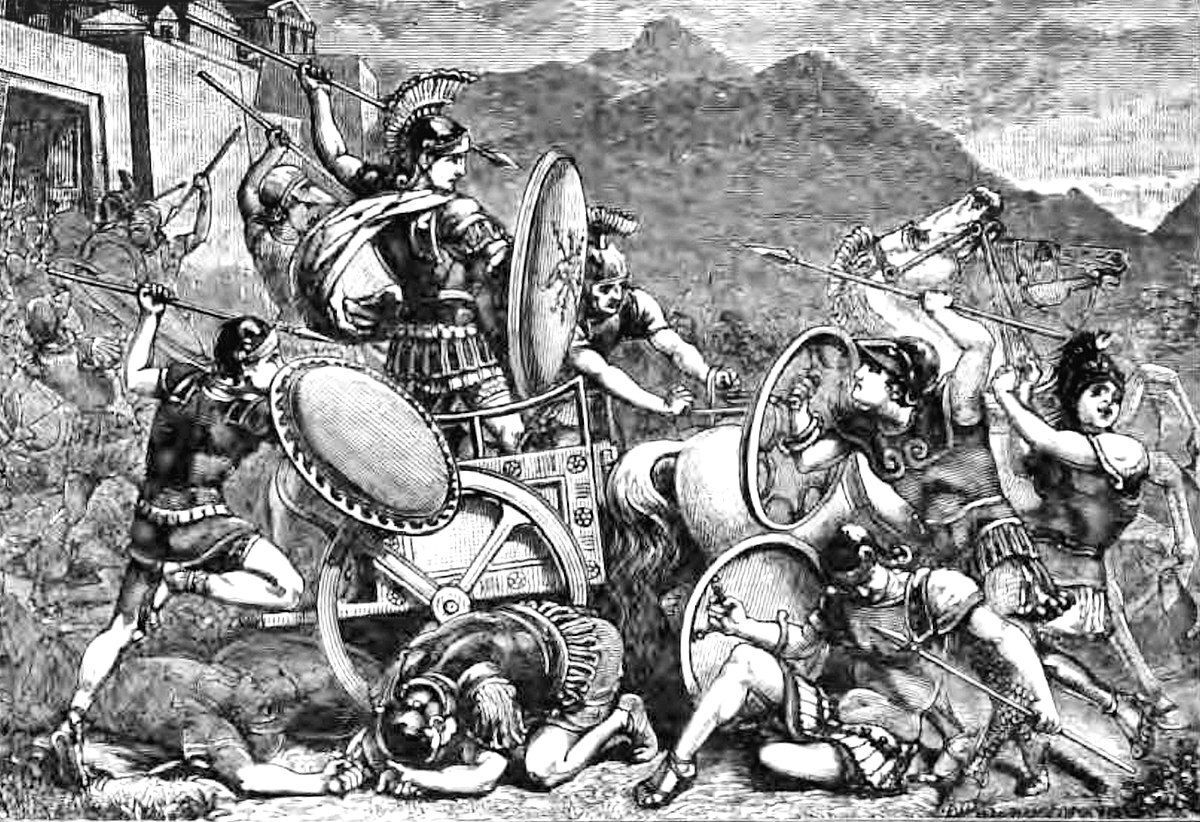
The Second Messenian War was a crucial conflict in ancient Greek history, taking place around 660-650 BC. This war followed the First Messenian War and was ignited by a helot rebellion in Messenia. The helots, seeking freedom, received support from neighboring states like Arcadia and Argos. On one side, Messenia allied with Arcadia, Sicyon, Elis, and Argos. On the other, Sparta joined forces with Corinth, Lepreum, and Cretan mercenaries. Key figures included Aristomenes for Messenia and Anaxander for Sparta. The war featured significant battles, daring escapes, and a prolonged siege at Mt. Eira. Ultimately, it solidified Spartan dominance and shaped the region's future.
Key Takeaways:
- The Second Messenian War, occurring around 660-650 BC, was sparked by a slave rebellion in Messenia and shaped the power dynamics of ancient Greece, leading to lasting impacts on Spartan society.
- The war saw valiant leaders, strategic battles, and prolonged sieges, leaving a legacy of resistance and subjugation. It influenced Spartan militarization and continues to captivate modern scholars.
The Second Messenian War: A Clash of Ancient Titans
The Second Messenian War was a significant conflict in ancient Greek history, occurring between the states of Messenia and Sparta. This war, which took place around 660-650 BC, was a continuation of the long-standing tensions and conflicts between these two regions. Here are 25 key facts about the Second Messenian War, providing a comprehensive understanding of this significant event.
Duration and Causes
Understanding the timeline and reasons behind the war helps set the stage for the events that unfolded.
- The Second Messenian War is believed to have occurred between 660 and 650 BC, approximately 40 years after the conclusion of the First Messenian War.
- The war was sparked by a slave rebellion among the helot population of Messenia, who were seeking to regain their freedom. This uprising was supported by the neighboring states of Arcadia and Argos.
Key Players and Belligerents
The war involved several key leaders and states, each playing a crucial role in the conflict.
- The belligerents involved in the Second Messenian War included Messenia, Arcadia, Sicyon, Elis, and Argos on one side, and Sparta, Corinth, Lepreum, and Cretan mercenaries on the other.
