philosophy.
Mach’s Legacy
Ernst Mach’s groundbreaking work continues to influence the fields of physics, psychology, and philosophy to this day. His ideas and concepts have shaped our understanding of the universe and the nature of human perception.
Awards and Recognition
Mach received numerous awards and honors throughout his career, including being elected as a member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences and the Vienna Academy of Sciences.
Mach’s Curiosity and Open-mindedness
Mach was known for his intellectual curiosity and openness to new ideas. He constantly sought to expand his knowledge and actively engaged in discussions with other prominent scientists and philosophers of his time.
The Mach Principle in Cosmology
While initially proposed in the context of inertia, the Mach Principle has also found application in cosmology, particularly in the study of the large-scale structure of the universe.
Conclusion
Ernst Mach was truly a remarkable figure, whose contributions to various fields, including physics, philosophy, and psychology, have left an indelible mark on the world. From his groundbreaking work on the speed of sound to his influential ideas on the nature of perception, Mach’s intellectual prowess and relentless pursuit of knowledge continue to inspire generations of scholars and researchers.
His multidisciplinary approach to understanding the physical world, coupled with his unwavering curiosity, propelled scientific progress and paved the way for future breakthroughs. Mach’s legacy serves as a testament to the power of interdisciplinary thinking and the significance of pushing the boundaries of human understanding.
In conclusion, learning about Ernst Mach opens up a fascinating window into the realm of scientific inquiry and deepens our appreciation for the complexity and interconnectedness of the universe.
FAQs
1. Who was Ernst Mach?
Ernst Mach was an Austrian physicist and philosopher who lived from 1838 to 1916. He made significant contributions to the fields of physics, philosophy of science, and psychology.
2. What is Mach’s principle?
Mach’s principle is the idea that the inertial properties of an object are determined by the distribution of matter in the universe. In simple terms, it suggests that the motion of an object is influenced by the masses and movements of other objects in the universe.
3. What is Mach’s principle of invariance?
Mach’s principle of invariance states that physical laws and phenomena should remain unchanged under certain transformations, such as changing the reference frame or the orientation of an experiment. It highlights the importance of considering the observer’s frame of reference when analyzing physical phenomena.
4. What is Mach’s work on the speed of sound?
Mach conducted extensive research on the speed of sound, leading to the development of the Mach number, which is a dimensionless quantity representing the ratio of an object’s velocity to the speed of sound in the surrounding medium. This work laid the foundation for supersonic aerodynamics and greatly influenced the design of high-speed aircraft.
5. What are Mach bands?
Mach bands are optical illusions characterized by the perception of exaggerated light and dark bands along edges or boundaries between different colors or shades. These bands are a result of the brain’s interpretation of visual stimuli and provide insights into the mechanisms of human perception.
6. How did Mach contribute to psychology?
Mach’s contributions to psychology primarily focused on the study of visual perception and the nature of sensations. His work laid the groundwork for the Gestalt psychology movement, which emphasizes the holistic and organized nature of perception.
7. What is Mach’s impact on philosophy?
Mach’s philosophical ideas challenged prevailing notions of scientific realism and influenced philosophers such as Ludwig Wittgenstein and Thomas Kuhn. His critiques of mechanistic reductionism and his support for empiricism continue to shape the philosophy of science.
If you're fascinated by the world of science and philosophy, why not explore the lives and ideas of other influential thinkers? Delve into the empiricism of David Hume, a philosopher who challenged traditional notions of knowledge and causality. Discover the passion for science education that drives Bill Nye, a beloved figure who has inspired countless young minds. Finally, learn about Karl Popper's groundbreaking contributions to the philosophy of science, which continue to shape our understanding of the scientific method and the pursuit of knowledge.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.