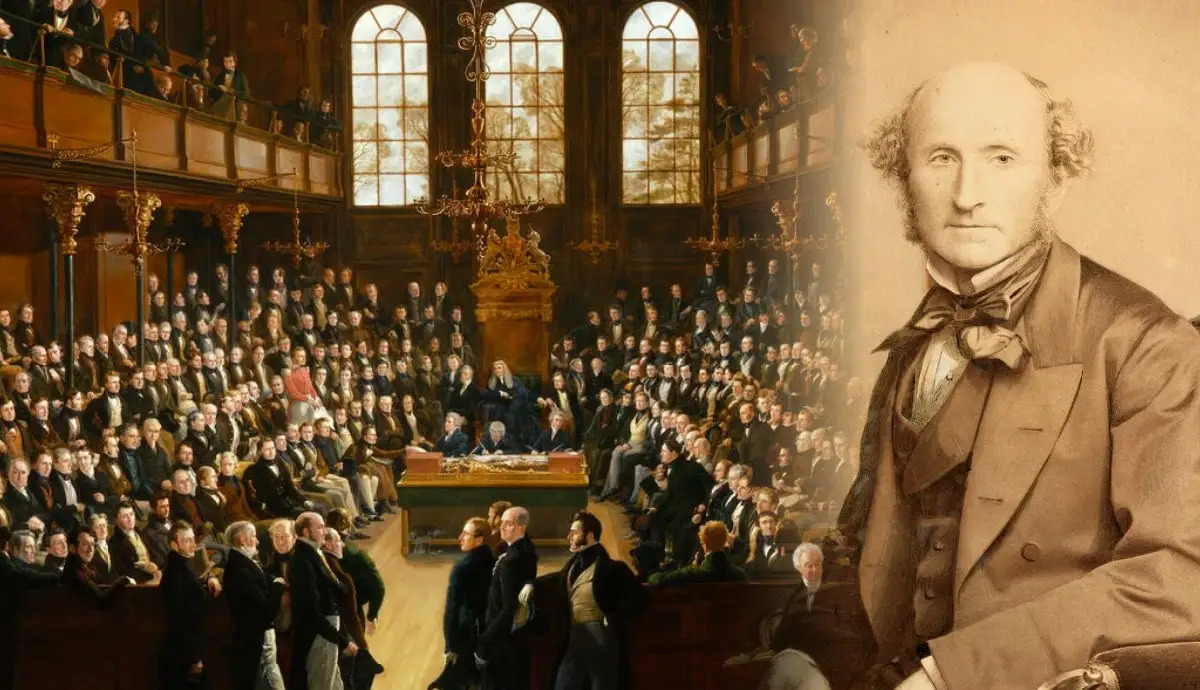
John Stuart Mill was a remarkable figure in the world of philosophy and political economy. Born in 1806 in London, England, Mill made significant contributions to the fields of ethics, logic, and social sciences. His ideas continue to shape and influence our understanding of liberty, utilitarianism, and individual rights.
In this article, we will explore 14 extraordinary facts about John Stuart Mill that shed light on his life, achievements, and intellectual legacy. From his prodigious upbringing to his advocacy for women’s rights, Mill’s ideas and principles still resonate with scholars and thinkers today. So, let’s delve into the fascinating world of John Stuart Mill and discover the man behind the influential philosophies.
Key Takeaways:
- John Stuart Mill was a brilliant philosopher and economist who championed women’s rights, free speech, and education reform, leaving a lasting impact on modern philosophy and economics.
- His influential works on utilitarianism, individual freedoms, and gender equality continue to shape our understanding of human rights, equality, and the pursuit of happiness.
A Philosopher and Economist
John Stuart Mill was a renowned philosopher and economist, known for his influential works on utilitarianism and political economy. His contributions to these fields have had a profound impact on modern philosophy and economics.
An Advocate for Women’s Rights
Mill was a strong advocate for women’s rights and believed in gender equality. He argued for equal rights in education and employment, and was instrumental in promoting women’s suffrage.
A Prodigy from Early Age
Mill was a prodigy from a young age, demonstrating exceptional intellectual abilities. By the age of three, he had already begun learning Greek, and by the age of eight, he had studied advanced subjects such as logic and algebra.
The Only Child of James Mill
Mill was the only child of James Mill, a Scottish philosopher, and historian. His father played a crucial role in his intellectual development, providing him with a rigorous education and introducing him to influential thinkers of the time.