- Key leaders during the Second Messenian War include Aristomenes, Androcles, Fidas, and Aristocrates II from the Messenian side, while Anaxander, Anaxidamus, Tyrtaeus, and Emperamus led the Spartan forces.
Major Battles and Strategies
The war saw several significant battles and strategic moves that shaped its outcome.
- The first battle of the war took place at Deres. Aristomenes, a skilled warrior, fought so valiantly that he was made the new king of Messenia by his people.
- In an attempt to regain their freedom, the Messenians invaded Laconia. This move was part of a broader strategy to challenge Spartan control over the region.
- Aristomenes led a bold move by crossing into Sparta and placing a shield in the temple of Athena to scare the Spartans. This action forced the Spartans to seek a leader from Athens.
- The Spartans consulted the Delphic oracle, which advised them to seek a leader from Athens. In response, they marched on the Messenians at Boar's Grave, where they met Aristomenes and his troops.
- The battle at Boar's Grave was a significant engagement where Aristomenes and his troops initially defeated the Spartans. However, the Spartans eventually gained the upper hand.
- The Spartans bribed Aristocrates, the king of Arcadia, into retreating through the Messenian lines during the Battle of the Great Foss. This betrayal led to a significant loss for the Messenians.
Fortifications and Sieges
The Messenians' resilience was evident in their fortifications and prolonged sieges.
- After their losses, the Messenians fortified themselves at Mt. Eira (Ira). From this stronghold, they launched several raids on surrounding towns, including some led by Aristomenes himself.
- Aristomenes was captured by the Spartans but managed to escape from his holding and return to the fortified city at Mt. Eira. This escape was a significant morale boost for the Messenians.
- The Messenians held out at Mt. Eira for over ten years, using the land as enemy territory and conducting raids on surrounding towns. This prolonged siege was a testament to their determination and resilience.
- Before the final fall of Mt. Eira, the Spartans allowed the women and children to be released along with Aristomenes. Those who did not escape were turned back into helots, while many who escaped fled to Italy or Rhodes.
Aftermath and Legacy
The war's conclusion had lasting impacts on both Messenia and Sparta, shaping their future.
- Aristomenes left for Rhodes where he died and was honored as a hero. His legacy continued to inspire resistance against Spartan rule.
- The Spartans eventually quelled the revolts following the death of the Argive commander. This suppression led to the Messenians being returned to their status as helots, further subjugating them under Spartan rule.
- The Second Messenian War marked a significant turning point in Spartan society, making it a strong militaristic power in the Mediterranean. This militarization was aimed at controlling the masses in the Peloponnese and preventing further rebellions by the helots.
- The Second Messenian War was crucial in shaping the political and social landscape of ancient Greece. It highlighted the enduring struggle for freedom and autonomy among the helot population and the relentless pursuit of power by the Spartans.
Historical and Literary Depictions
The war has been depicted in various literary works and historical accounts, providing insights into this period.
- The Second Messenian War has been depicted in various literary works, including F. L. Lucas's "Messene Redeemed," a verse drama based on Pausanias' accounts of Messenian history.
- Despite its historical importance, archaeological evidence for the Second Messenian War is limited. This scarcity of material evidence underscores the reliance on literary sources like Tyrtaios and Pausanias for understanding this period.
- Tyrtaios, a poet who fought on the side of the Spartans during the Second Messenian War, is one of the few reliable literary sources for this period. His poems provide some of the few indisputable facts about both wars.
- Pausanias' accounts of the Second Messenian War are based on earlier sources, including Rhianus and Myrôn. However, Pausanias himself admits that these sources are unreliable, highlighting the challenges in reconstructing historical events from fragmentary and biased accounts.
Impact on Spartan Conquest and Modern Scholarship
The war's influence extended beyond its immediate context, affecting Spartan conquest and modern historical studies.
- The Second Messenian War was instrumental in solidifying Spartan control over Messenia. The war marked the final subjugation of the Messenian population, turning them into permanent helots under Spartan rule.
- The Second Messenian War continues to be a subject of interest in modern scholarship. Historians like Paul Cartledge and W.G. Forrest have extensively studied this period, highlighting its significance in understanding the evolution of Sparta into a unique city-state with a strong militaristic constitution.
- The legacy of the Second Messenian War extends beyond its immediate context, influencing the political and social structures of both Messenia and Sparta for centuries to come. Understanding this period through various historical and literary sources provides a rich tapestry of insights into the complexities of ancient Greek society and politics.
The Lasting Impact of the Second Messenian War
The Second Messenian War was a game-changer in ancient Greek history. This conflict, driven by the helot rebellion and supported by neighboring states, showcased the fierce determination of the Messenian people. Key battles like Deres and Boar's Grave highlighted the strategic prowess of leaders like Aristomenes. Despite their valiant efforts, the Messenians eventually succumbed to Spartan dominance, leading to their return as helots. The war's outcome solidified Sparta's militaristic society, shaping its future as a dominant power in the Mediterranean. Literary works and historical accounts, though limited, provide valuable insights into this pivotal period. The Second Messenian War's legacy continues to captivate historians and scholars, offering a glimpse into the complexities of ancient Greek politics and society. Understanding this war helps us appreciate the enduring struggle for freedom and the relentless pursuit of power that defined ancient Greece.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.