Published “On Liberty” in 1859
One of Mill’s most well-known works is “On Liberty,” published in In this book, he argues for the importance of individual freedoms and the limitations of state interference in personal matters.
A Member of Parliament
Mill served as a Member of Parliament for the Westminster constituency from 1865 to During his time in Parliament, he advocated for electoral reform and spoke out against slavery.
Influenced by Jeremy Bentham
Mill was heavily influenced by the ideas of Jeremy Bentham, an English philosopher and social reformer. Mill adopted Bentham’s utilitarian principles but expanded upon them, emphasizing the importance of individual rights and happiness.
An advocate for Free Speech
Mill strongly believed in the importance of free speech and the exchange of ideas. He argued that through open and robust discourse, society could progress and achieve greater knowledge and understanding.
Published “Utilitarianism” in 1861
In “Utilitarianism,” published in 1861, Mill further developed and defended the concept of utilitarianism. He argued that actions are morally right if they promote the greatest happiness for the greatest number of people.
A Critic of Colonization
Mill was critical of British imperialism and colonization. He argued against the subjugation of indigenous populations and believed in the importance of respecting their rights and cultures.
An Advocate for Education Reform
Mill believed in the transformative power of education and campaigned for education reforms. He advocated for accessible and comprehensive education for all, including the working class.
Published “The Subjection of Women” in 1869
In “The Subjection of Women,” published in 1869, Mill expanded on his beliefs regarding gender equality. He argued against the subordination of women within society and called for their emancipation.
A Devoted Free Thinker
Mill was a devoted advocate for intellectual freedom and encouraged individuals to question prevailing beliefs and challenge established norms. He believed in the power of reason and rationality in shaping society.
His Autobiography was published posthumously
Mill’s autobiography, a candid account of his life and intellectual development, was published posthumously. In it, he reflects on his upbringing, education, and influential relationships throughout his life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, John Stuart Mill was an extraordinary figure in the field of philosophy and political economy. His contributions to utilitarianism, liberalism, and women’s rights have left a lasting impact on society. Mill’s emphasis on individual freedom, rationality, and the pursuit of knowledge continue to shape our understanding of ethics and politics.Mill’s remarkable intellectual prowess, coupled with his dedication to social reform, set him apart as a pioneering thinker. His views on personal autonomy, democracy, and education continue to resonate with contemporary debates. From his groundbreaking works such as “On Liberty” and “Utilitarianism” to his advocacy for women’s suffrage, Mill’s ideas continue to inspire and challenge us today.It is important to recognize and appreciate the extraordinary facts about John Stuart Mill and the lasting influence he has had on our understanding of philosophy, politics, and human rights.
FAQs
1. What were John Stuart Mill’s major contributions to philosophy?
John Stuart Mill made significant contributions to the philosophy of utilitarianism, arguing for the greatest happiness principle as a guiding ethical framework. He also emphasized the importance of individual liberty, rationality, and the pursuit of knowledge.
2. Did John Stuart Mill support women’s rights?
Yes, John Stuart Mill was a strong advocate for women’s rights. He argued for gender equality and was one of the first male proponents of women’s suffrage in the 19th century.
3. What were Mill’s views on individual freedom?
Mill believed in the importance of individual freedom and autonomy. He argued for limited government intervention in personal matters and emphasized the need to protect individual liberties from societal and governmental constraints.
4. Which were Mill’s most influential works?
Two of John Stuart Mill’s most influential works are “On Liberty” and “Utilitarianism.” In “On Liberty,” he discusses the importance of individual freedom and the limits of state authority. In “Utilitarianism,” he presents his ethical theory based on promoting the greatest happiness for the greatest number of people.
5. How does John Stuart Mill’s thinking impact modern society?
Mill’s ideas continue to shape modern society in numerous ways. His emphasis on individual freedom, rationality, and the pursuit of knowledge has influenced democratic ideals, human rights movements, and the philosophy of ethics.
If you're fascinated by the world of philosophy and its impact on society, you might also enjoy exploring the wisdom of Epictetus, a Stoic philosopher who believed in the power of reason and self-discipline. For those intrigued by the concept of utilitarianism, delving into the life and ideas of Jeremy Bentham, a key figure in the development of this ethical theory, could be enlightening. Lastly, if you're passionate about the right to express oneself freely, our article on the history and importance of freedom of speech is sure to captivate your interest.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.